Introduction Alarm Types - Interface, Card, and System
Software Reference for SwitchBlade x3100 Series Switches (Alarms and Troubleshooting)
8-4
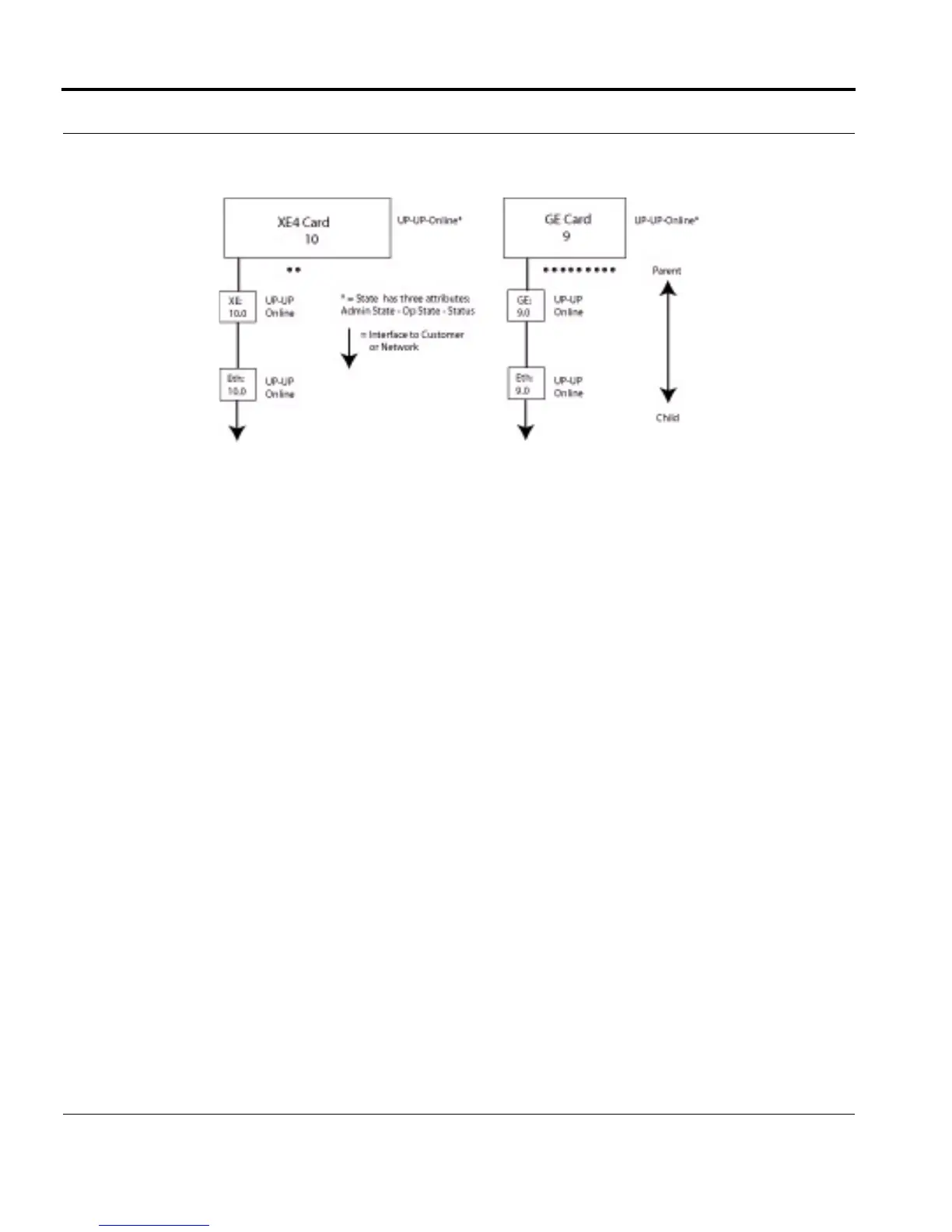
In Figure 8-1, the hierarchy and state of components are shown when the system is in service and there are no
errors. This figure will be used to illustrate various error conditions.
FIGURE 8-1 Component Hierarchy - No Error Conditions
8.2.2 Alarm Types - Interface, Card, and System
The SBx3112 switch has following types of alarms:
1. Interface - These are alarms that involve components that face outward from the system. In most cases
these are customer facing, although they can be network facing. These alarms usually indicate that service
(or a particular service type) cannot be provided to a customer.
When an interface fails in a previously working system, it is usually in one of two states:
• Failed - The interface cannot provide any service, and the user must assume that all services for that
interface are lost. The Op State is DOWN. An alarm is usually produced (the severity depending on
whether the component is disabled or enabled).
• Degraded - The interface can still provide service, but at a degraded level. The OP state is still UP. An
alarm may be produced, with severity at a lesser level than an interface in the Failed state.
Note: When these alarms occur, there is an associated log with a category of PORT or INTF. Refer to the
Log Reference for SwitchBlade® x3100 Series Switches.
2. non-CFC Card - These are alarms associated with a specific card. Since the card supports multiple inter-
faces, the loss of a card usually means the potential loss of multiple interfaces. When a card fails in a previ-
ously working system, the card is usually in one of two states:
• Failed - The card cannot provide any service, and the user must assume that any associated interfaces
cannot provide service(s) as well. The Op State is DOWN. An alarm is usually produced (the severity
depending on whether the alarm is disabled or enabled).
• Degraded - The card can still provide service, but the interfaces it supports may not be able to provide
a full level of service.The Op State is still UP. An alarm is usually produced (the severity depending on
whether the alarm is disabled or enabled).

 Loading...
Loading...











