8.5 Converting Input Values (Scaling Function)
132
When a calibration factor is stated in the sensor's inspection records
Set the [Method] item on the [Scaling] sheet to [Ratio].
The value of the calibration factor (0.001442 [G]) is set as the conversion ratio.
(* 10
-6
strain = με)
Move the cursor to the channel to set, and making settings as follows.
Using a strain gauge with a Gauge Factor other than 2.0
The 8969 Strain Unit measures the Gauge Rate as 2.0.
When using the other strain gauge, the Gauge Factor
needs to be set as the conversion ratio. For example, if the
Gauge Factor is 2.1, the conversion ratio is 0.952 (2
÷2.1).
The scaling (conversion ratio) needs to be calculated to include both Gauge Fac-
tor and physical value conversions. In this case, the conversion ratio setting is
the product of the conversion ratios of the Gauge Factor and measurement unit
scaling.
The Gauge Factor component of the conversion ratio is 0.952, and the physical
value component is 0.001442*
Conversion Ratio = 0.952 x 0.001442 = 0.0013728
As in Example 3, enter [0.0013728] as the conversion ratio.
* To convert measurement values to physical values when using a strain gauge,
calculate using the Young's modulus or Poisson's ratio of the measurement
object. The conversion method depends on the conditions in which the strain
gauge is used.
See: "Appendix 2.5 Scaling Method When Using Strain Gauges"( p.A9)
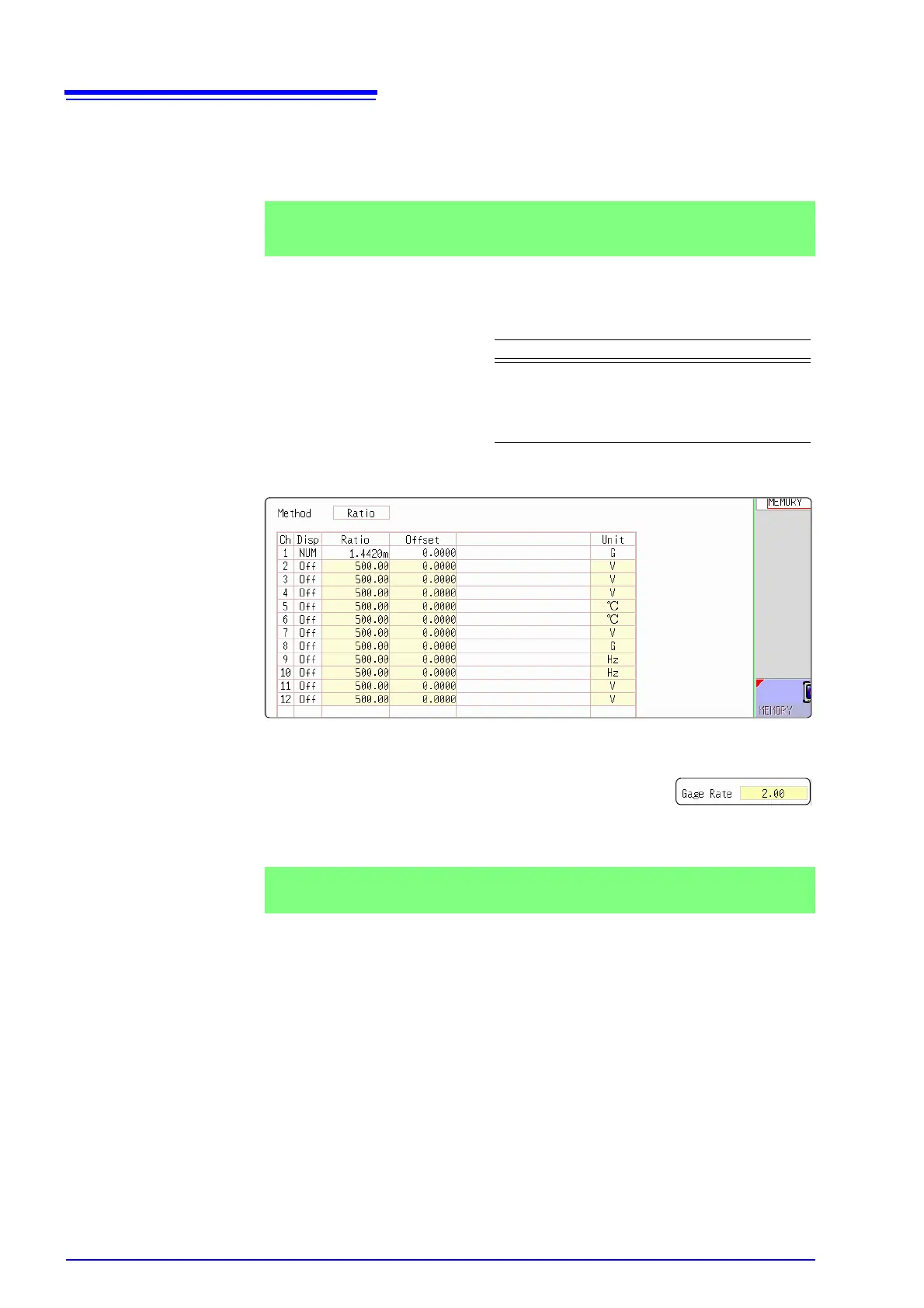
Example 3
Measure using a sensor with a calibration factor of 0.001442 G / 1 x 10
-6
strain
*
, and display the measured data in [G] units.
Setting Items Setting Choice
Disp NUM
Unit G
Ratio
(Conversion ratio)
0.001442 [G]
(displays as 1.4420m)
This value cannot be
changed.
Example 4
Measure using a strain gauge (2.1 Gauge Factor), and display the mea-
sured data in [G] units.
 Loading...
Loading...