Section 06: ELECTRICAL
PA1553
20
gassing of electrolyte occurs or battery
temperature exceeds 125ºF (52ºC), the charging
rate must be reduced or temporarily stopped to
allow cooling and to avoid damaging the battery.
Battery temperature can be estimated by
touching or feeling the battery case. The battery
is sufficiently charged when the green dot in the
built-in hydrometer is visible. No further charging
is required. Shake or tilt the battery at hourly
intervals during charging to mix the electrolyte
and see if the green dot appears.
WARNING
Always turn off the charger before connecting
or disconnecting to a battery.
NOTE
The charge rate must be doubled when the
batteries are charged by the booster
terminals, because of the series-parallel
circuit.
Battery charging consists of a charge current in
amperes for a period of time in hours. Thus, a 25
ampere charging rate for 2 hours would be a 50
ampere-hour charge to the battery. Most
batteries, whose load test values are greater
than 200 amperes, will have the green dot visible
after at least a 75 ampere-hour charge. In the
event that the green dot does not appear,
replace the battery.
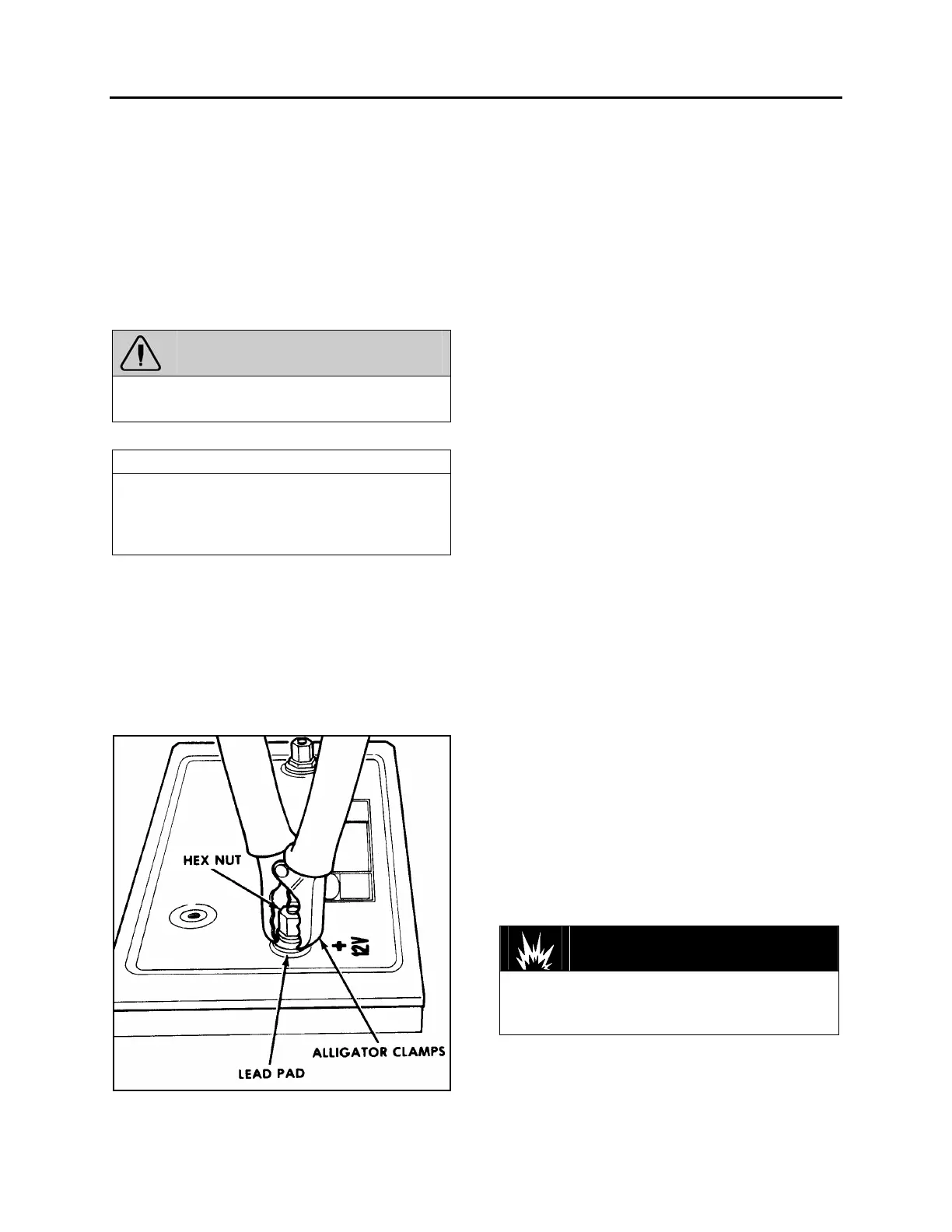
FIGURE 17: ALLIGATOR CLAMPS AND BATTERY 06065
3.6.1 Battery Charging Guide
Fast Charging Rate
20 amps @ 3-¾ hours
30 amps @ 2-½ hours
40 amps @ 2 hours
50 amps @ 1-½ hours
Slow Charging Rate
5 amps @ 15 hours
10 amps @ 7-½ hours
The time required for a charge will vary
according to the following factors:
Size of Battery
For example, a completely discharged large
heavy-duty battery requires more than twice the
recharging time of a completely discharged small
passenger car battery.
Temperature
For example, a longer time will be needed to
charge any battery at 0
o
F (-18
o
C) than at 80
o
F
(27
o
C). When a fast charger is connected to a
cold battery, the current accepted by the battery
will be very low at first, and then in time, the
battery will accept a higher rate as it warms up.
State of Charge
For example, a completely discharged battery
requires more than twice as much charge than a
half-charged battery. Since the electrolyte is
nearly pure water and a poor conductor in a
completely discharged battery, the current
accepted is very low at first. Later, as the
charging current causes the electrolyte acid
content to increase, the charging current will
likewise increase.
Charger Capacity
For example, a charger which can supply only 5
amperes will require a much longer period of
charging than a charger that can supply 30
amperes or more.
3.6.2 Emergency Jump Starting With Auxiliary
(Booster) Battery.
DANGER
Do not jump start vehicles equipped with
maintenance-free batteries if the test indicator
is light yellow.
Both booster and discharged batteries should be
treated carefully when using jumper cables. A
vehicle with a discharged battery may be started

 Loading...
Loading...