6.5.21 Codec Management
6.5.21.1 Basics
Sharing of common codecs, either from independent systems with the I/O
sharing option, or from an A/B desk, is called codec management.
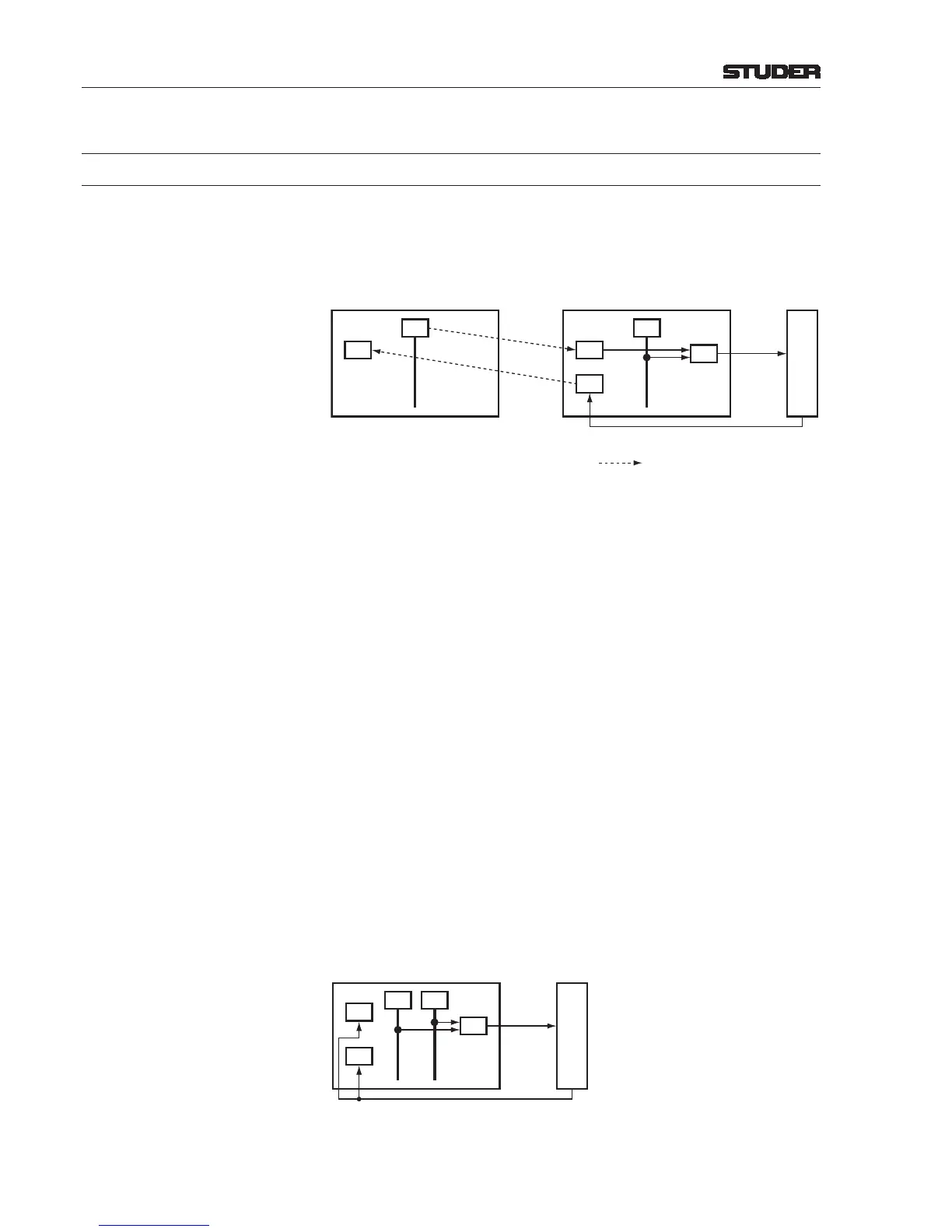
I/O Sharing The concept is explained on a dual, I/O sharing system; the goal is that a codec
connected to system A may also be used on system B.
• Two logical I/O sharing connections ( ) are required.
• The net logical input (NetLI) on system B consumes the logical input (LI)
from system A.
• A net patch input (NetPI) on system A consumes the N–X bus of system
B that is specied as N–X control of NetLI.
This allows system B sending any signal to the codec, as long as NetPI is
routed to the patch output (PO) connected to the codec’s input.
Both systems may “listen” to the codec’s output at the same time, but only
one system can provide its N–X bus output to PO. In the output routing, the
source for PO is either the I/O sharing NetPI, or the local N–X bus assigned
to the producer system’s (local) LI.
The source for PI is usually controlled on the desk where LI or NetLI is locat-
ed. It may also be controlled from the Routing - Output page of system A
to which the codec is directly connected (MCR).
Note: A logical output (LO) could also be used instead of a patch output (PO) for
the connection to the codec’s input. However, since patch outputs are not part
of the output routing snapshot, they will not be affected by loading an output
routing snapshot on system A.
A/B desk In case of an A/B desk conguration, I/O sharing is not required. Both desks
may “listen” to the codec’s output at the same time – logical input A (LI A)
on system A, and logical input B (LI B) on system B. Only one system can
provide its N–X bus output to the patch output (PO). In the output routing,
the source for PO is either the N–X B bus specied as N–X control in LI B,
or the N–X A bus assigned to LI A.
 Loading...
Loading...