DMG 3200/3100/3000 – User Manual
Page 109 (306)
6.3 Scrambling
This section provides a brief overview on how scrambling is performed within the unit. It
introduces the different components required and their purpose and explains how to setup the
scrambler card to establish ECM and EMM channels as well as their actual streams.
For information on how to conduct scrambling, add an EMM to an output transport stream, etc.
refer to Chapter 8.3.
The scrambler module is composed of two components:
• SCS – a software component responsible for managing the interfaces used by external
ECMG, EMMI, and EIS services.
• SCR – a hardware component responsible for encryption (DVB-CSA or AES) of the
services.
The functional diagram below shows these components and their relations with the rest of the
system.
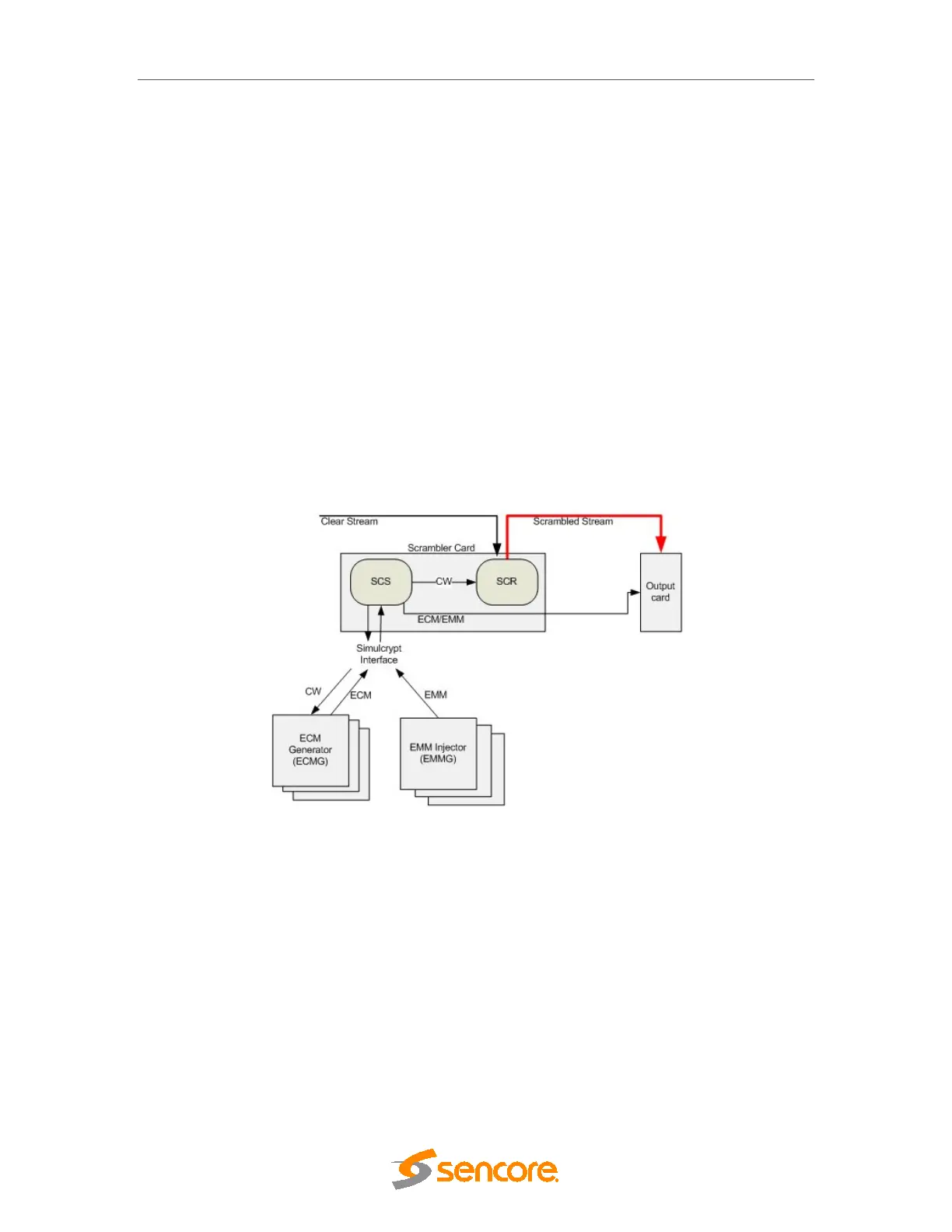
Figure 6.17- Scrambler Module Architecture
The SCS module is the master of the scrambling system. It is aware of the ECMG and the
scrambler module. Upon configuration, the SCS card generates a CW, sends it to the ECMG,
which returns the ECM. The SCS then sends the CW to the hardware component scrambling
the live content and transfers the ECM to the correct output card for playout.
Before it is possible to define an output stream with the scrambling properties it is necessary to
define the ECM generator, as the SCS needs to know where to contact the encryption system.
Next step is to define an ECM. The ECM definition associates a CW id and access criteria. The
output can now be defined and scrambled. When configuring the output to be scrambled the
ECM selection list implicitly represents the CW and access criteria while the scrambler indicates
the scrambler card.
 Loading...
Loading...