PLC concepts
5.1 Execution of the user program
S7-1200 Programmable controller
System Manual, V4.2, 09/2016, A5E02486680-AK
107
Understanding event execution priorities and queuing
The CPU limits the number of pending (queued) events from a single source, using a
different queue for each event type. Upon reaching the limit of pending events for a given
event type, the next event is lost. You can use a time error interrupt OB (Page 96) to
respond to queue overflows.
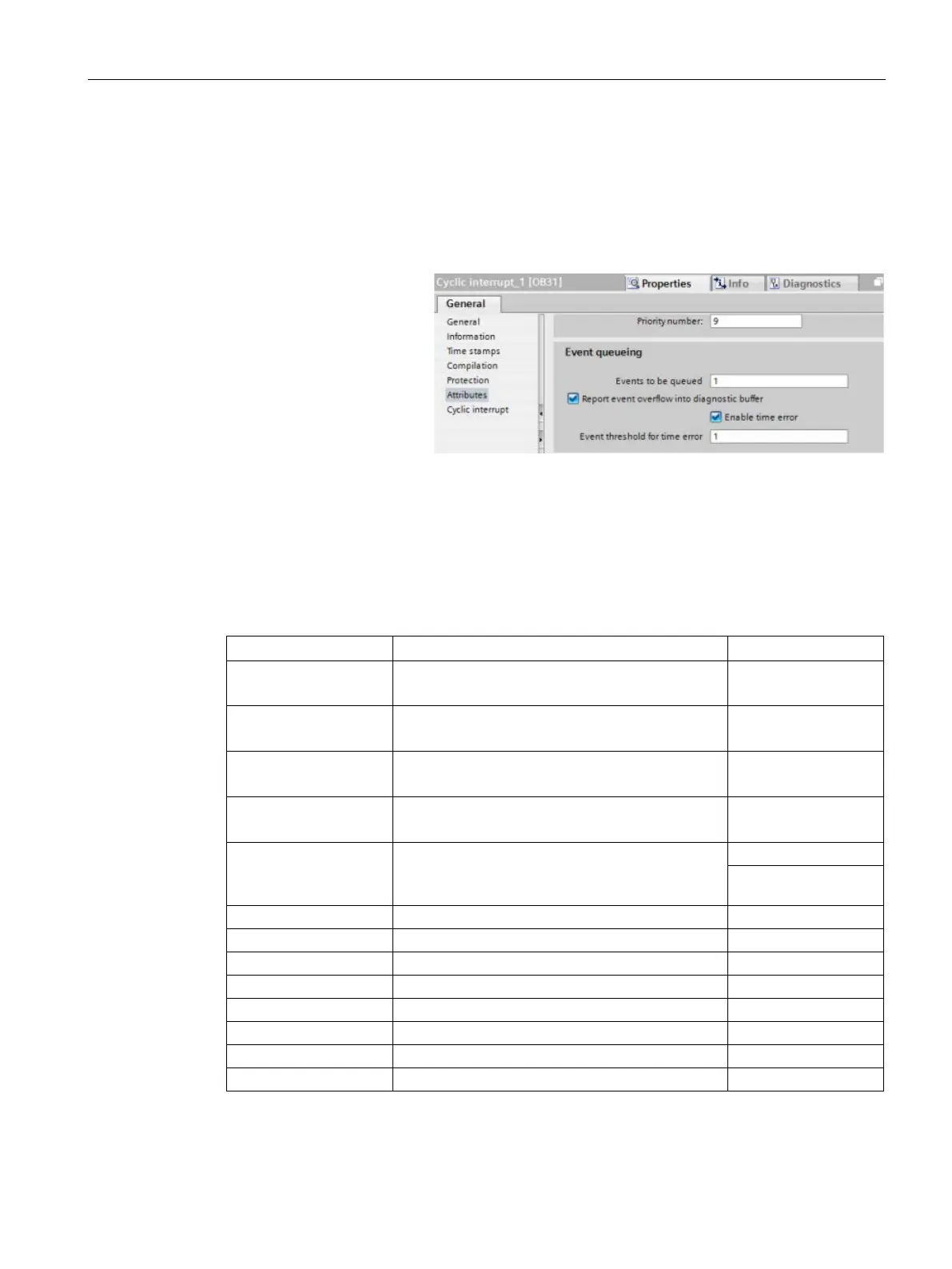
7 allows you
to configure some specific
event queueing parameters
for the Cycl
ic interrupt OB
For further information on CPU overload behavior and event queueing, refer to the STEP 7
Information System.
Each CPU event has an associated priority. In general, the CPU services events in order of
priority (highest priority first). The CPU services events of the same priority on a "first-come,
first-served" basis.
Table 5- 16 OB events
Program cycle 1 program cycle event
1
4
Startup 1 startup event
1
1
4
Time delay Up to 4 time events
3
Cyclic interrupt Up to 4 events
8
Hardware interrupt Up to 50 hardware interrupt events
2
1 OB per event, but you can use the same OB for
18
1 event (only if configured)
3
4
1 event (only if configured)

 Loading...
Loading...


















