5. CONFIGURATION
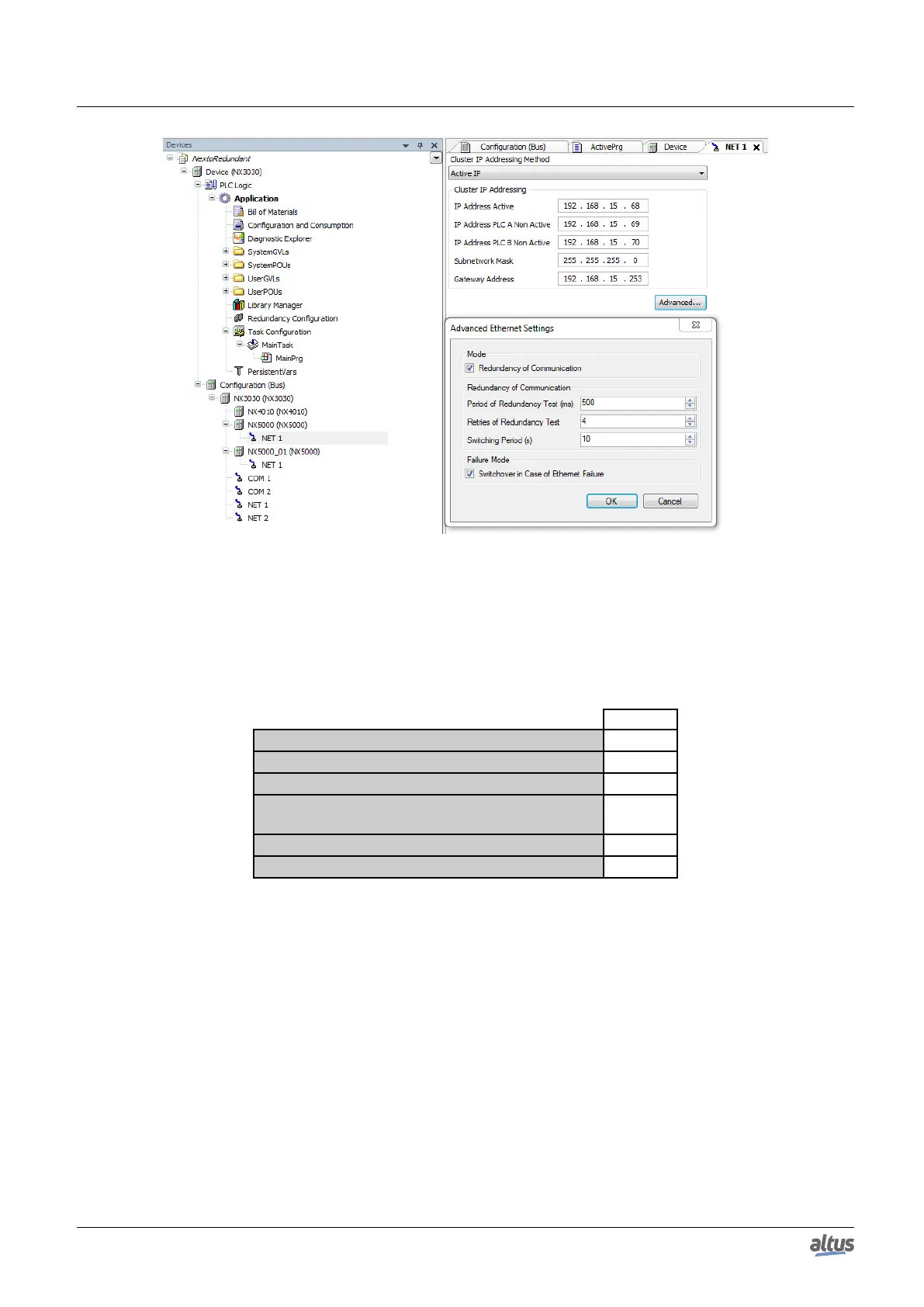
Figure 54: NX5000 Redundancy Parameter
5.5. Protocols Configuration
Independently of the protocols used in each application, the Nexto Series CPUs has some maximum limits for each CPU
model. There are basically two different types of communication protocols: symbolic and direct representation mappings. The
maximum limit of mappings as well as the maximum protocol quantity (instances) is defined on table below:
NX3030
Mapped Points 20480
Mappings 5120
Requests 512
NETs – Client or Server Instances (Per NET / To-
tal)
4 / 16
COM (n) – Master or Slave Instances 1
Control Centers 3
Table 65: Protocols Limits per CPU
Notes:
Mapped Points: It refers to the maximum number of mapped points supported by the CPU. Each mapping supports one
or more mapped points, depending on the size of the data when used with variables of type ARRAY.
Mappings: A “mapping” is the relationship between an internal application variable and an object of the application
protocol. This field informs the maximum number of mappings supported by the CPU. It corresponds to the sum of all
mappings made within the instances of communication protocols and their respective devices.
Requests: The sum of the requests of the communications protocols, declared on devices, may not exceed the maximum
number of requests supported by the CPU.
NETs – Clients or Servers Instances: This field defines the maximum number of protocol instances per Ethernet interface,
and also the total maximum distributed along all the Ethernet interfaces of the system.
COM (n) – Master or Slave Instances: Due to its characteristics, each serial interface supports only one communication
protocol instance. Examples of instances compatible with serial interfaces: MODBUS RTU Master and MODBUS RTU Slave.
Control Centers: “Control Center” is all client device connected to the CPU through protocol IEC 60870-5-104. This
field informs the maximum of client devices of control center type supported by the CPU. Correspond to the sum of all client
94

 Loading...
Loading...