n
D Control
Overshoot refers to a control loop tendency to overcompensate for an error condition, causing a new error in the opposite direction. Derivative action
provides an anticipatory function that exerts a “braking” action on the control loop. When combined, the proportional integral, and derivative actions
provide quick response to error, close adherence to the setpoint, and control stability.
n
PID Operation
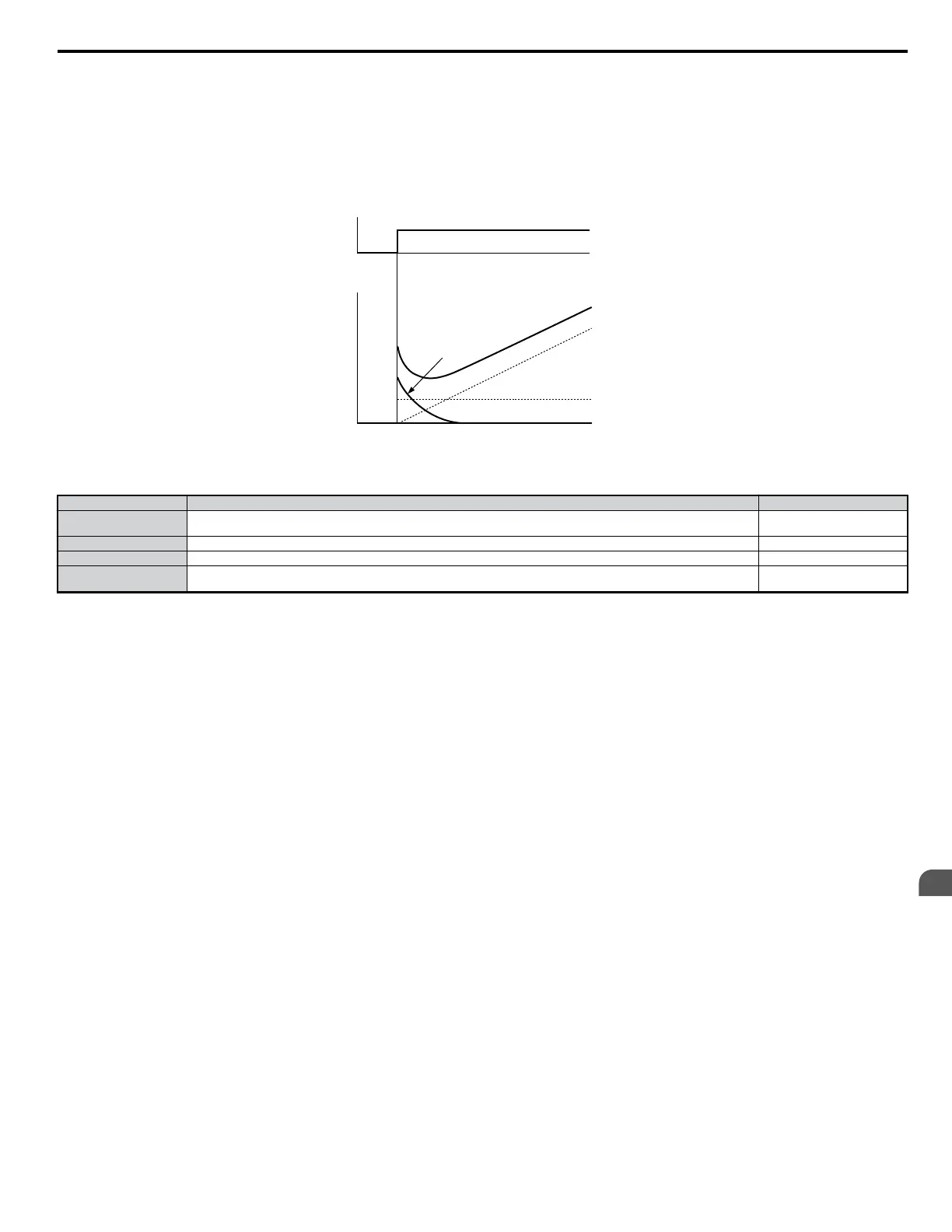
To better demonstrate how PID input works, the diagram below shows how the output changes as the deviation between the target value and the feedback
level are kept constant.
Offset
I Control
Amount
D Control
Time
PID Control
Time
P Control
n
Using PID Control
Applications for PID control are listed in the table below.
Application Description Sensors Used
Speed Control
Machinery speed is fed back and adjusted to meet the target value.
Synchronous control is performed using speed data from other machinery as the target value.
Tachometer
Pressure Maintains constant pressure using pressure feedback. Pressure sensor
Fluid Control Keeps flow at a constant level by feeding back flow data. Flow rate sensor
Temperature Control Maintains a constant temperature by controlling a fan with a thermostat.
Thermocoupler
Thermistor
5.2 b: Setup
YASKAWA ELECTRIC SIEP C710606 18A YASKAWA AC Drive – V1000 Technical Manual (Preliminary)
123
5
Parameter Details

 Loading...
Loading...