221
Configuring DLSw
Overview
The APPN AIW developed Data Link Switching (DLSw) for tunneling unroutable, non-IP based
protocol such as IBM SNA over a TCP/IP network.
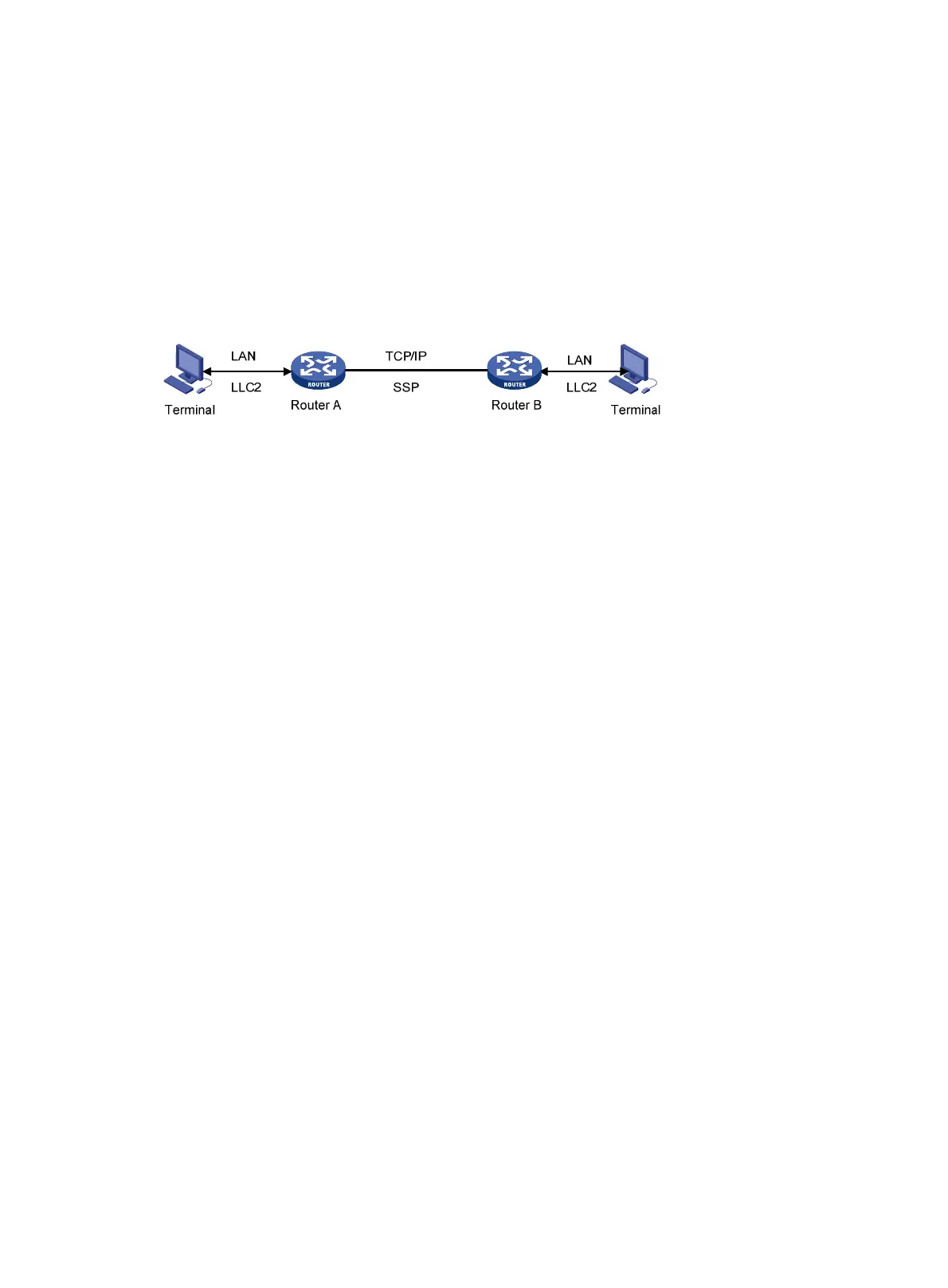
Figure 75 sho
ws the DLSw mechanism.
Figure 75 DLSw mechanism
1. The local DLSw router converts the LLC2 frames from the local SNA device into SSP frames
that can be encapsulated in TCP packets.
2. The local DLSw router forwards the SSP frames across the WAN over a TCP connection to the
remote router.
3. The remote router converts the SSP frames back into LLC2 frames and sends them to the peer
SNA device.
DLSw enables the SNA devices to communicate with each other as if they were on the same
network.
Different from transparent bridging, DLSw does not forward LLC2 frames transparently to the peer.
Instead, it converts LLC2 frames into SSP frames for data encapsulation in TCP packets. The local
termination mechanism of DLSw eliminates the requirement for link layer acknowledgments and
keepalive messages to flow across a WAN. It also solves the data link control timeout problem.
DLSw also enables transmission of SDLC traffic across a TCP/IP WAN by first converting SDLC
frames to LLC2 frames, and then transporting them to the remote end through DLSw. DLSw can
interconnect LAN and SDLC media.
The following DLSw versions are available: version 1.0 and version 2.0. DLSw v1.0 is implemented
based on RFC 1795, and DLSw v2.0 is implemented based on RFC 2166 and is intended to improve
product maintainability and to reduce network cost. In addition, DLSw v2.0 provides enhancements
by means of UDP explorer frames sent in multicast and unicast modes. When the peer is also
running DLSw v2.0, the two ends can use UDP packets to explore reachability, and a TCP
connection is established only when data transmission is required.
SDLC is an IBM data link layer protocol, for use in IBM SNA networks.
For more information on LLC, see the IEEE 802.2 standard.
Differences between DLSw v1.0 and DLSw v2.0
DLSw v1.0 problems
DLSw v1.0 has problems in the following aspects:
• TCP connection—In DLSw v1.0, immediately after a pair of peers is configured, the local peer
attempts to establish a TCP connection with the remote peer (by first establishing two TCP
connections and then bringing down one of them after capabilities exchange), regardless of
whether a connection is needed. All packets, including explorer frames, circuit setup requests
and data packets, are transmitted over the TCP connection. This wastes network resources.

 Loading...
Loading...




