Operation Manual - Multicast Protocol
Quidway S6500 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
Multicast Overview
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-2
over the network if the there is a large number of users in need of this infomration. As
the bandwidth would turn short, the unicast mode is incapable of massive transmission.
II. Broadcast
In broadcast mode, every user on the network receives the information regardless of
their needs. See
Figure 1-2 Data transmission in broadcast mode.
Server
Broadcast
User
User
A
User B
User C
User D
E
Figure 1-2 Data transmission in broadcast mode
Suppose the Users B, D, and E need the information, the information source Server
broadcasts the information through the router; User A and User C can also receive the
information. In that case, information security and rewards to services are not
guaranteed. Moreover, bandwidth is terribly wasted when only a few part of users are in
need of the information.
In short, the unicast mode is useful in networks with scattered users, and the multicast
mode is suitable for networks with dense users. When the number of users is uncertain,
the adoption of unicast or multicast mode results in low efficiency.
1.1.2 Advantages of Multicast
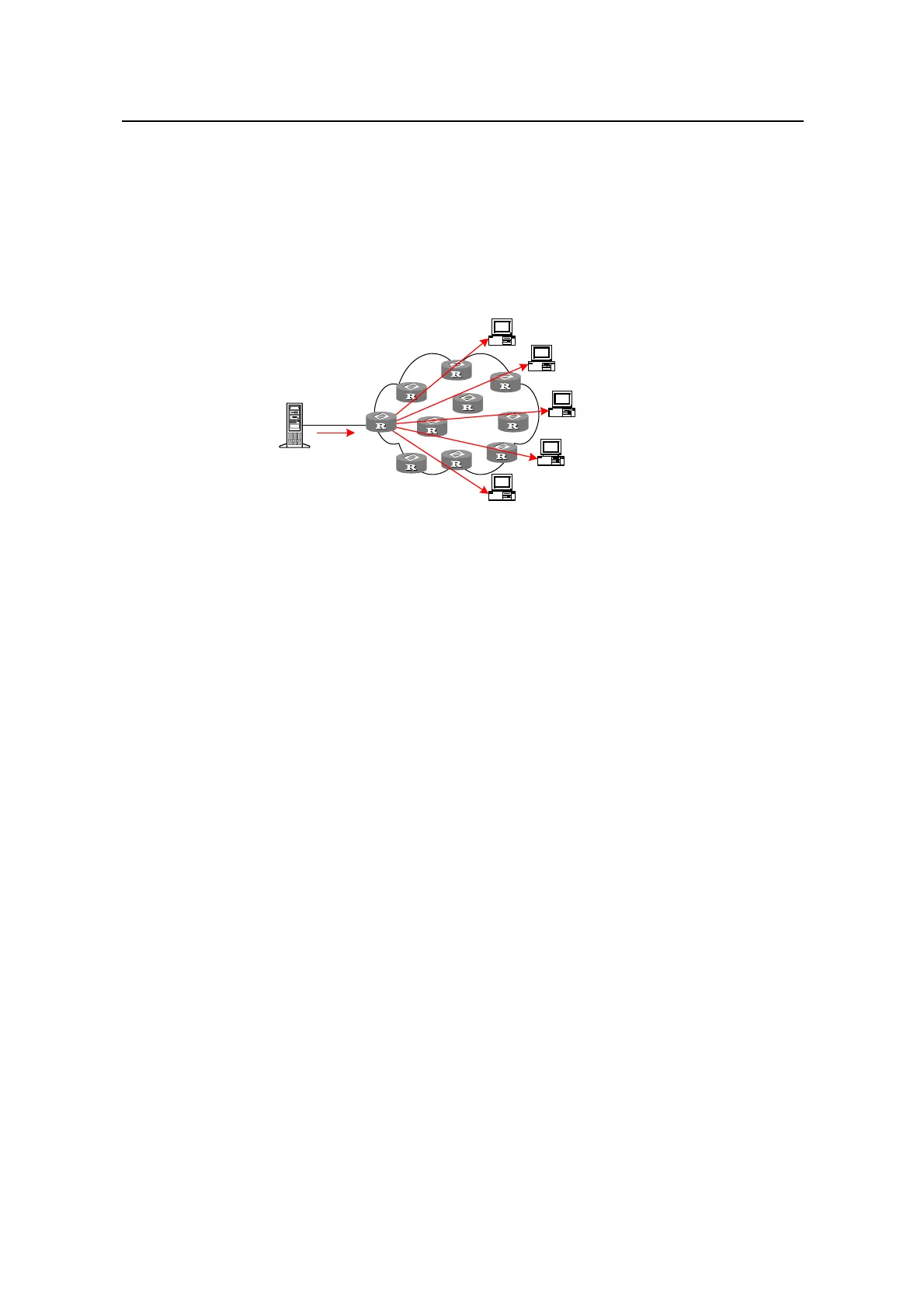
I. Multicast
IP multicast technology solves those problems. It allows the multicast source to send
the information once only, and ensures that the information will not be duplicated or
distributed unless it reaches a fork in the tree route established by the multicast routing
protocol. See
Figure 1-3 Data transmission in multicast mode.

 Loading...
Loading...











