True random number generator (RNG) RM0440
838/2126 RM0440 Rev 4
26.4 RNG interrupts
In the RNG an interrupt can be produced on the following events:
• Data ready flag
• Seed error, see
Section 26.3.7: Error management
• Clock error, see
Section 26.3.7: Error management
Dedicated interrupt enable control bits are available as shown in Table 205.
The user can enable or disable the above interrupt sources individually by changing the
mask bits or the general interrupt control bit IE in the RNG_CR register. The status of the
individual interrupt sources can be read from the RNG_SR register.
Note: Interrupts are generated only when RNG is enabled.
26.5 RNG processing time
The conditioning stage can produce four 32-bit random numbers every 16x clock
cycles, if the value is higher than 213 cycles (213 cycles otherwise).
More time is needed for the first set of random numbers after the device exits reset (see
Section 26.3.4: RNG initialization). Indeed, after enabling the RNG for the first time, random
data is first available after either:
• 128 RNG clock cycles + 426 AHB cycles, if f
AHB
< f
threshold
• 192 RNG clock cycles + 213 AHB cycles, if f
AHB
≥ f
threshold
With f
threshold
= (213 x f
RNG
)/ 64
26.6 RNG entropy source validation
26.6.1 Introduction
In order to assess the amount of entropy available from the RNG, STMicroelectronics has
tested the peripheral using German BSI AIS-31 statistical tests (T0 to T8). The results can
be provided on demand or the customer can reproduce the tests.
26.6.2 Validation conditions
STMicroelectronics has tested the RNG true random number generator in the following
conditions:
• RNG clock rng_clk= 48 MHz (CED bit = ’0’ in RNG_CR register) and rng_clk = 400 kHz
(CED bit = ‘1’ in RNG_CR register).
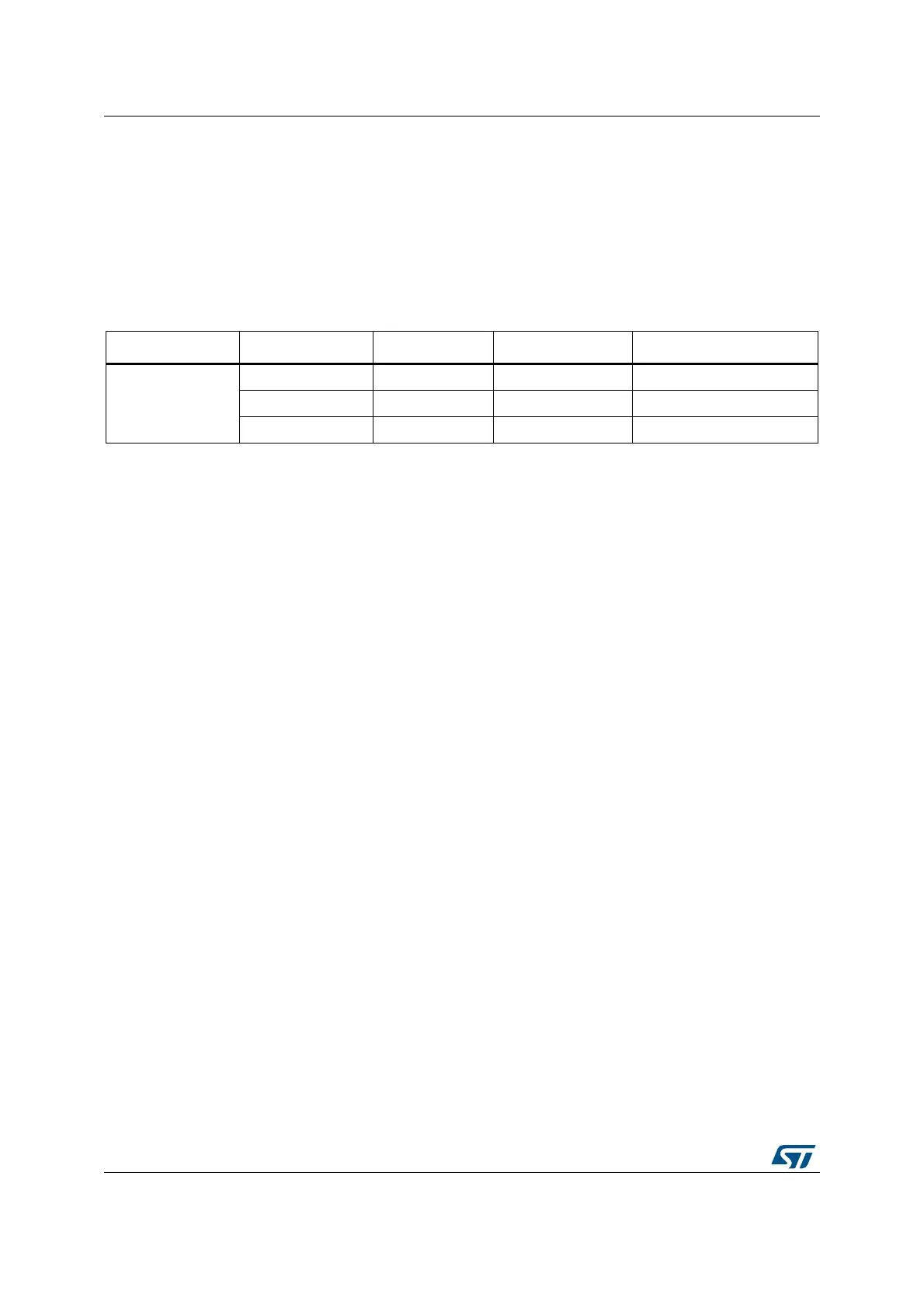
Table 205. RNG interrupt requests
Interrupt acronym Interrupt event Event flag Enable control bit Interrupt clear method
RNG
Data ready flag DRDY IE None (automatic)
Seed error flag SEIS IE Write 0 to SEIS
Clock error flag CEIS IE Write 0 to CEIS

 Loading...
Loading...