321
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter main interface view.
interface
serial
interface-number
N/A
3. Enable X.25.
link-protocol x25
N/A
4. Return to system view.
quit
N/A
5. Create an X.25
subinterface.
interface serial
interface-number
.
subnumber
[
p2mp
|
p2p
]
p2mp
applies by default.
If the link layer protocol of an interface is LAPB, HDLC, or PPP, no subinterface can be created on it.
Configuring X.25 datagram transmission
Configuring basic X.25 datagram transmission functionality
Introduction to X.25 datagram transmission
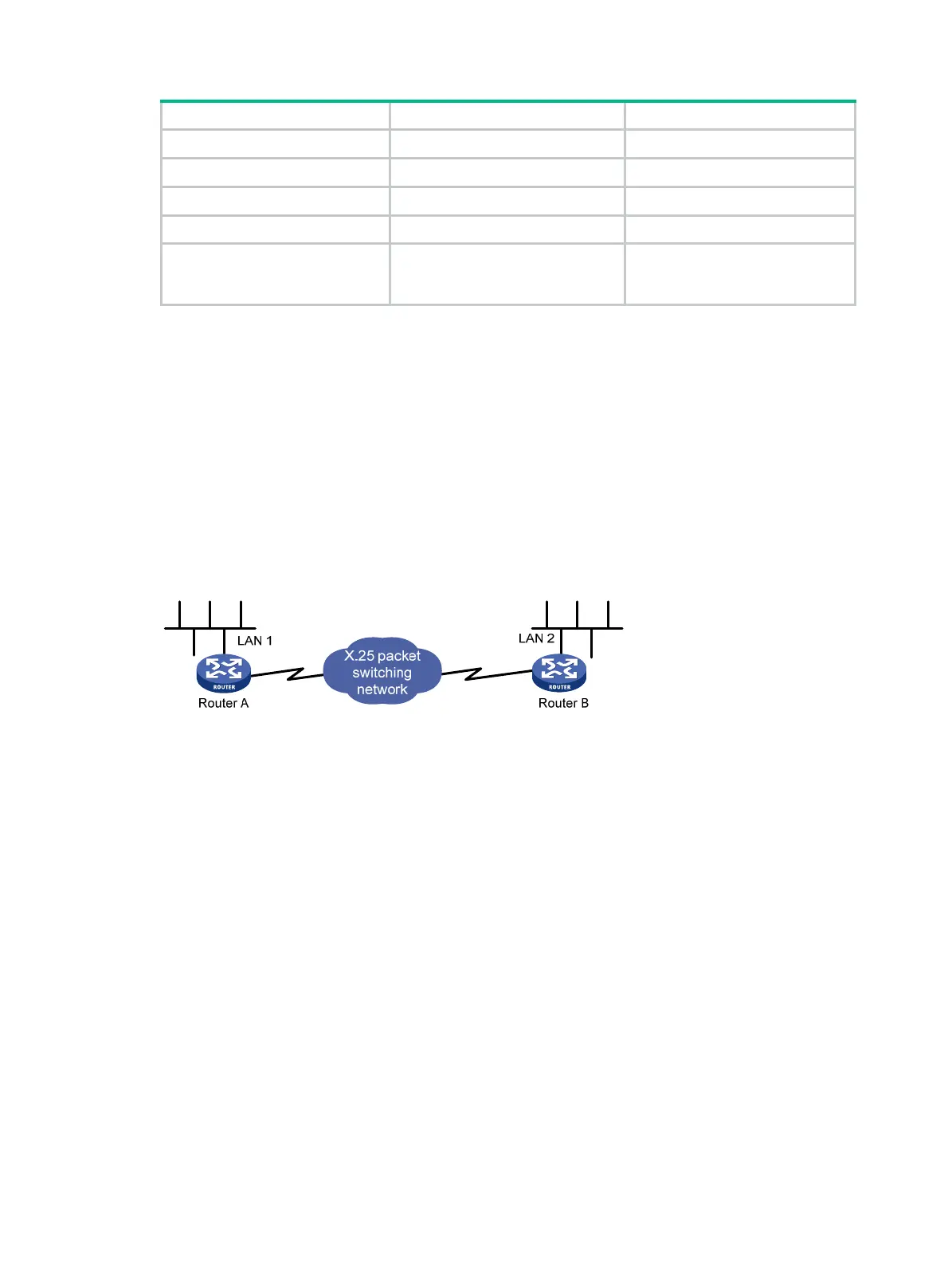
X.25 service enables two remote X.25 hosts to communicate across an X.25 packet switching
network. As shown in Figure 125, LAN 1
and LAN 2 communicate remotely across an X.25 packet
switching network.
Figure 125 Interconnecting LANs through X.25
LAN 1 and LAN 2 communicate with each other by sending datagrams that use IP addresses, and
X.25 uses X.121 addresses. To correctly tunnel IP datagrams across an X.25 network, the routers
must have an IP-to-X.121 address mapping table. This section describes how to establish an
IP-to-X.121 mapping.
1. Mapping a protocol address to an X.121 address
An X.25 interface has its own X.121 address and internetworking protocol (such as IP protocol)
address. When X.25 initiates a call through this interface, the source address (calling DTE
address) in the call request packet is the X.121 address of this interface.
Then, how can the router target the destination of the call, or how can the router determine the
X.121 address for the IP address destination? For this purpose, the router will look up the
protocol-address-to-X.121 address mappings that have been configured on the router. A direct
call destination has its own protocol address and X.121 address. In this case, a destination
protocol-address-to-X.121 address mapping must be created on the source. Through the
mapping, X.25 can find the destination X.121 address according to the destination protocol
address to initiate a call successfully. This is why the address mapping will be established for
X.25.
Such a mapping should be created for every destination.
2. Creating a PVC
A PVC can be created for the data transmission which features large but stable traffic size and
requires the service quality of a leased line. A PVC does not need any call process and will
always exist once set up. Before creating a PVC, it is unnecessary to create an address
mapping, because an address mapping is created implicitly when a PVC is created.

 Loading...
Loading...




