Basic instructions
8.8 Program control operations
S7-1200 Programmable controller
316 System Manual, V4.2, 09/2016, A5E02486680-AK
When the "Tag_1" operand in network 1 has the signal state "1", the RUNTIME instruction
executes. The starting point for the runtime measurement is set with the first call of the
instruction and buffered as reference for the second call of the instruction in the "Mem"
operand.
The function block FB1 executes in network 2.
When the FB1 program block completes and the "Tag_1" operand has the signal state "1",
the RUNTIME instruction in network 3 executes. The second call of the instruction calculates
the runtime of the program block and writes the result to the output RET_VAL_2.
SCL program control statements
8.8.10.1
Overview of SCL program control statements
Structured Control Language (SCL) provides three types of program control statements for
structuring your user program:
● Selective statements: A selective statement enables you to direct program execution into
alternative sequences of statements.
● Loops: You can control loop execution using iteration statements. An iteration statement
specifies which parts of a program should be iterated depending on certain conditions.
● Program jumps: A program jump means an immediate jump to a specified jump
destination and therefore to a different statement within the same block.
These program control statements use the syntax of the PASCAL programming language.
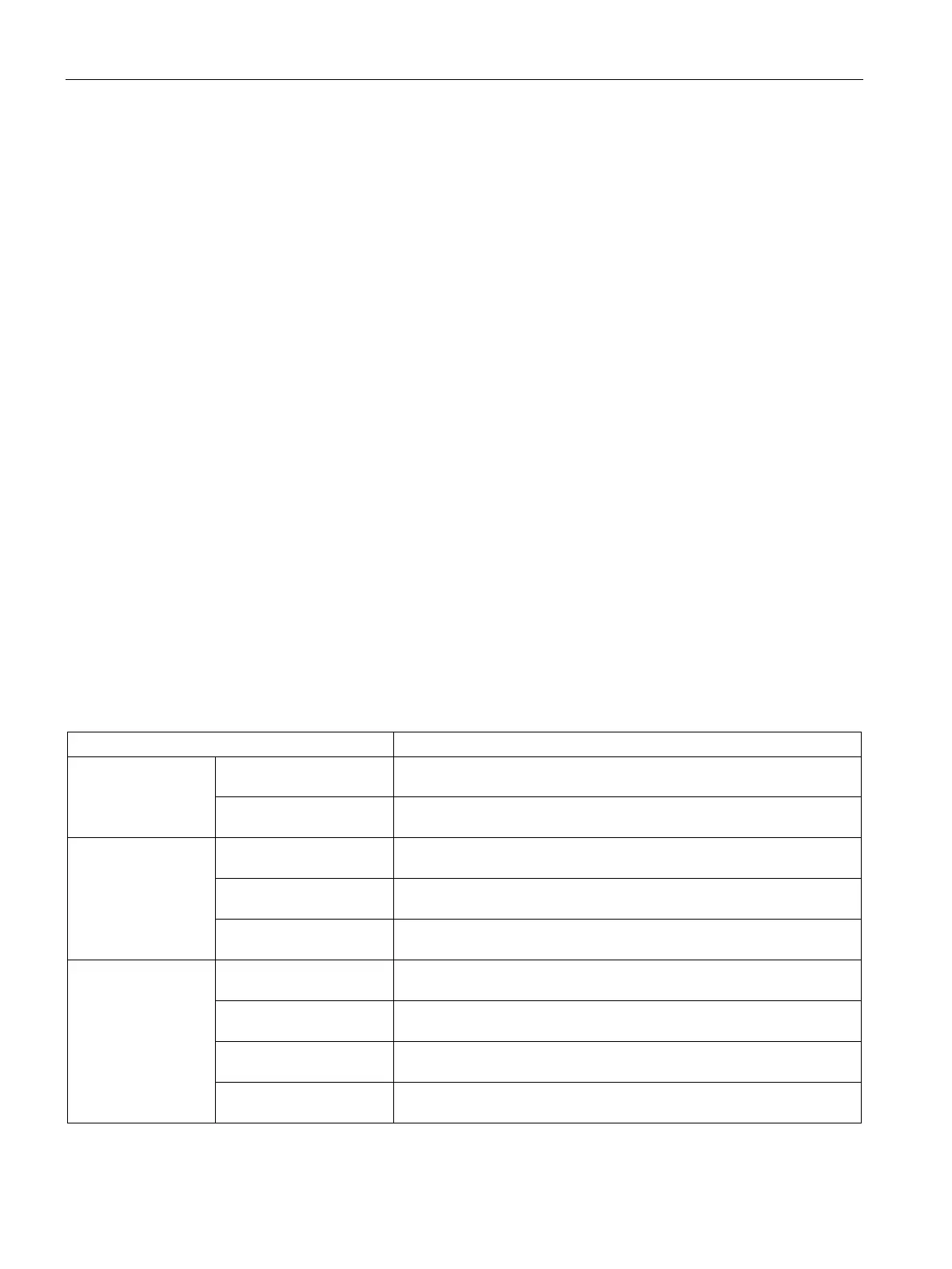
Table 8- 152 Types of SCL program control statements
Program control statement
Selective IF-THEN statement
Enables you to direct program execution into one of two alternative
branches, depending on a condition being TRUE or FALSE
CASE statement
Enables the selective execution into 1 of
n
alternative branches, based
on the value of a variable
Loop FOR statement
Repeats a sequence of statements for as long as the control variable
remains within the specified value range
WHILE-DO statement
Repeats a sequence of statements while an execution condition con-
REPEAT-UNTIL state-
Repeats a sequence of statements until a terminate condition is met
Program jump CONTINUE statement
Stops the execution of the current loop iteration
EXIT statement
Exits a loop at any point regardless of whether the terminate condition
GOTO statement
Causes the program to jump immediately to a specified label
RETURN statement
Causes the program to exit the block currently being executed and to
return to the calling block

 Loading...
Loading...


















