123
You can restore multiple files at a time, but only one startup file or configuration file can be included in
these files for restoration.
Rebooting the device
CAUTION:
Before rebooting the device, save the configuration. Otherwise, all unsaved configuration will be los
after reboot. After the device reboots, you need to re-log in to the Web interface.
To reboot the device:
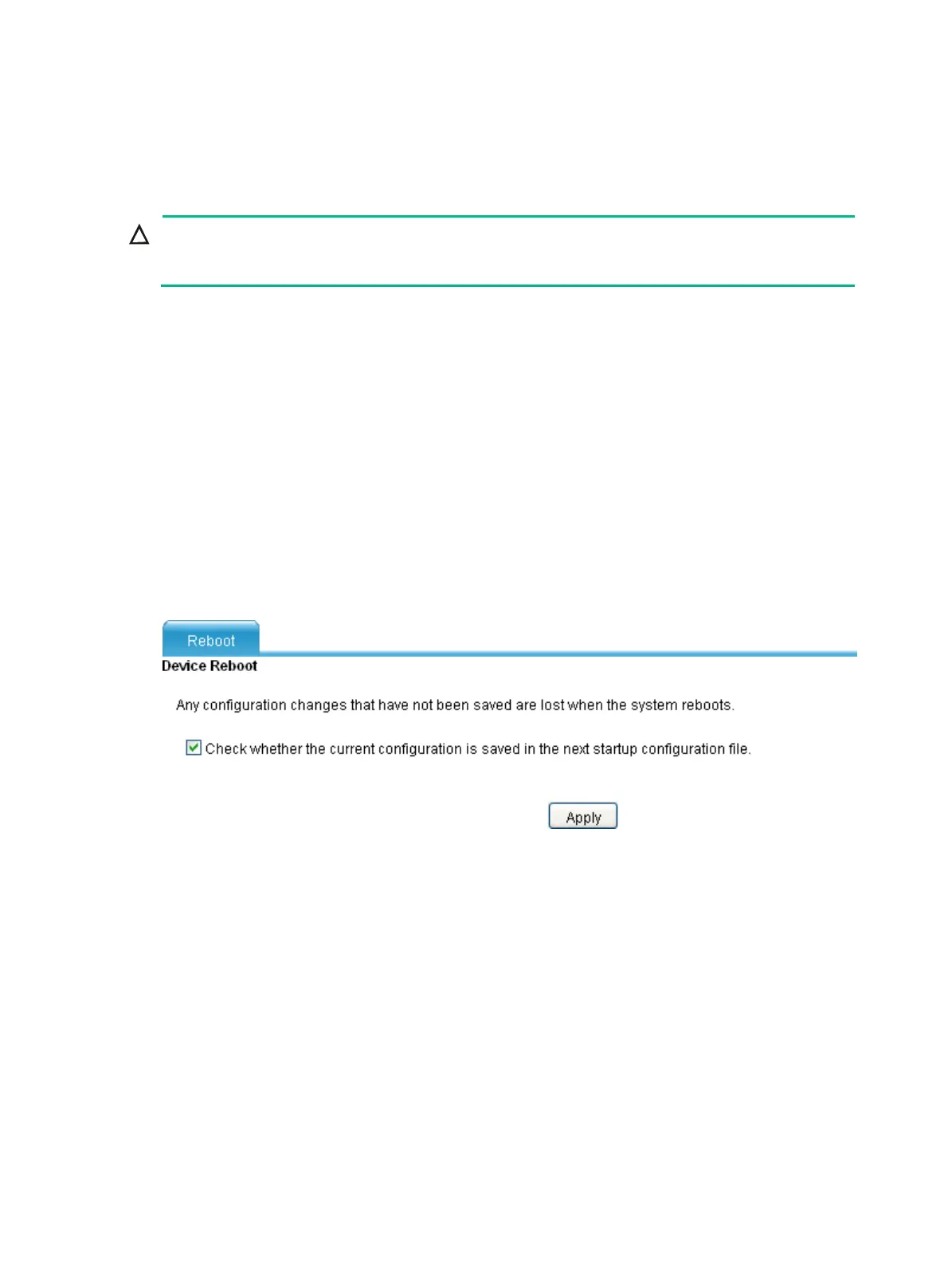
1. From the navigation tree, select System Management > Reboot.
The device reboot configuration page appears.
You can verify whether the current configuration has been saved to the next-startup
configuration file.
If you select the Check whether the current configuration is saved in the next startup
configuration file option, the system checks the configuration before rebooting the device.
If the check is successful, the system reboots the device. Otherwise, a dialog box appears,
telling you that the current configuration and the saved configuration are inconsistent, and
the reboot fails. In this case, save the current configuration manually before you can reboot
the device.
If you do not select the option, the system reboots the device directly.
2. Click Apply.
Figure 511 Rebooting the device
Managing services
This module provides six types of services: FTP, Telnet, SSH, SFTP, HTTP, and HTTPS. You can
enable or disable these services to enhance system performance and security and implement
secure device management.
This module also provides the function to modify HTTP and HTTPS port numbers, and the function
to associate the FTP, HTTP, or HTTPS service with an ACL, reducing attacks of illegal users on
these services.
The description of the services is as follows:
• FTP service—Transfers files between server and client over a TCP/IP network.
• Telnet service—Provides remote login and virtual terminal functions on the network.
• SSH service—Offers a method for securely logging in to a remote device. By encryption and
strong authentication, SSH protects devices against attacks such as IP spoofing and plain text
password interception.

 Loading...
Loading...




