5. CONFIGURATION
Station Alias: These settings are only visible if the option Optional is activated or if the slave device supports alias
addresses (defined in the Device Description File).
Enable: If the setting Optional is not activated, this setting can be activated if explicitly supported by the device description
of the slave. It allows direct assignment of an alias address in order to get the slaves address independent of its position within
the bus. If the option Optional is activated, this checkbox is disabled.
Write to EEPROM: This command is only visible in online mode. It allows to write the defined address to the EEPROM
of the slave. If not supported by the slave this command will have no effect and the device will not work as Optional Slave.
Actual Address: This field, only visible in online mode, displays the actual address of the slave. It can be used to check
the success of the Write to EEPROM command.
5.5.12.4.2. FMMU/Sync
This dialog will only be provided on a tab of an EtherCAT Slave configuration editor if the Autoconfig Mode in the Master
is disabled. It shows the FMMUs and Sync Managers of the slave as defined by the Device Description file. These settings
may be reworked, for example for configuring a slave-to-slave communication.
ATTENTION
These are Expert Settings, which usually are not necessary for standard applications.
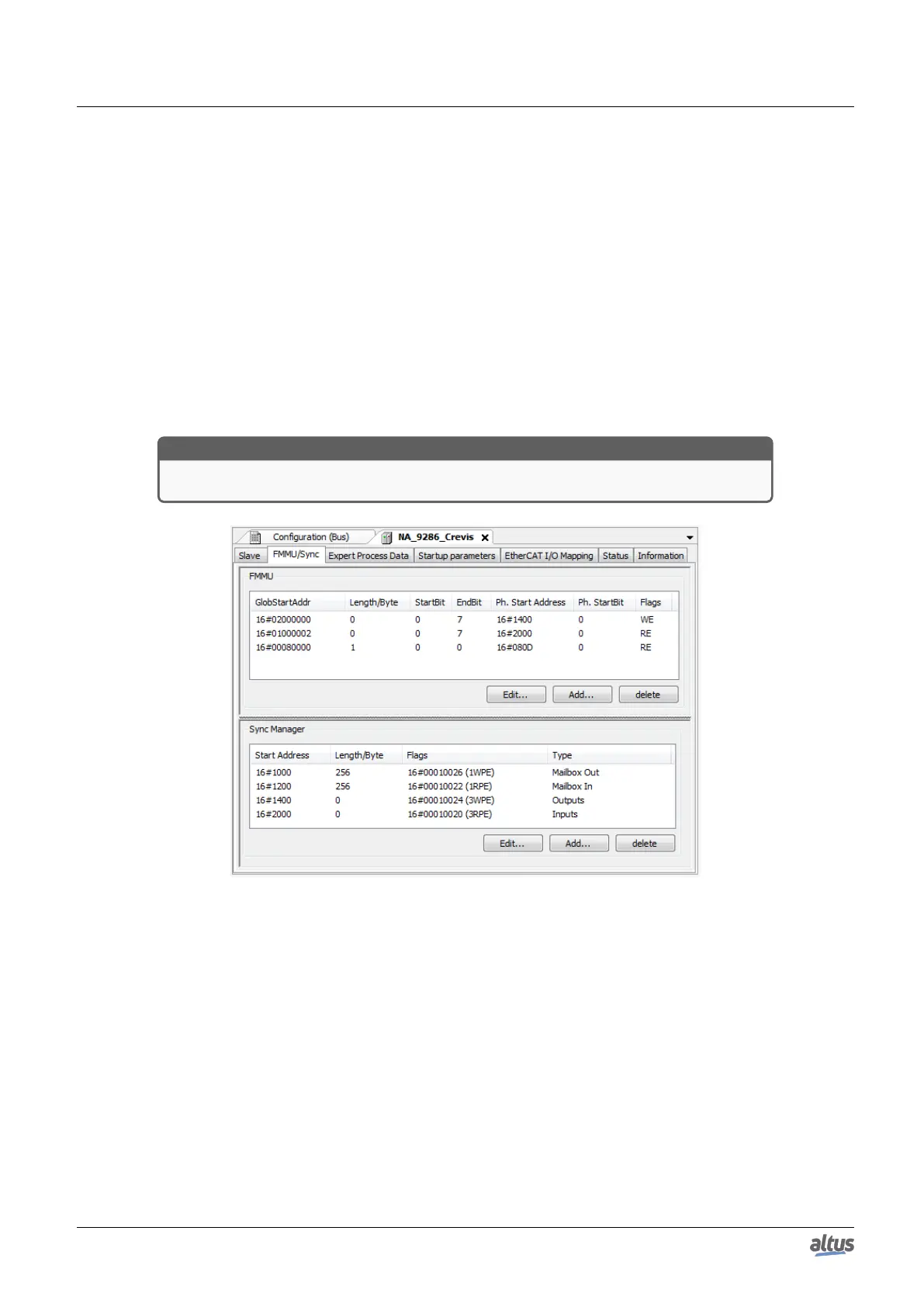
Figure 101: FMMU/Sync Dialog
5.5.12.4.3. FMMU/Sync - FMMU
This table shows the Fieldbus Memory Management Units (FMMU) of the slave which are used for handling the process
data. Each mapping of the logical address GlobStartAddr on a physical address Ph. Start Address is defined. Bitwise mapping
is possible. New units can be added and existing ones can be edited by the Edit FMMU dialog, to be opened via the Add and
Edit... buttons.
5.5.12.4.4. FMMU/Sync - Sync Manager
This table shows the Synchronization Manager(s) of the slave. For each available Sync Manager Type (Mailbox In, Mailbox
Out, Inputs, Outputs) a physical Start Address, the Access type, the Buffer and the physical address, where the Interrupts have
to be sent to, are defined. New Sync Managers can be added resp. the existing ones can be edited in the dialog Edit SyncMan,
which is to be opened by buttons Add and Edit....
184

 Loading...
Loading...