14
Introduction to Variable-Frequency Drives Section 1-3
1-3 Introduction to Variable-Frequency Drives
1-3-1 The Purpose of Motor Speed Control for Industry
Omron inverters provide speed control for 3-phase AC induction motors. You
connect AC power to the inverter, and connect the inverter to the motor. Many
applications benefit from a motor with variable speed, in several ways:
• Energy savings - HVAC
• Need to coordinate speed with an adjacent process - textile and printing
presses
• Need to control acceleration and deceleration (torque)
• Sensitive loads - elevators, food processing, pharmaceuticals
1-3-2 What is an Inverter
The term inverter and variable-frequency drive are related and somewhat
interchangeable. An electronic motor drive for an AC motor can control the
motor's speed by varying the frequency of the power sent to the motor.
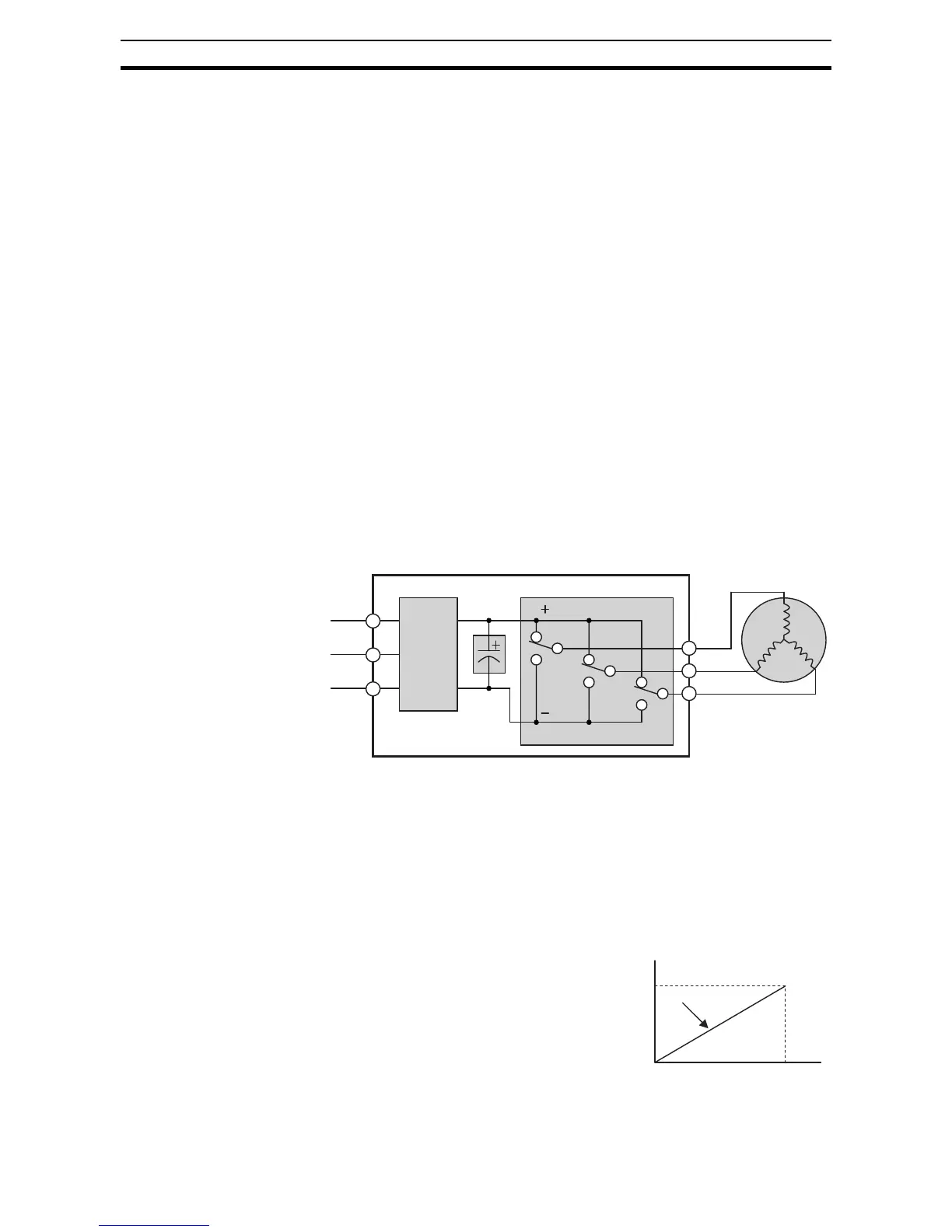
An inverter, in general, is a device that converts DC power to AC power. The
figure below shows how the variable-frequency drive employs an internal
inverter. The drive first converts incoming AC power to DC through a rectifier
bridge, creating an internal DC bus voltage. Then the inverter circuit converts
the DC back to AC again to power the motor. The special inverter can vary its
output frequency and voltage according to the desired motor speed.
The simplified drawing of the inverter shows three double-throw switches. In
Omron inverters, the switches are actually IGBTs (insulated gate bipolar tran-
sistors). Using a commutation algorithm, the microprocessor in the drive
switches the IGBTs on and off at a very high speed to create the desired out-
put waveforms. The inductance of the motor windings helps smooth out the
pulses.
1-3-3 Torque and Constant Volts/Hertz Operation
In the past, AC variable speed drives used
an open loop (scalar) technique to control
speed. The constant-volts-hertz operation
maintains a constant ratio between the
applied voltage and the applied frequency.
With these conditions, AC induction motors
inherently delivered constant torque across
the operating speed range. For some appli-
cations, this scalar technique was ade-
quate.
Rectifier
Motor
InverterConverter Internal
DC Bus
Power
Input
L1
L2
L3
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
Variable-frequency Drive
Output
voltage
V
0
Output frequency
100%
f
Constant torque

 Loading...
Loading...