Virtual LANs (VLANs) Introduction
4-45
Software Reference for SwitchBlade x3100 Series Switches (Layer Two Switching)
When devices cannot include VLAN tagging, the VLAN membership is determined by which port its packets
arrive on; all untagged traffic arriving on a certain port belongs to that VLAN.
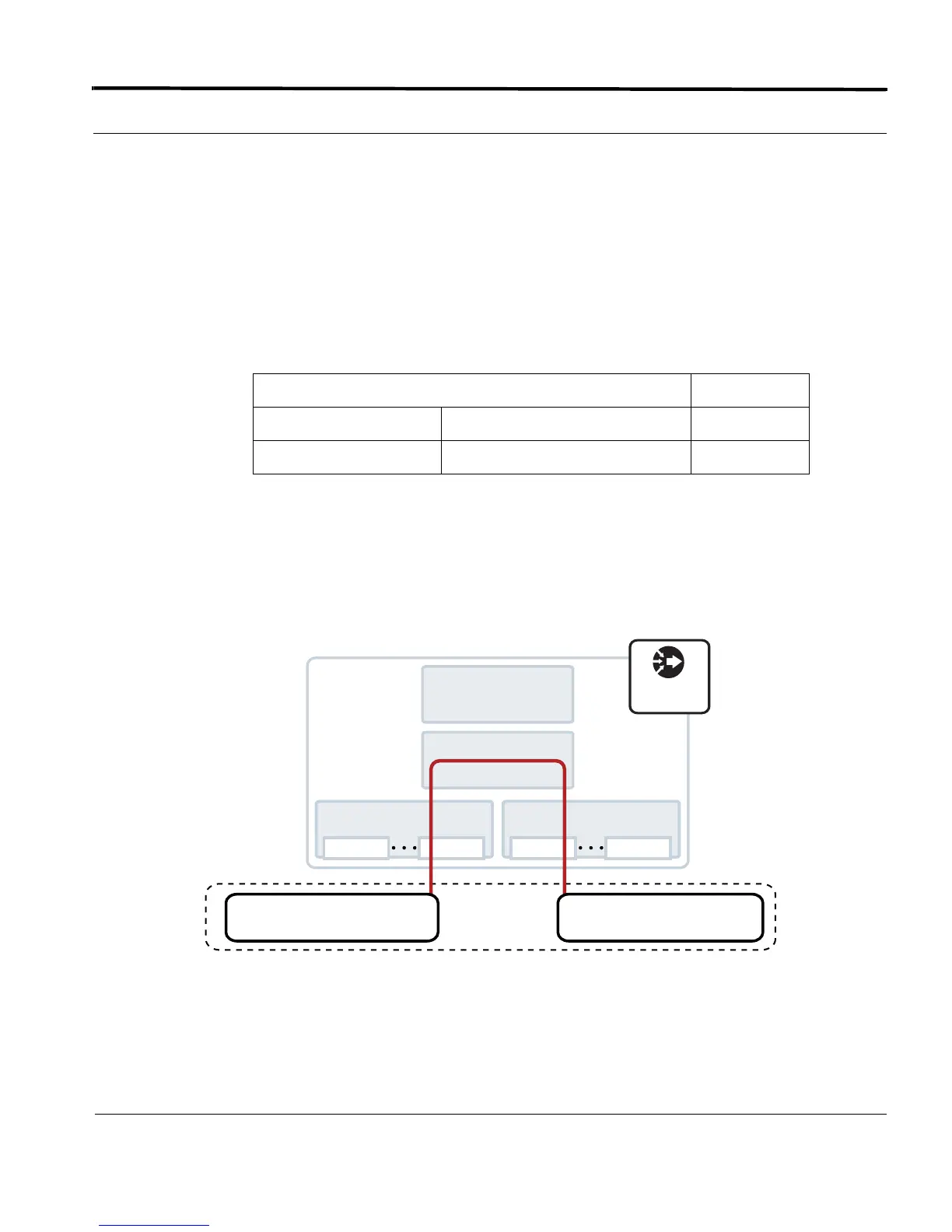
4.4.2.2 Standard VLAN Configuration
Figure 4-3 shows a sample configuration for setting up a VLAN in STD mode. The following explanation is
based on this figure.
When a standard VLAN is configured, the Forwarding Database and VLAN/port mappings are set as follows:
When the Control Module receives the Source Address and VID, it performs two steps:
1. Learning - The Source Address-VLAN ID pair are checked against the FDB, and if it is not there the values
are added.
2. Forwarding - The Destination Address is checked against the port mapping, and if the port mapping exists, it
forwards the data onto that port. Otherwise, it floods all ports for that VLAN.
FIGURE 4-3 Standard VLAN Configuration in the SBx3112
TABLE 4-7
FDB Port Mapping
VID=5 MAC=00:50:94:31:33:00 8.4
VID=5 MAC=00:50:94:31:60:3D 9.8
Port 0.0
CM
Port to Port Forwarding
Slot 8 Slot 9
Std_VLAN_Cnfg_3112
VLAN=Marketing
Port 4 Port 8
MAC=00:50:94:31:33:00
VID=5
MAC=00:50:94:31:60:3D
VID=5
SBx3112
SBx3100
 Loading...
Loading...











