328
Configuring ARP
Overview
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used to resolve an IP address into a physical address,
such as an Ethernet MAC address.
In an Ethernet LAN, a device uses ARP to resolve the IP address of the next hop to the
corresponding MAC address.
For more information about ARP, see HPE FlexNetwork MSR Router Series Comware 5 Layer 3—IP
Services Configuration Guide.
Gratuitous ARP
Gratuitous ARP packets
In a gratuitous ARP packet, the sender IP address and the target IP address are the IP address of
the sending device, the sender MAC address is the MAC address of the sending device, and the
target MAC address is the broadcast address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff.
A device sends a gratuitous ARP packet for either of the following purposes:
• Determine whether its IP address is already used by another device. If the IP address is already
used, the device is informed of the conflict by an ARP reply.
• Inform other devices of a change of its MAC address.
Gratuitous ARP packet learning
With this feature enabled, a device, upon receiving a gratuitous ARP packet, adds an ARP entry that
contains the sender IP and MAC addresses in the packet to its ARP table. If the corresponding ARP
entry exists, the device updates the ARP entry.
With this feature disabled, the device uses received gratuitous ARP packets to update existing ARP
entries, but not to create new ARP entries.
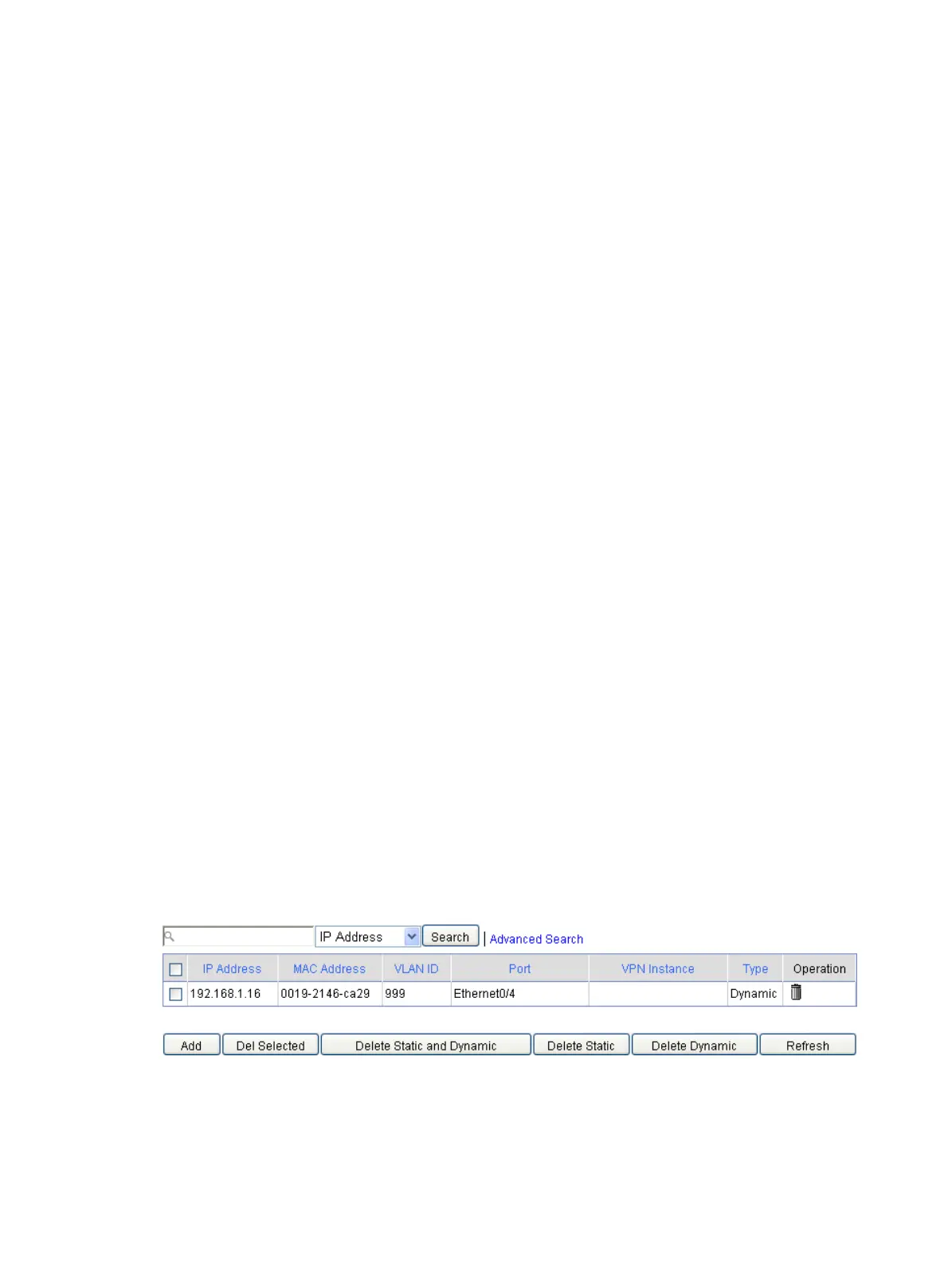
Displaying ARP entries
From the navigation tree, select Advanced > ARP Management > ARP Table.
This ARP table management page displays all ARP entries.
Figure 343 Managing ARP Table
Creating a static ARP entry
1. From the navigation tree, select Advanced > ARP Management > ARP Table.

 Loading...
Loading...




