Programming concepts
7.3 Using blocks to structure your program
S7-1200 Programmable controller
188 System Manual, V4.2, 09/2016, A5E02486680-AK
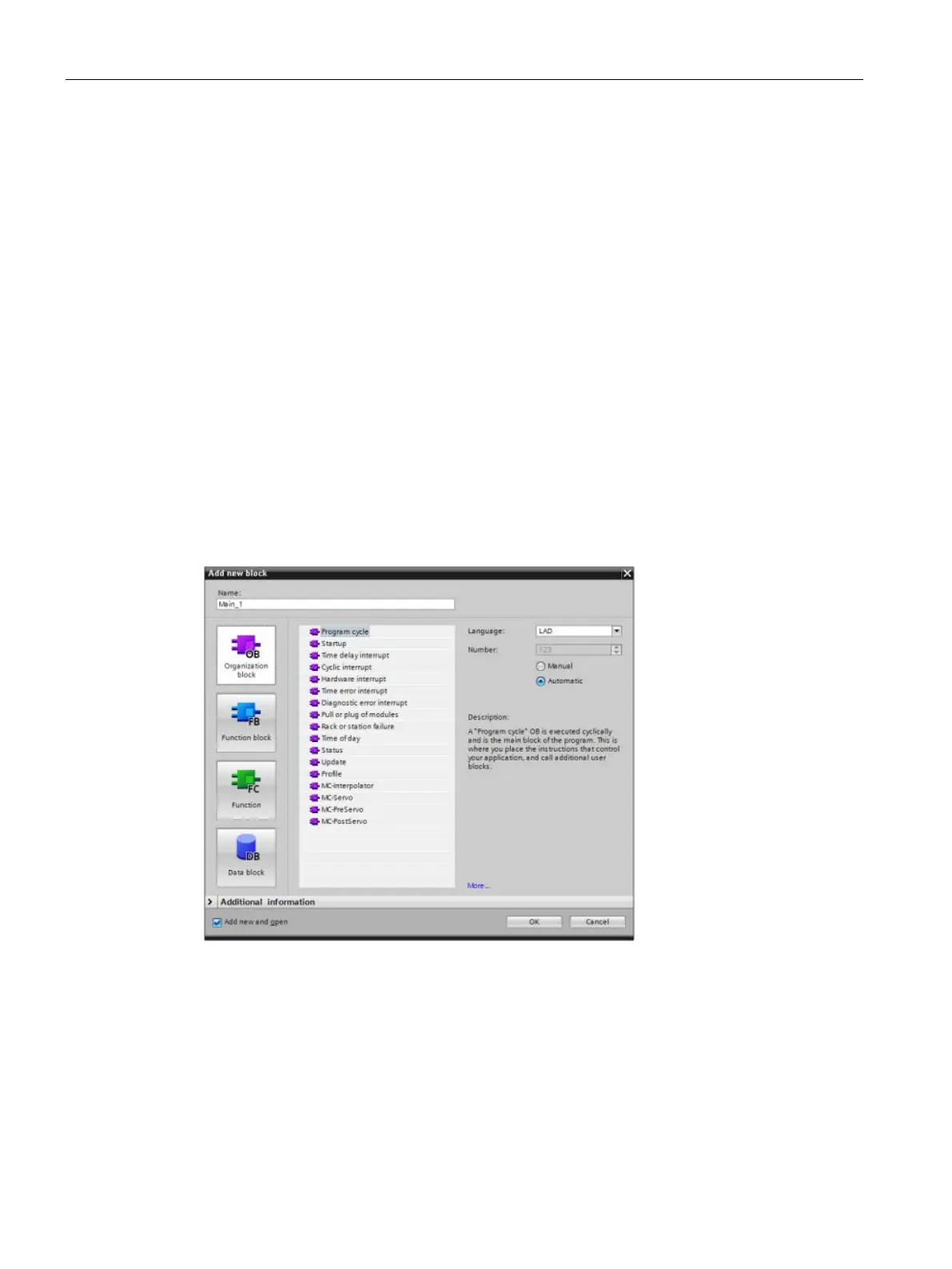
Organization blocks provide structure for your program. They serve as the interface between
the operating system and the user program. OBs are event driven. An event, such as a
diagnostic interrupt or a time interval, causes the CPU to execute an OB. Some OBs have
predefined start events and behavior.
The program cycle OB contains your main program. You can include more than one program
cycle OB in your user program. During RUN mode, the program cycle OBs execute at the
lowest priority level and can be interrupted by all other event types. The startup OB does not
interrupt the program cycle OB because the CPU executes the startup OB before going to
RUN mode.
After finishing the processing of the program cycle OBs, the CPU immediately executes the
program cycle OBs again. This cyclic processing is the "normal" type of processing used for
programmable logic controllers. For many applications, the entire user program is located in
a single program cycle OB.
You can create other OBs to perform specific functions, such as for handling interrupts and
errors, or for executing specific program code at specific time intervals. These OBs interrupt
the execution of the program cycle OBs.
Use the "Add new block" dialog to create new OBs in your user program.
Interrupt handling is always
event
-driven. When such
an event occurs, the CPU
interrupts the execution of
the user program and calls
the OB that was configured
to ha
ndle that event. After
finishing the execution of
the interrupting OB, the
CPU resumes the exec
u-
tion of the user program at
the point of interruption.
The CPU determines the order for handling interrupt events by priority. You can assign
multiple interrupt events to the same priority class. For more information, refer to the topics
on organization blocks (Page 92) and execution of the user program (Page 83).

 Loading...
Loading...


















