Chapter 1 Introduction
1-11
1.3 Characteristics
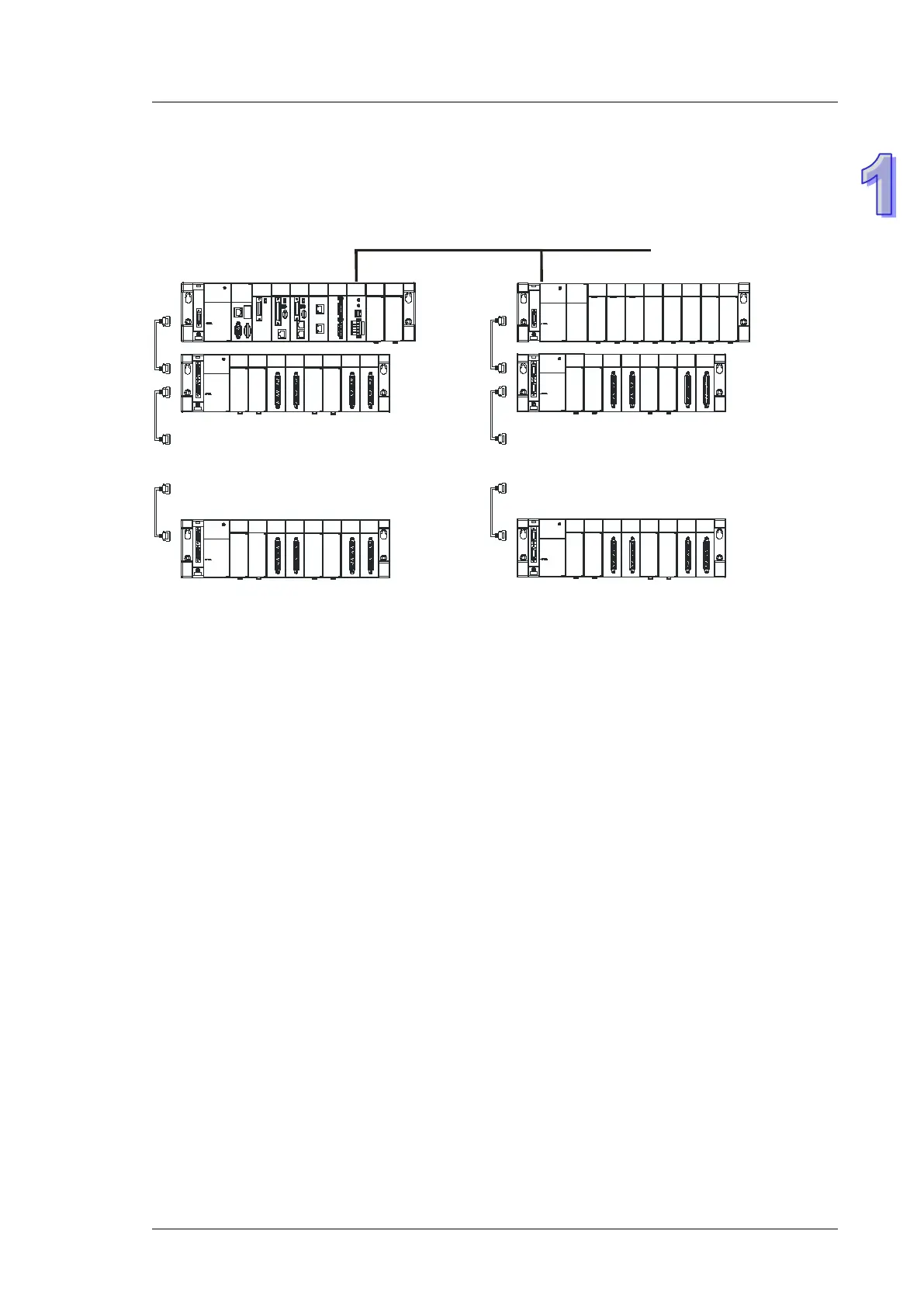
AH500 system illustration
7 backplanes
} }
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
...
Remote I/O
7 backplanes
Features of AH500 Series CPU module:
1. High efficiency
AH500 basic series CPU module: A 32-bit high-speed processor is used. The instructions are
executed at a speed of 3K steps/ms. (Fifty percent of the instructions are basic instructions, and fifty
percent of the instructions are applied instructions.)
AH500 advanced series CPU module: A 32-bit high-speed processor is used. The instructions are
executed at a speed of 12K steps/ms. (Fifty percent of the instructions are basic instructions, and fifty
percent of the instructions are applied instructions.)
AH500 redundant series CPU module: A 32-bit high-speed processor is used. The instructions are
executed at a speed of 12K steps/ms. (Fifty percent of the instructions are basic instructions, and fifty
percent of the instructions are applied instructions.)
2. Supporting more inputs and outputs
The AH500 series CPU module supports up to 4,352 local digital I/O or 544 analog I/O.
A complete AH500 system consists of eight backplanes at most, including a main backplane. Twelve
I/O modules at most can be installed on a main backplane, and eight I/O modules at most can be
installed on an extension backplane. Therefore, for the AH500 series CPU, sixty-eight digital
input/output modules at most or sixty-eight analog input/output modules at most can be installed.
Eight RTU modules at most can be installed on the main backplane.
I/O backplanes employ Ethernet communication protocol. Communication distance between
backplanes can be as far as 100 meters. If using fiber cables with fiber optics modules
AHAADP01/02EF-5A for extension backplanes, the communication distance can reach as far as 2
kilometers.
3. Multiple I/O modules
The I/O modules supported by the AH500 series CPU module are digital input/output modules, analog
input/output modules, temperature measurement modules, network modules, motion control modules,
and RTU modules. Refer to section 1.1.2 for more details.

 Loading...
Loading...











