Basic instructions
8.3 Counter operations
S7-1200 Programmable controller
244 System Manual, V4.2, 09/2016, A5E02486680-AK
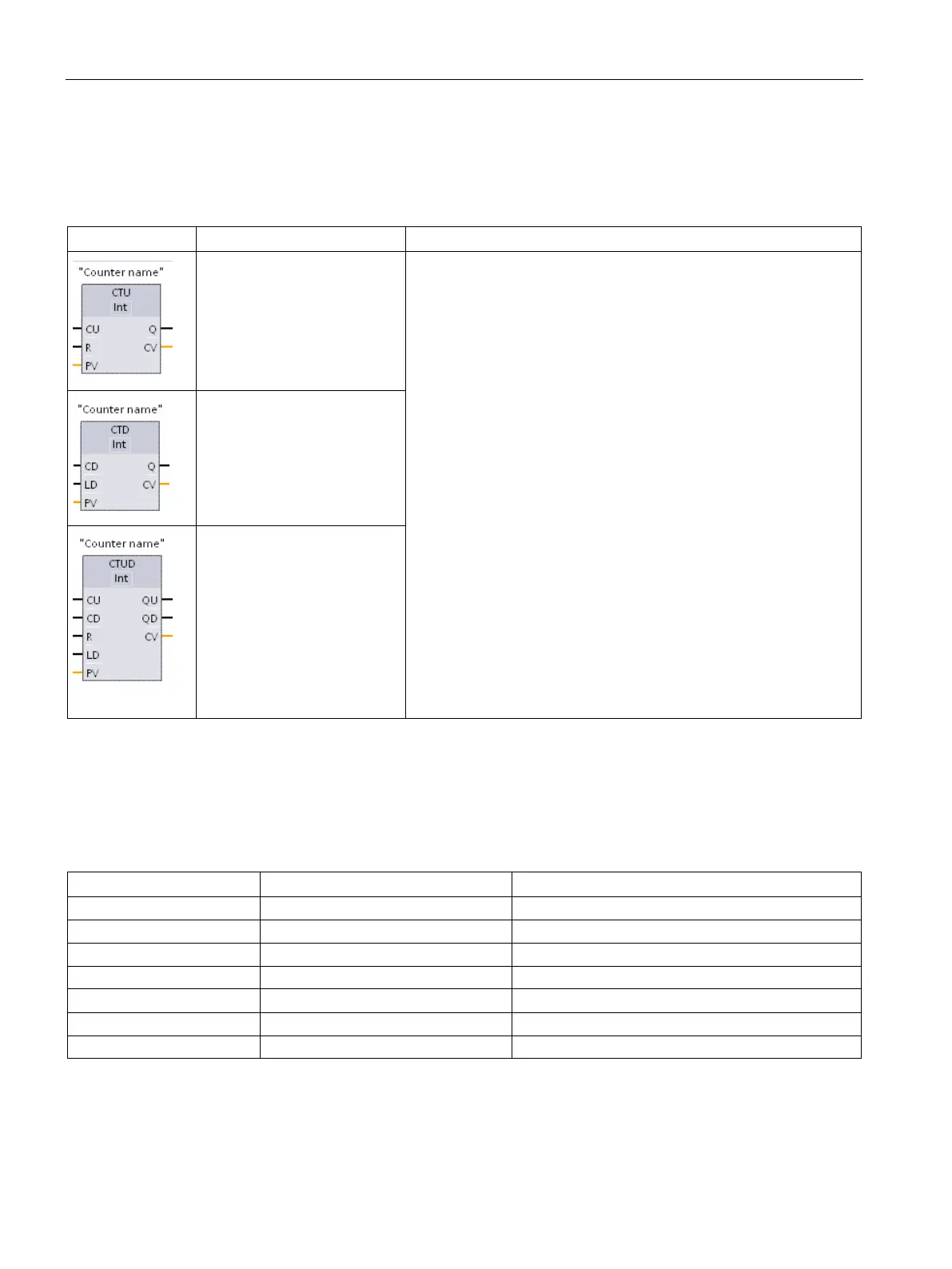
Table 8- 23 Counter instructions
(
CU:=_bool_in,
R:=_bool_in,
PV:=_in,
Q=>_bool_out,
Use the counter instructions to count internal program events and
external process events. Each counter uses a structure stored in a
data block to maintain counter data. You assign the data block when
the counter instruction is placed in the editor.
• CTU is a count-up counter
• CTD is a count-down counter
• CTUD is a count-up-and-down counter
(
CD:=_bool_in,
LD:=_bool_in,
PV:=_in,
Q=>_bool_out,
D(
CU:=_bool_in,
CD:=_bool_in,
R:=_bool_in,
LD:=_bool_in,
PV:=_in_,
QU=>_bool_out,
QD=>_bool_out,
For LAD and FBD: Select the count value data type from the drop-down list below the instruction name.
STEP 7 automatically creates the DB when you insert the instruction.
3
In the SCL examples, "IEC_Counter_0_DB" is the name of the instance DB.
Table 8- 24 Data types for the parameters
Count up or count down, by one count
Reset count value to zero
Load control for preset value
SInt, Int, DInt, USInt, UInt, UDInt
Q, QU Bool True if CV >= PV
SInt, Int, DInt, USInt, UInt, UDInt
The numerical range of count values depends on the data type you select. If the count value is an unsigned integer
type, you can count down to zero or count up to the range limit. If the count value is a signed integer, you can count
down to the negative integer limit and count up to the positive integer limit.

 Loading...
Loading...


















