Gocator Line Profile Sensors: User Manual
How Gocator Works • 70
Geometric Features
Many of Gocator’s measurement tools can output data structures such as points, lines, planes, and
circles. These structures are called geometric features and contain the components you would expect: a
point geometric feature contains X, Y, and Z components (representing the location of the point in 3D
space). Examples of point geometric features output by Gocator’s measurement tools are hole center
points, the tip and base of studs, or a position on a surface.
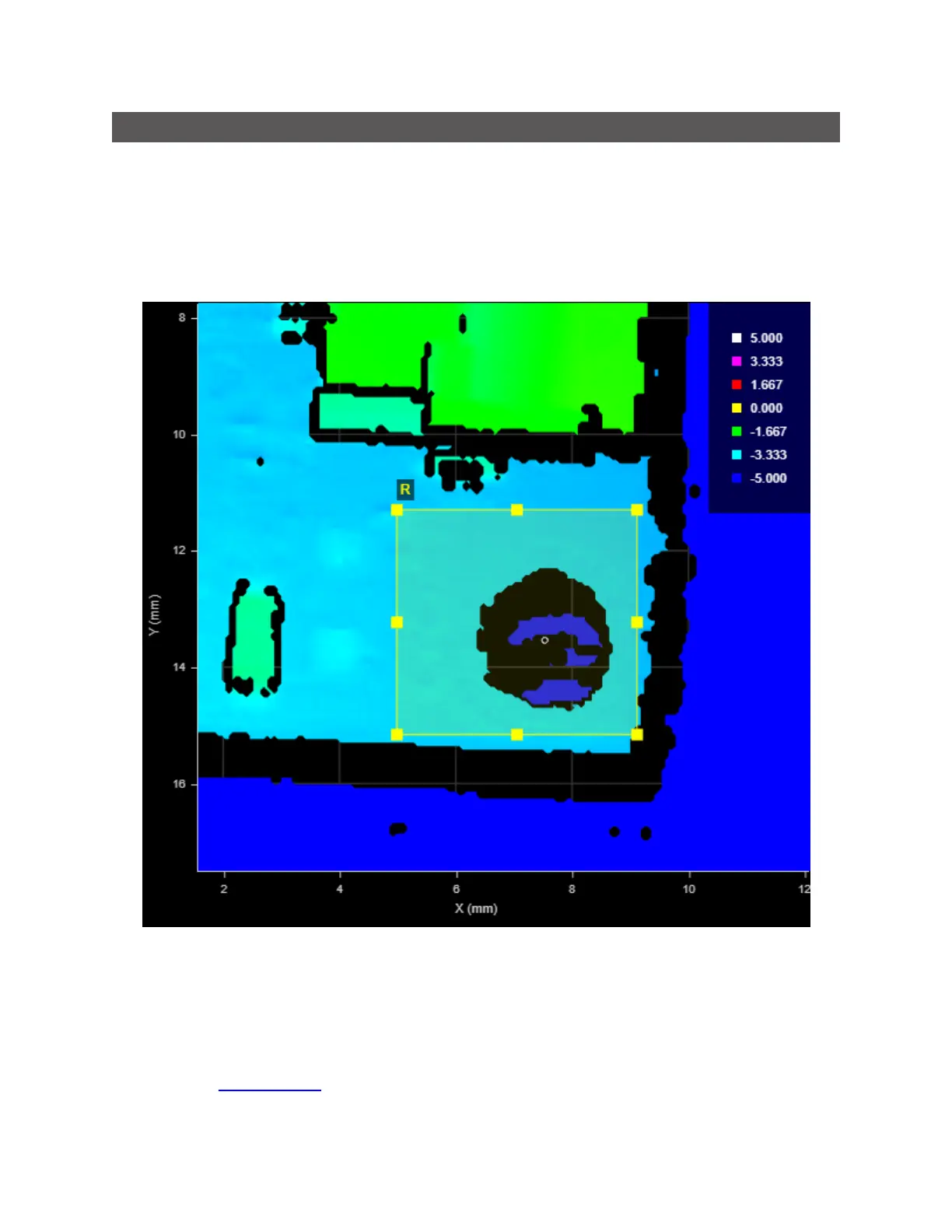
Geometric features are rendered as overlays on a tool's input data.
Point geometric feature (a hole's Center Point)rendered
on a tool's input as a small white circle
Gocator’s “Feature” tools (such as Feature Dimension and Feature Intersect) use geometric features as
inputs. For example, because the point geometric feature representing the center of a hole has X, Y, and
Z components, you can perform dimensional measurements between it and another geometric feature,
such as another hole or an edge. For more information on Feature tools, see Feature Measurement on
page 408. The Feature Create tool takes one or more geometric features as input and generates new
 Loading...
Loading...
