Extended instructions
9.8 Pulse
S7-1200 Programmable controller
492 System Manual, V4.2, 09/2016, A5E02486680-AK
Table 9- 190 STATUS parameter error code value
0x8090 Pulse generator with the specified hardware ID is in use.
0x8091 Frequency out-of-range. The desired frequency exceeds the maximum frequency of the
0x80A1 PTO identifier (hardware ID) does not address a valid PTO.
0x80D0 Pulse generator with the specified hardware ID is not activated. Activate the pulse gen-
erator in the CPU properties under "Pulse generators (PTO/PWM)".
0x80D1 Pulse generator with the specified hardware ID has no PTO selection. Select PTO in
Operation of the pulse outputs
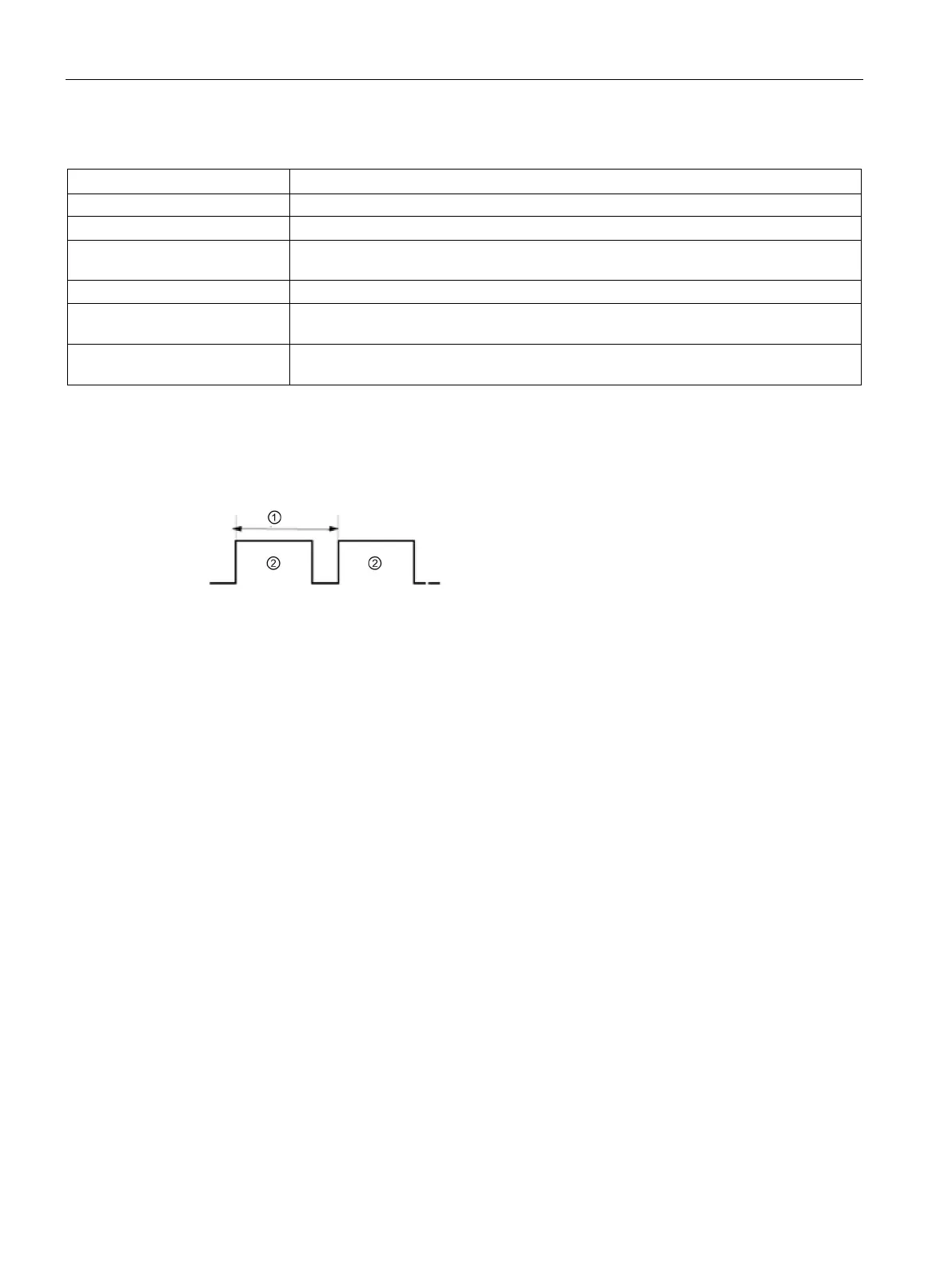
Pulse width can be expressed as hundredths of the
cycle time (0 to 100), as thousandths (0 to 1000), as
ten thousandths (0 to 10000), or as S7 analog format.
The pulse width can vary from 0
(no pulse, always off)
to full scale (no pulse, always on).
Since the PWM output can be varied from 0 to full scale, it provides a digital output that in
many ways is the same as an analog output. For example, the PWM output can be used to
control the speed of a motor from stop to full speed, or it can be used to control position of a
valve from closed to fully opened.
You configure frequency in the hardware configuration. You control pulse width from the user
program.
Four pulse generators are available for controlling high-speed pulse output functions: PWM
and Pulse train output (PTO). PTO is used by the motion control instructions. You can assign
each pulse generator to either PWM or PTO, but not both at the same time.
You can use onboard CPU outputs, or you can use the optional signal board outputs. The
output point numbers are shown in the following table (assuming the default output
configuration). If you have changed the output point numbering, then the output point
numbers will be those you assigned. Note that PWM requires only one output, while PTO
can optionally use two outputs per channel. If an output is not required for a pulse function, it
is available for other uses. Refer to the table below for I/O assignment.

 Loading...
Loading...


















