CDM-570/570L Satellite Modem with Optional IP Module Revision 12
Ethernet IP Module Interface MN/CDM570L.IOM
13–14
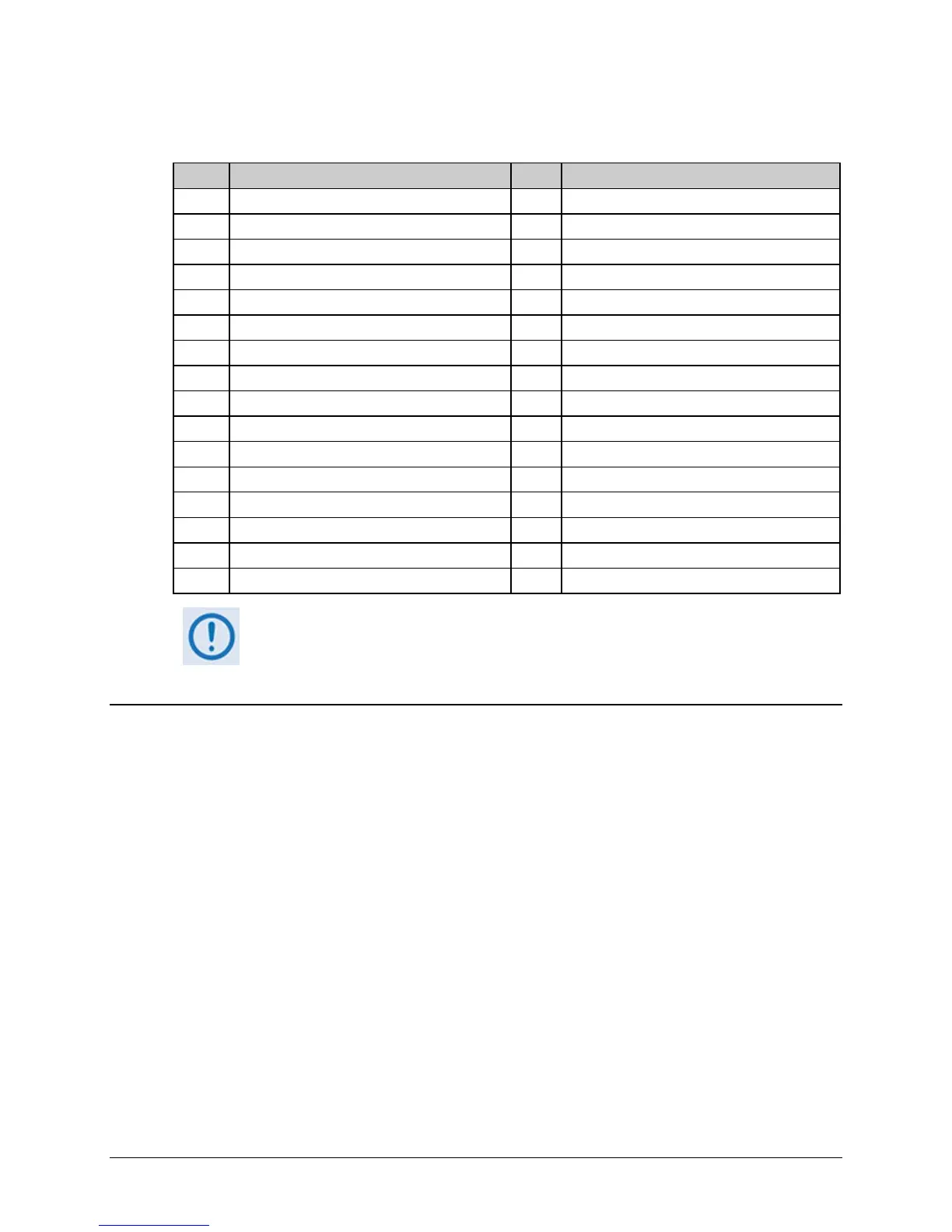
The following table can be used as a reference for some well known Port numbers:
Port Description Port Description
1 TCP Port Service Multiplexer (TCPMUX) 118 SQL Services
7 ECHO 119 Newsgroup (NNTP)
20 FTP - Data 137 NetBIOS Name Service
21 FTP - Control 139 NetBIOS Datagram Service
22 SSH Remote Login Protocol 150 NetBIOS Session Service
23 Telnet 156 SQL Server
25 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) 161 SNMP
42 Host Name Server (Nameserv) 179 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
53 Domain Name System (DNS) 190 Gateway Access Control Protocol (GACP)
69 Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) 197 Directory Location Service (DLS)
70 Gopher Services 396 Novell Netware over IP
80 HTTP 443 HTTPS
108 SNA Gateway Access Server 444 Simple Network Paging Protocol (SNPP)
109 POP2 546 DHCP Client
110 POP3 547 DHCP Server
115 Simple File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) 1080 Socks
Once the QoS Rules are defined, each type of traffic flow should be isolated and sent
to verify that it is being sent in the intended QoS Rule.
13.4.5.2 Minimum/Maximum Bandwidth QoS Mode
QoS Rules can be assigned to up to 32 different types of flows to be user-defined. Flows can be
defined by any combination of Protocol (FTP, UDP, RTP, etc.), Source/Destination IP (specific
or range), and/or Layer 3 Source/Destination Port.
Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) – The Min/Max BW QoS mode allows selection
of Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED).
WRED allows for more graceful dropping of packets as QoS queues get full. Typically, without
WRED, packets are dropped based upon a simple tail drop algorithm that is applied to packets as
they are being added to the QoS queues. This can result in large numbers of contiguous packets
being dropped, which causes many protocols such as RTP and TCP to ungracefully degrade
performance in a over-consumed or bursty scenario. WRED applies a randomization, which
means that the percentage change to drop packets increases as the queue becomes full, and
minimizes the chances of global synchronization. Thus, WRED allows the transmission line to be
used fully at all times.
Maximum Bandwidth – This can be assigned to a flow to restrict the Maximum Bandwidth that
any particular flow will utilize; otherwise, the default of no bandwidth restriction can be selected.
 Loading...
Loading...