272
[LNS-l2tp1] tunnel authentication
[LNS-l2tp1] tunnel password simple aabbcc
3. Configure the user:
In the dial-up network window, enter vpdnuser as the username and Hello as the password.
4. Verify the configuration:
# After the dial-up connection is established, the user host can obtain an IP address (for
example, 192.168.0.2) and can ping the private IP address of the LNS (192.168.0.1).
# On the LNS, use the display l2tp tunnel command to check the established L2TP tunnels.
[LNS] dis l2tp tunnel
Total tunnel = 1
LocalTID RemoteTID RemoteAddress Port Sessions RemoteName
1 1 1.1.2.1 1701 1 LAC
# On the LNS, use the display l2tp session command to check the established L2TP
sessions.
[LNS] display l2tp session
Total session = 1
LocalSID RemoteSID LocalTID
23142 729 1
Configuration example for client-initiated VPN
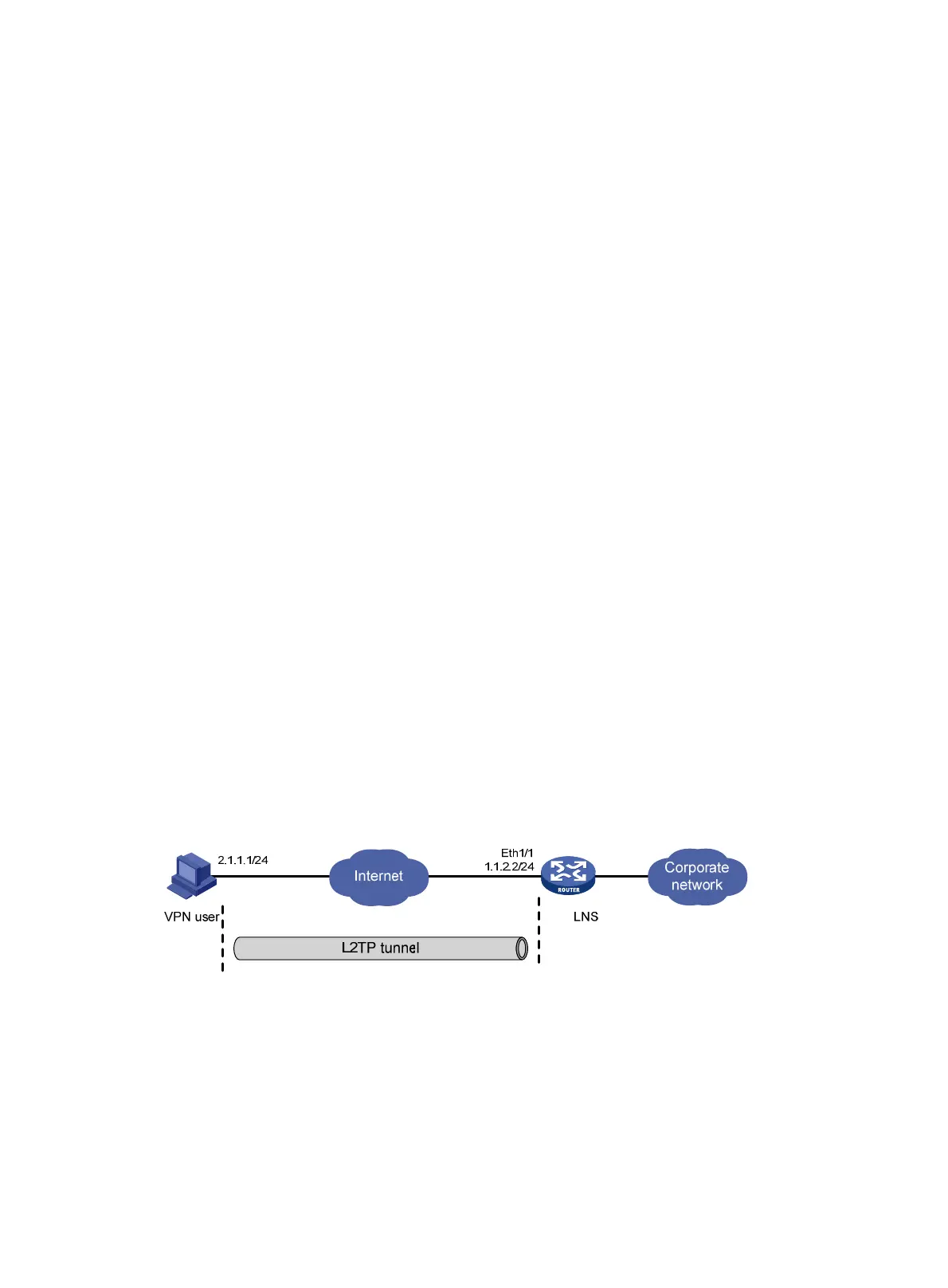
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 97, a VPN user accesses the corporate headquarters in the following procedure:
1. Configure an IP address and route for the user host, making sure that the host is reachable to
the LNS.
2. The user initiates a tunneling request to the LNS.
3. After the LNS accepts the connection request, an L2TP tunnel is set up between the LNS and
the VPN user.
4. The VPN user communicates with the headquarters over the tunnel.
Figure 97 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the LNS:
# Configure IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Configure the route between the LNS and the user host. (Details not shown.)
# Create a local user named vpdnuser, set the password, and enable the PPP service. The
username and password must match those configured on the client.
<LNS> system-view
[LNS] local-user vpdnuser

 Loading...
Loading...




