DMG 3200/3100/3000 – User Manual
Page 296 (306)
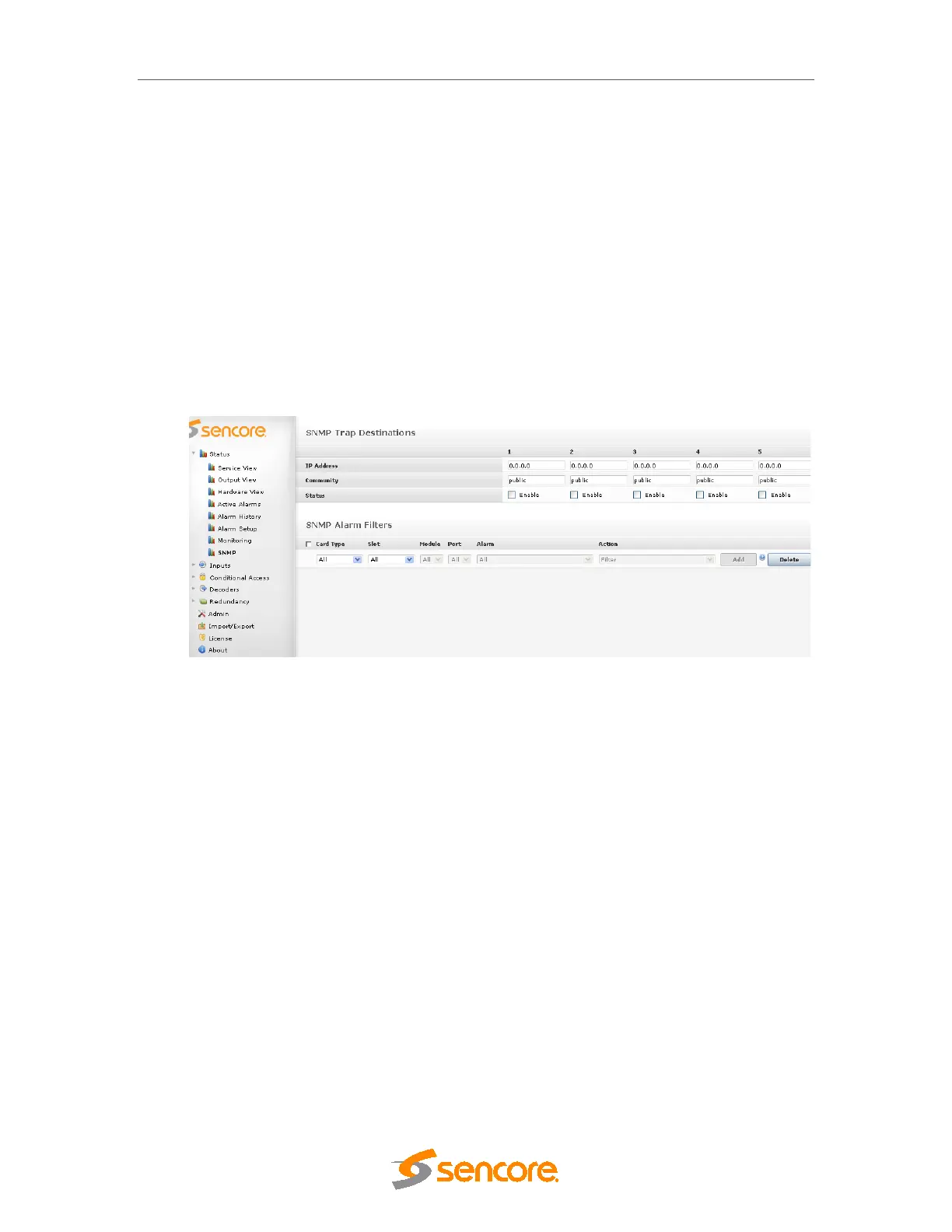
11.2 SNMP
The SNMP agent is located on the MMI module, and uses the same IP address. A number of
variables can be configured, including the SNMP configuration file (containing the public and
private community strings, for user access and alarms); and the trap destination table. This is
explained below.
11.2.1 Configuration of SNMP Alarm Filter via the GUI
The ordinary alarm filter and the root cause filter is before the SNMP filter, and any alarms
which are filtered away by those mechanisms, and hence are not shown in the active alarm list,
are never sent via SNMP.
Figure 11.12 – Five Trap Destinations and the Alarm Filter can be set in the GUI.
The SNMP alarm filter provides filtering based on slot, port and alarm ID, like the Alarm Setup
before it, and it is operated the same way.
11.2.2 Configuration of SNMP Trap Destination Table via the GUI
Five different trap destinations are set in the GUI. After changing status, or IP address or
community, press Apply to start forwarding alarms.
11.2.3 Configuration of Trap Destination Table via SNMP
The trap destination table must be edited to receive traps. It has five entries, hence allowing five
different trap destinations to be used at the same time. Additional rows cannot be created. The
tdIpAddr field contains the IP address of the NMS, while the tdRowStatus field is used to
determine whether traps should be forwarded. To enable traps towards a specified address the
corresponding tdRowStatus field must be set to active (1). To disable traps, set the
tdRowStatus field to notInUse (2). Errors are reported when trying to send traffic towards IP
address 0.0.0.0, which is the default IP address.
11.2.4 Interpretation of Traps
Each trap is uniquely identified with the combination of msgId, msgSlot, msgPort, and
msgInstance fields. The type of error is specified with the msgId field, while the location is

 Loading...
Loading...