LAGs
68
Managed Switches
Link Aggregation Concepts
Link aggregation allows the switch to treat multiple physical links between two endpoints as a
single logical link. All the physical links in a given LAG must operate in full-duplex mode at the
same speed. LAGs can be used to directly connect two switches when the traffic between
them requires high bandwidth and reliability, or to provide a higher-bandwidth connection to a
public network. Management functions treat a LAG as if it is a single physical port. You can
include a LAG in a VLAN. You can configure more than one LAG for a given switch.
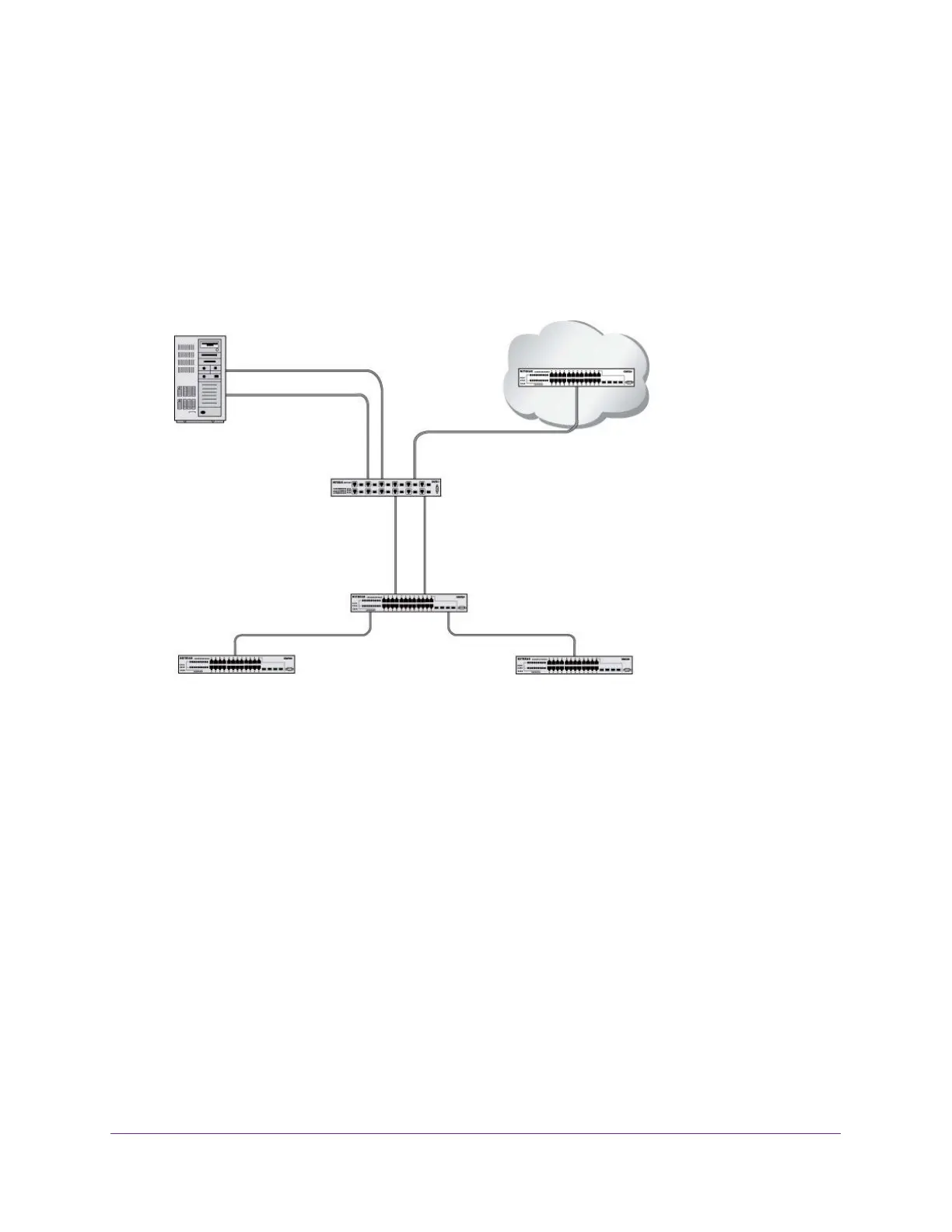
Figure 8. Example network with two LAGs
LAGs offer the following benefits:
• Increased reliability and availability. If one of the physical links in the LAG goes down,
traffic is dynamically and transparently reassigned to one of the other physical links.
• Better use of physical resources. Traffic can be load-balanced across the physical links.
• Increased bandwidth. The aggregated physical links deliver higher bandwidth than each
individual link.
• Incremental increase in bandwidth. A physical upgrade could produce a tenfold increase
in bandwidth; LAG produces a twofold or fivefold increase, which is useful if only a small
increase is needed.
Server
Subnet 3
Port 1/0/3
LAG_10
Port 1/0/2
LAG_10
Layer 3 Switch
Layer 2 Switch
Subnet 2 Subnet 3
Port 1/0/9
LAG_20
Port 1/0/8
LAG 20
 Loading...
Loading...











