Appendix 5 FFT Definitions
A18
Aliasing ______________________________________________________
When the frequency of a signal to be measured is higher than the sampling rate,
the observed frequency is lower than that of the actual signal, with certain fre-
quency limitations. This phenomena occurs when sampling occurs at a lower fre-
quency than that defined by the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem, and is
called aliasing.
If the highest frequency component of the input signal is f
max
and the sampling
frequency is f
s
, the following expression must be satisfied:
Therefore, if the input includes a frequency component higher than f
s
/2, it is
observed as a lower frequency (alias) that does not really exist.
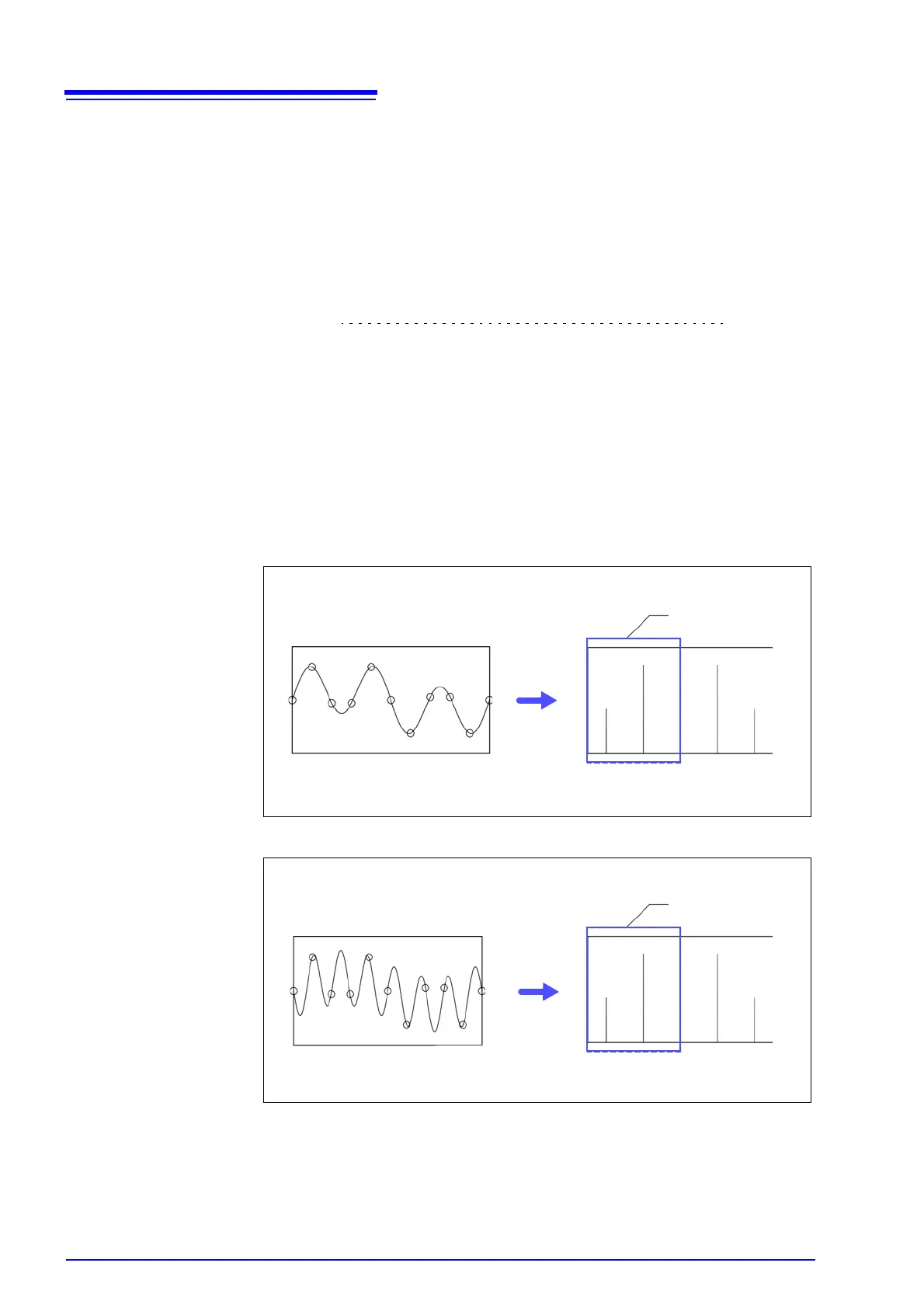
The following diagrams show the results of spectrum analysis of composite
waveforms having components of 1 kHz and 3 kHz, and of 1 kHz and 7 kHz.
If sampling frequency f
s
is 10 kHz, the spectral component of an input frequency
above 5 kHz (in this case, 7 kHz) is observed as an alias at 5 kHz or below.
In this example the difference between the 3 and 7 kHz components is indiscern-
ible.
Composite waveform of 1 kHz and 3 kHz components sampled at 10 kHz
Time
Portion Displayed on
Screen
Spectrum
1357
Frequency
[kHz]
Composite waveform of 1 kHz and 7 kHz components sampled at 10 kHz
Time
Spectrum
Frequency
[kHz]
1357
Portion Displayed on
Screen
 Loading...
Loading...