303
Figure 695 All IP-based network
Features
SIP trunk has the following features:
1. Only one secure and QoS guaranteed SIP trunk link is required between a SIP trunk device and
the ITSP. The SIP trunk link can carry multiple concurrent calls, and the carrier only
authenticates the link instead of each SIP call carried on this link.
2. The internal calls of the enterprise are placed by the enterprise IP-PBX. The outbound calls of
the enterprise are forwarded by the SIP trunk device to the ITSP, and are finally routed to the
PSTN by the device in the ITSP. Enterprises do not need to maintain the PSTN trunk.
Consequently, they save the costs of hardware and maintenance.
3. By setting destination addresses, the enterprise can select to connect to multiple ITSPs, to
make full use of the ITSPs all over the world, and save call costs.
4. With the SIP trunk device deployed, the entire network can use the SIP protocol to better
support IP communication services, like voice, conference, and instant messaging.
5. A SIP trunk device differs from a SIP proxy server. The SIP trunk device initiates a new call
request to the ITSP on behalf of the user after receiving a call request from the user, and both
the user and the ITSP communicate only with the SIP trunk device. During the forwarding
process, the SIP trunk device forwards both signaling messages and RTP media messages.
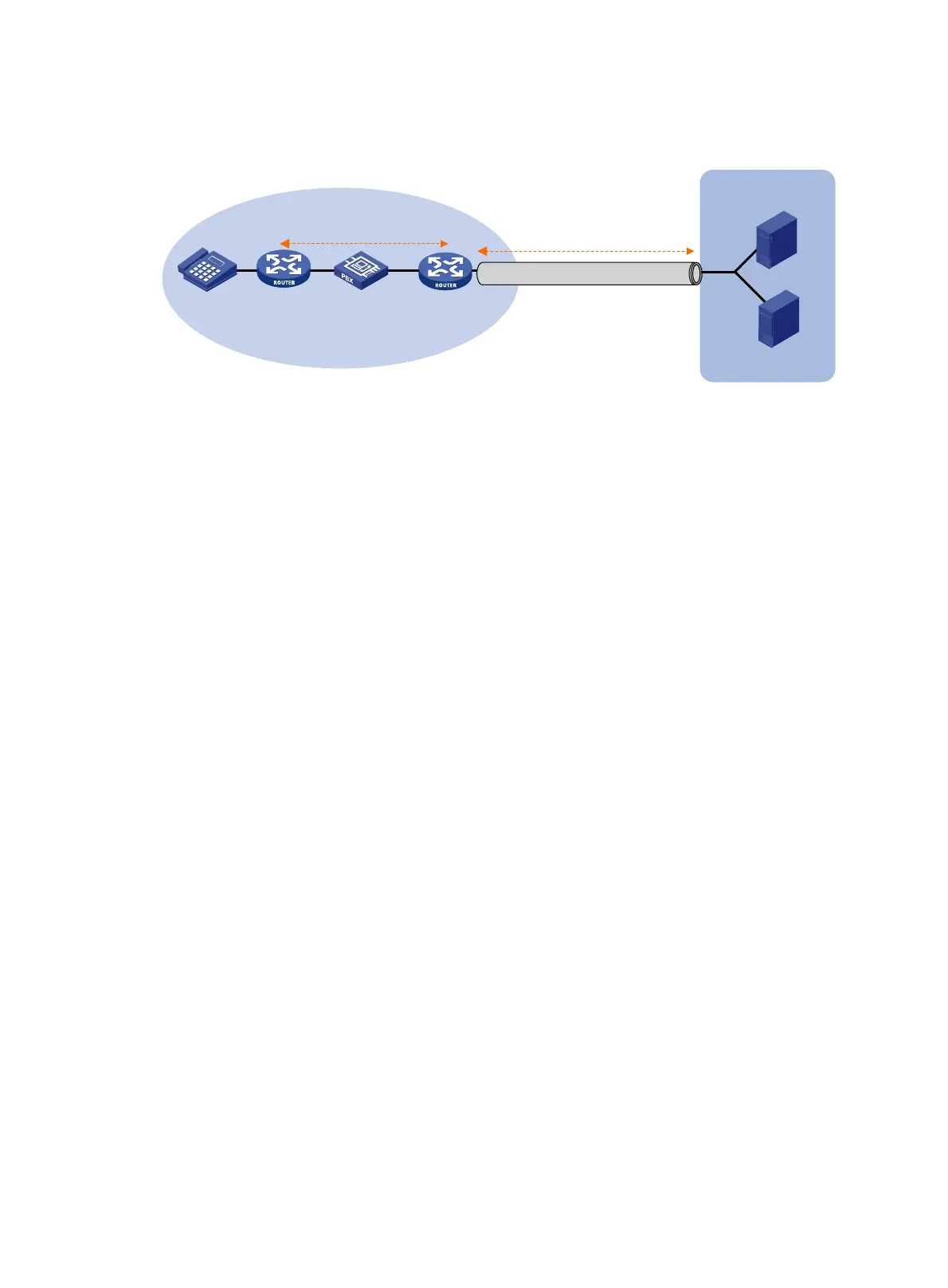
Typical applications
The SIP trunk device is deployed between the enterprise IP-PBX and the ITSP. All internal calls are
placed by the enterprise IP-PBX. All outbound calls are forwarded by the SIP trunk device to the
ITSP through the SIP trunk link. Figure 696 sh
ows a typical SIP
trunk network.
SIP trunk device
SIP server
SIP trunk
Router
Enterprise
intranet
ITSP
SIP
SIP
SIP server
All IP-based network
IP-PBX

 Loading...
Loading...




