MCLAG Packet Flow Configuring Multi-chassis Link Aggregation
page 10-18 OmniSwitch AOS Release 7 Network Configuration Guide June 2013
MCLAG Packet Flow
Layer 2 Switching over MCLAG
Since hosts A and B are within the same IP subnet and VLAN, host A has a directly connected route to
reach B through the outgoing interface connected to switch S1. Host A needs to determine the MAC
address of host B.
ARP Request Over MCLAG
1 Since both hosts are in the same IP subnet, host A will send an ARP request as follows:
• Source MAC = MAC
A
• Destination MAC = ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff (Broadcast)
• Target IP = IP
B
Depending on the hash algorithm or use of a fixed primary port for non-unicast traffic, switch S
1
will
select a different port of the aggregate MCLAG A to send the ARP request. In this example, assume that
the request goes through one of the ports connected to M1 represented by L
A1
.
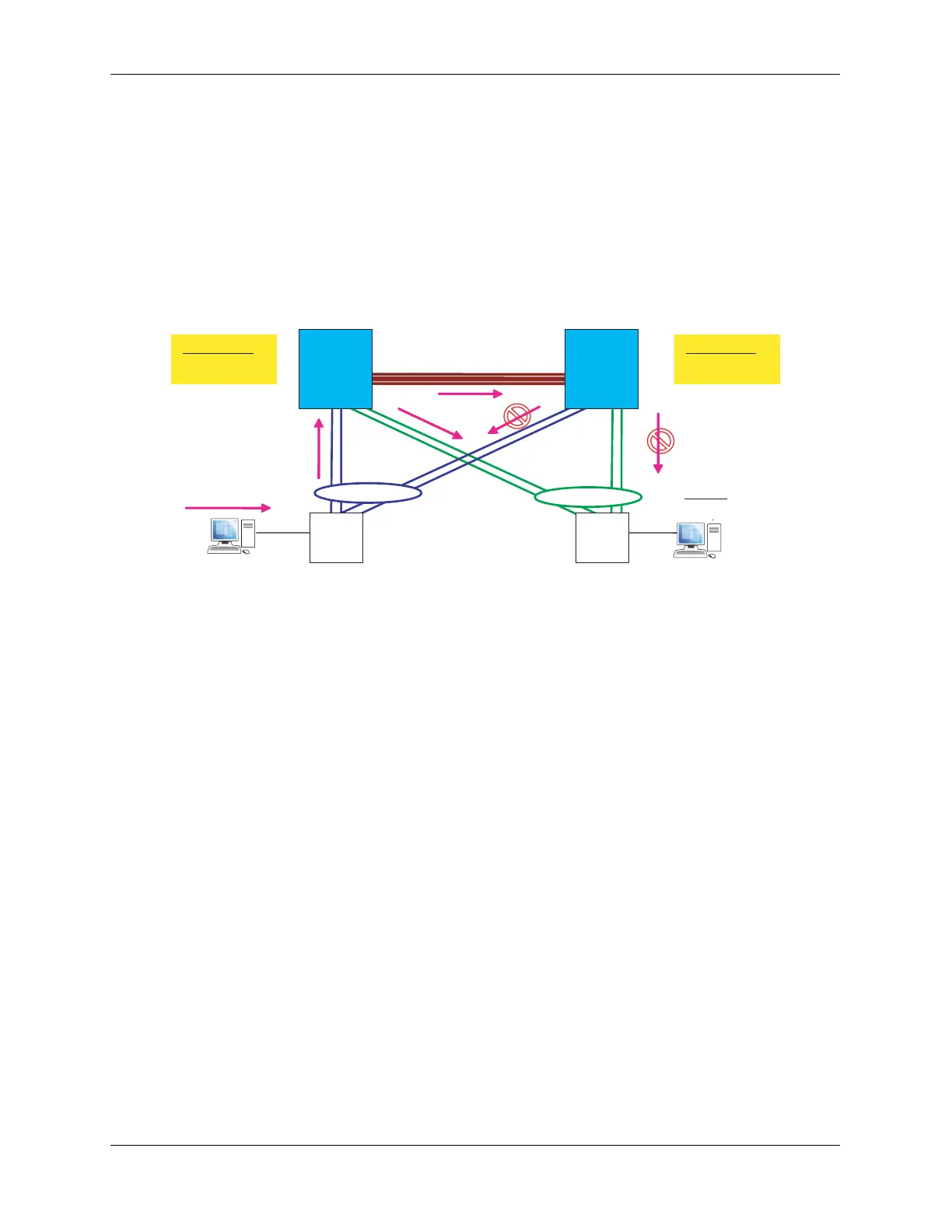
2 Loop Prevention
• The broadcast packet is simply flooded within the system as indicated by the arrows.
• The MCLAG will prevent the flooded packets received by M
2
through the Virtual Fabric Link from
being sent out its local MCLAG ports.
• This way, S
2
will not get duplicate copies of the original packet that would otherwise flow through two
distinct paths: S
1
==> M
1
==> S
2
and S
1
==> M
1
==> M
2
==> S
2
.
3 Step 3: MAC
A
Learning
• Switch M
1
will learn MAC@= MAC
A
on the MCLAG aggregate L
A
.
• Switch M
2
will learn MAC@= MAC
A
on the MCLAG aggregate L
A
as well.
M
1
S
1
MC-LAG-A
M
2
S
2
Host B
(MAC
B
, IP
B
)
MC-LAG-B
ARP Req.
L
A1
L
A2
L
B1
L
B2
MAC Table
MAC
A
⇒ L
A
MAC Table
MAC
A
⇒ L
A
 Loading...
Loading...