152
7. Drag the icon of a specific device in the WiNet topology and place it to a position as needed. If
the browser is configured to accept cookies, the latest position information of each device is
stored after you click Network Snapshot.
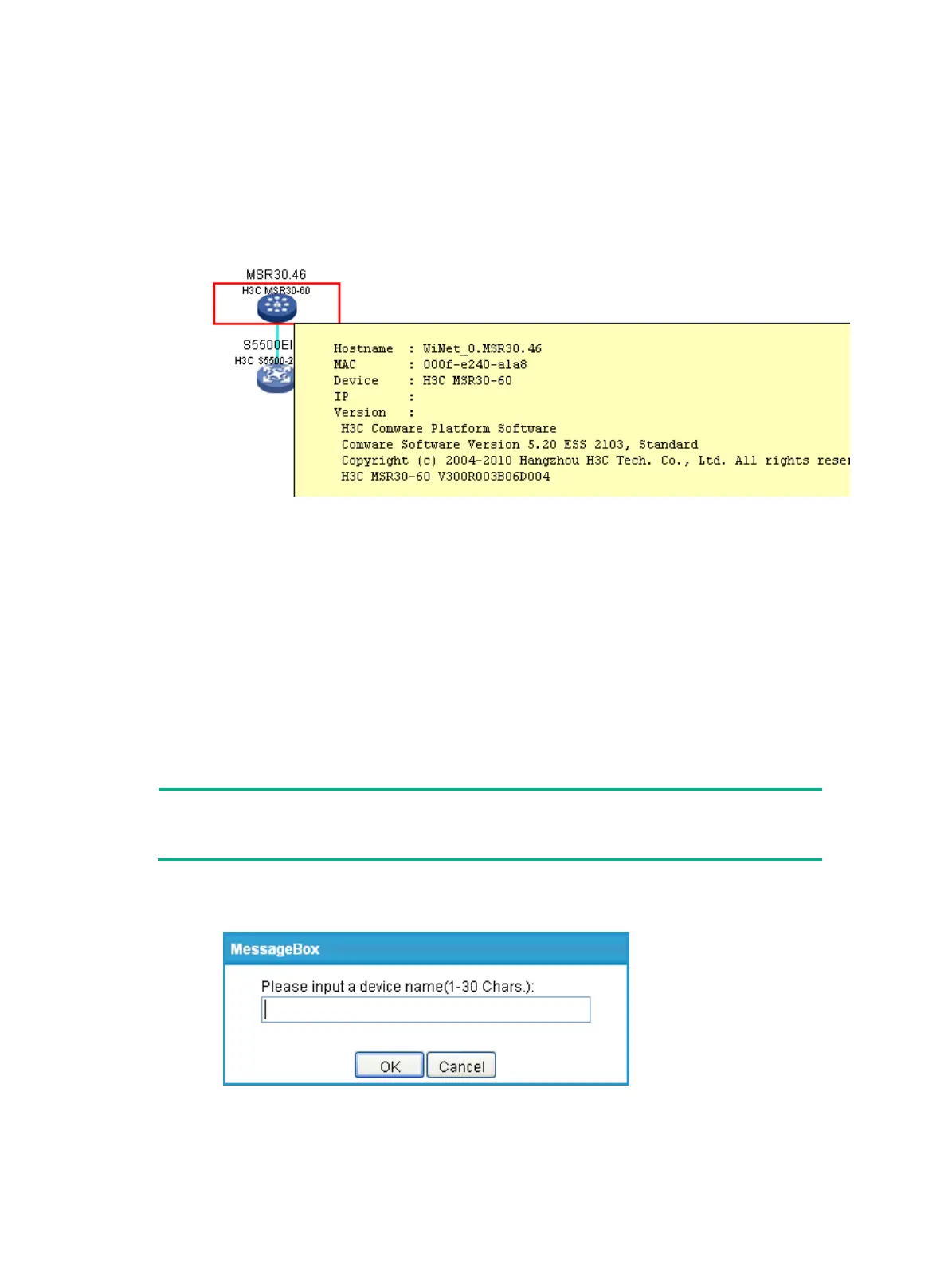
8. Double-click a device on the WiNet topology map to show details about the device, including
the hostname, MAC address, device model, IP address, version, number of hops, and WiNet
information, as shown in Figure 537.
Figure 537
Dev
ice details
9. View the WiNet topology information, including the role of each device and connection status
between devices. The connection status can be:
Normal link—Indicates a connection existing in the baseline topology and the current
topology.
New link—Indicates a connection not existing in the baseline topology but in the current
topology.
Blocked loops—Indicate connections blocked by STP. If a normal link is blocked, it is
displayed as a black broken line; if a new link is blocked, it is displayed as a blue broken line.
Down link—Indicates a connection existing in the baseline topology but not in the current
topology.
10. Click a device in the topology diagram to view its panel diagram. You can manage the device as
follows:
NOTE:
Support for displaying of the device panel, device renaming, and Layer 2 portal authentication
on interfaces depends on the device model.
a. Click Rename Device and enter a new system name for the device.
Figure 538 Rename a device
b. Select one or multiple Layer 2 Ethernet interfaces on the panel diagram of the device, and
click Port Guard to enable Layer 2 portal authentication on the interfaces.

 Loading...
Loading...




