Section 07 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Subsection 02 (CHARGING SYSTEM)
BATTERY
Troubleshooting
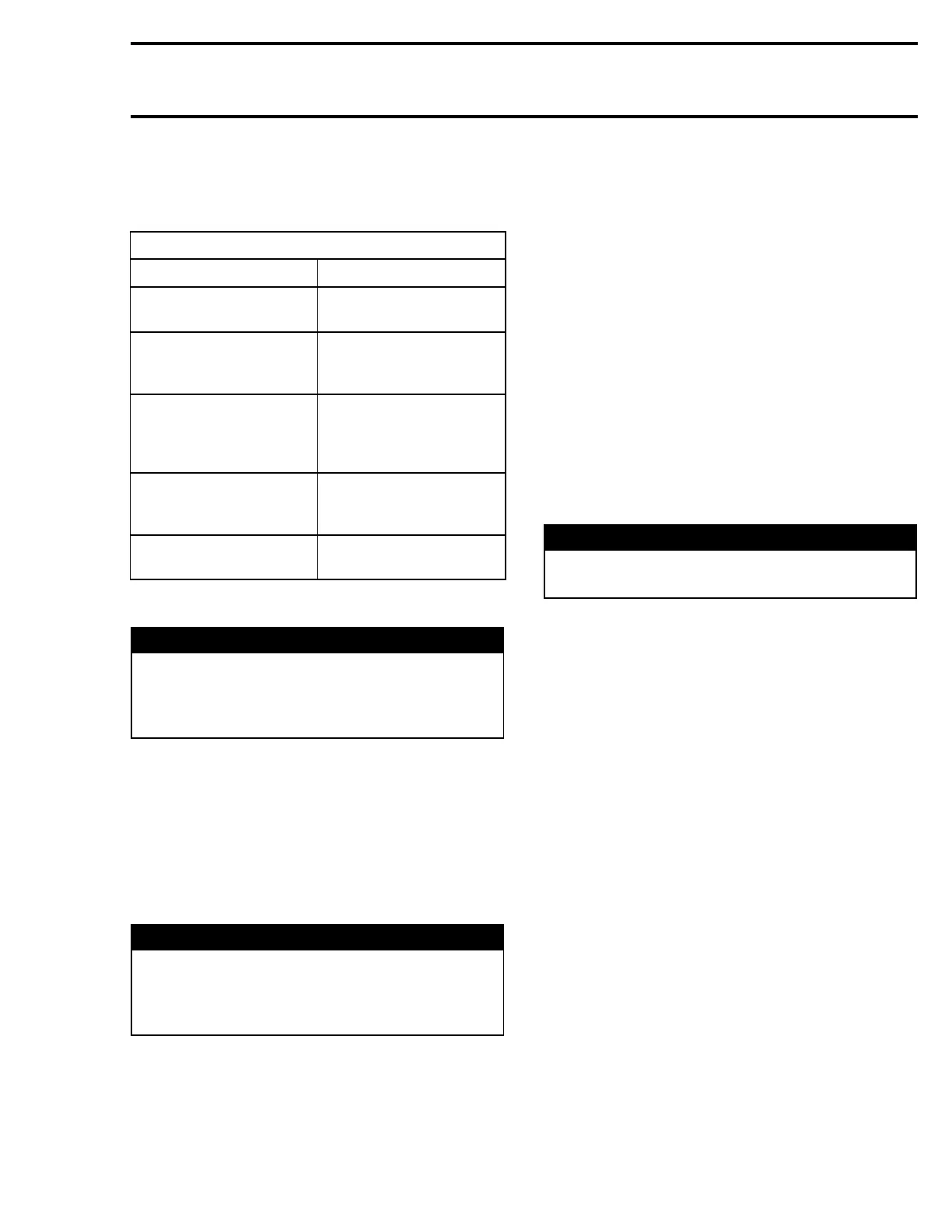
SYMPTOM: DISCHARGED OR WEAK BATTERY
CAUSE REMEDY
Battery posts and/or
cable terminal oxidized.
Clean and coat with
dielectric grease.
Loose or bad
connections.
Check wiring and
connector cleanliness,
damaged or short circuit.
Faulty battery (sulfated,
doesn't keep a full
charge, damaged casing,
loose post).
Replace.
Burnt fuse(s) or faulty
rectifier.
First check fuse(s). If
it is in good condition,
check rectifier/regulator.
Faulty battery charging
coil (or stator).
Replace.
Removal
WARNING
Battery BLACK negative cable must always be
disconnected first and connected last. Never
charge or boost battery while installed in wa-
tercraft.
Proceed as follows:
– Disconnect the BLACK negative cable first.
– Disconnect the RED positive cable last.
– Remove the vent line from the battery.
– Remove the holding strap(s).
– Withdraw battery from watercraft being careful
not lean it so that electrolyte flows out of vent
elbow.
WARNING
Electrolyte is poisonous and dangerous.
Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing.
Wear a suitable pair of non-absorbent gloves
when removing the battery by hand.
CAUTION: Should any electrolyte spillage oc-
cur, immediately wash off with a solution of
baking soda and water.
Cleaning
Clean the battery casing, caps, cables and battery
posts using a solution of baking soda and water.
CAUTION: Do not allow cleaning solution to en-
ter battery.
Remove corrosion from battery cable terminals
and battery posts using a firm wire brush. Rinse
with clear water and dry well.
Inspection
Visually inspect battery casing for cracks or other
possible damage. If casing is damaged, replace
battery and thoroughly clean battery tray and close
area with water and baking soda.
Inspect battery posts for security of mounting.
Inspect for cracked or damaged battery caps, re-
place defective caps.
WARNING
Battery caps do not have vent holes. Make
sure that vent line is not obstructed.
Electrolyte Level
Check electrolyte level in each cell, add distilled
water up to upper level line.
CAUTION: Addonlydistilledwaterinanacti-
vated battery.
Battery Testing
There are 2 types of battery tests: electrolyte
reading and load test. An electrolyte reading is
made on a battery without discharging current. It
is the simplest and commonly used. A load test
gives more accuracy of the battery condition.
Electrolyte Reading
Check charge condition using either a hydrometer
or multimeter.
With a multimeter, voltage readings appear in-
stantly to show the state of charge. Always
respect polarity. A fully charge battery will have a
reading of 12.6 Vdc.
A hydrometer measures the charge of a battery in
terms of specific gravity of the electrolyte. A fully
charge battery will have a specific gravity between
1.265 to 1.280.
smr2005-058 175
 Loading...
Loading...











