6 ECG, Arrhythmia, ST and QT Monitoring
169
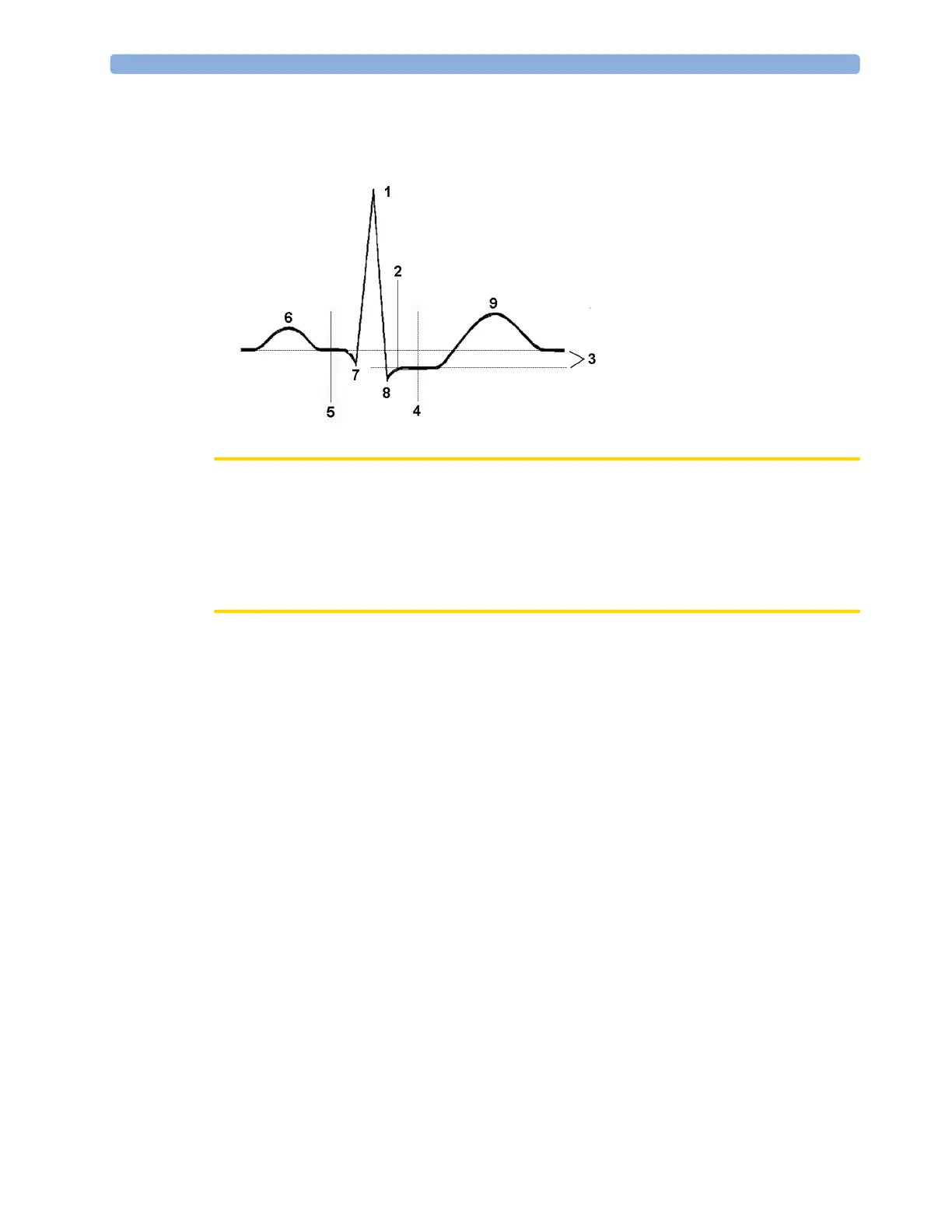
The isoelectric (ISO) point provides the baseline, the ST point is at the midpoint of the ST segment.
The J point is where the QRS complex changes its slope; as it is a fixed distance away from the ST
point, it can be useful to help you position the ST point correctly.
CAUTION
If using ST analysis, the ST measurement points need to be adjusted when you start monitoring, and if
the patient's heart rate or ECG morphology changes significantly, as this may affect the size of the QT
interval and thus the placement of the ST point. Artifactual ST segment depression or elevation may
occur if the isoelectric point or the ST point is incorrectly set.
Always ensure that ST measurement points are appropriate for your patient.
Setting ISO and J-Point Detection Mode
There are two modes for ISO and J-point detection: Auto and Manual. In Manual mode you can set
the measurement points yourself. In
Auto mode the measurement points will be determined
automatically.
To set the detection mode, in the
Setup ST Analysis window,
1 Select ISO/J Point.
2 Select Auto or Manual mode.
Adjusting ST Measurement Points
If the ISO and J-point detection mode is set to Manual, all three measurement points can be set. In
Auto mode, only the ST point can be changed.
To adjust the ST measurement points, in the
Setup ST Analysis menu,
1 Select Adjust ST Points to open the Adjust ST Points window.
Alternatively, you can use the
Adjust ST points pop-up key in the ST View window.
2 Select a suitable ECG lead for ST measurement, with a visible J-point and a visible P wave. Use the
up and down arrow keys to scroll through the ST snippets for the other ECG leads.
1 R-wave peak at 0 msec
2 J point, for example, 48 msec
3 Difference = ST value
4 ST measurement point, for
example, J + 60 msec
5 Isoelectric point set to -80 msec
6 P
7 Q
8 S
9 T

 Loading...
Loading...











