scans for access points that contain a matching SSID and authentication type. The phone associates with
the access point with the highest RSSI that matches with the network profile.
3
(For a Cisco Unified IP Phone 9971 in a wireless LAN only) Authenticate with the access point. The Cisco
Unified IP Phone begins the authentication process. The following table describes the authentication
process:
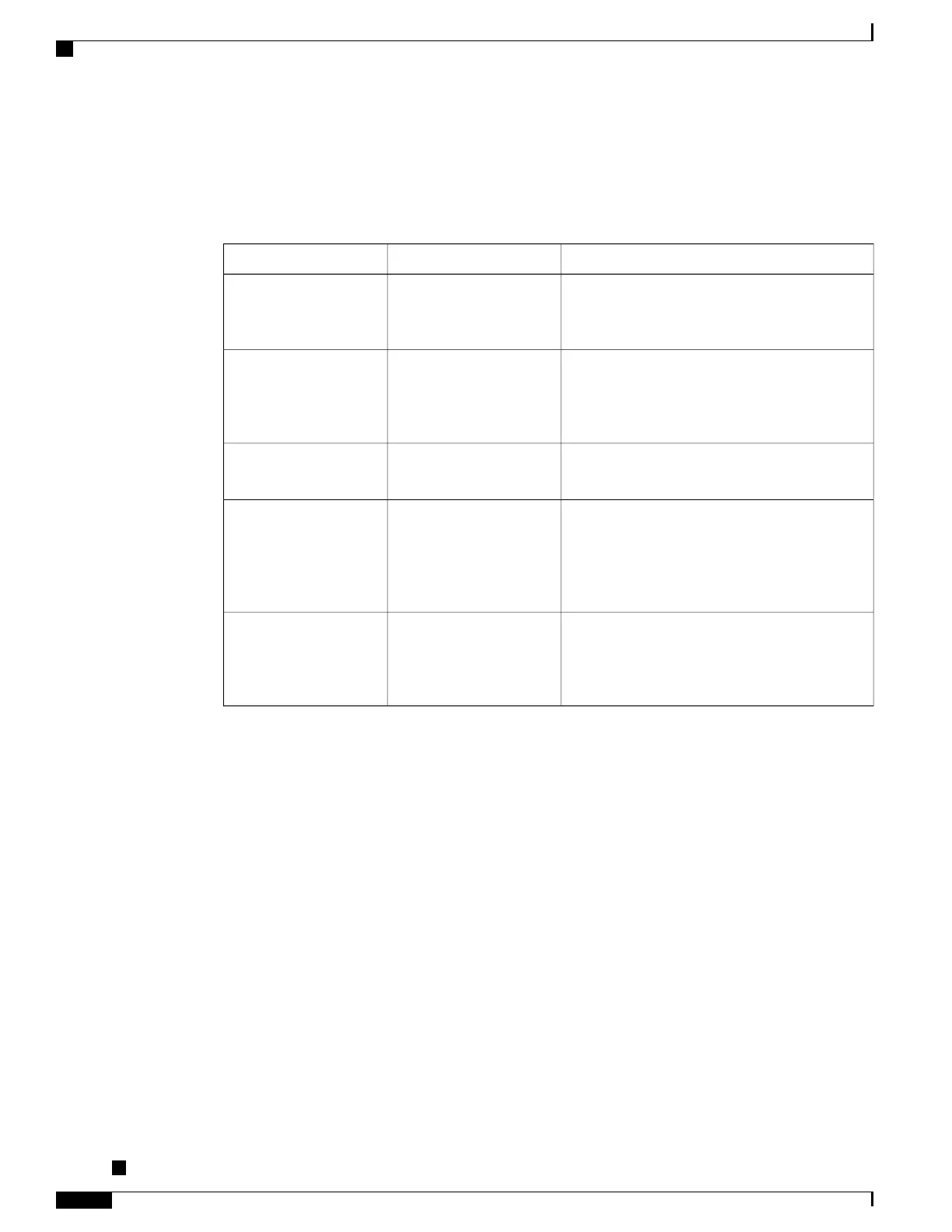
DescriptionKey Management OptionsAuthentication Type
Any device can authenticate to the access point.
For added security, static WEP encryption might
optionally be used.
NoneOpen
The phone encrypts the challenge text by using
the WEP key and the access point must verify the
WEP key that was used to encrypt the challenge
text before network access is available.
NoneShared Key
The RADIUS server authenticates the username
and password before network access is available.
NoneLEAP or EAP-FAST
The phone looks for an access point with one of
the key management options enabled. The
username and password are authenticated by the
RADIUS server before network access is
available.
WPA, WPA2, or CCKMAuto (AKM)
The phone looks for an access point that has one
of the key management options enabled.
Authentication uses the configured
WPA-Pre-shared key or WPA2-Pre-shared key
WPA-Pre-shared key,
WPA2-Pre-shared key
Auto (AKM)
4
Load the stored phone image. The Cisco Unified IP Phone has nonvolatile flash memory in which the
phone stores firmware images and user-defined preferences. At startup, the phone runs a bootstrap loader
that loads a phone firmware image that is stored in flash memory. Using this image, the phone initializes
the software and hardware.
5
Configure the VLAN. If the Cisco Unified IP Phone is connected to a Cisco Catalyst switch, the switch
next informs the phone of the voice VLAN that is defined on the switch. The phone needs to know the
VLAN membership before it can proceed with the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) request
for an IP address.
6
Obtain an IP address. If the Cisco Unified IP Phone is using DHCP to obtain an IP address, the phone
queries the DHCP server to obtain one. If you are not using DHCP in your network, you must assign static
IP addresses to each phone locally.
7
Request the CTL file. The TFTP server stores the CTL file. This file contains the certificates that are
necessary for establishing a secure connection between the phone and Cisco Unified Communications
Manager.
For more information, see the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Security Guide, “Configuring the
Cisco CTL Client” chapter.
Cisco Unified IP Phone 8961, 9951, and 9971 Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
10.0
16
Phone Startup Overview

 Loading...
Loading...







