Implementing VLANs
9-2 Configuring VLANs
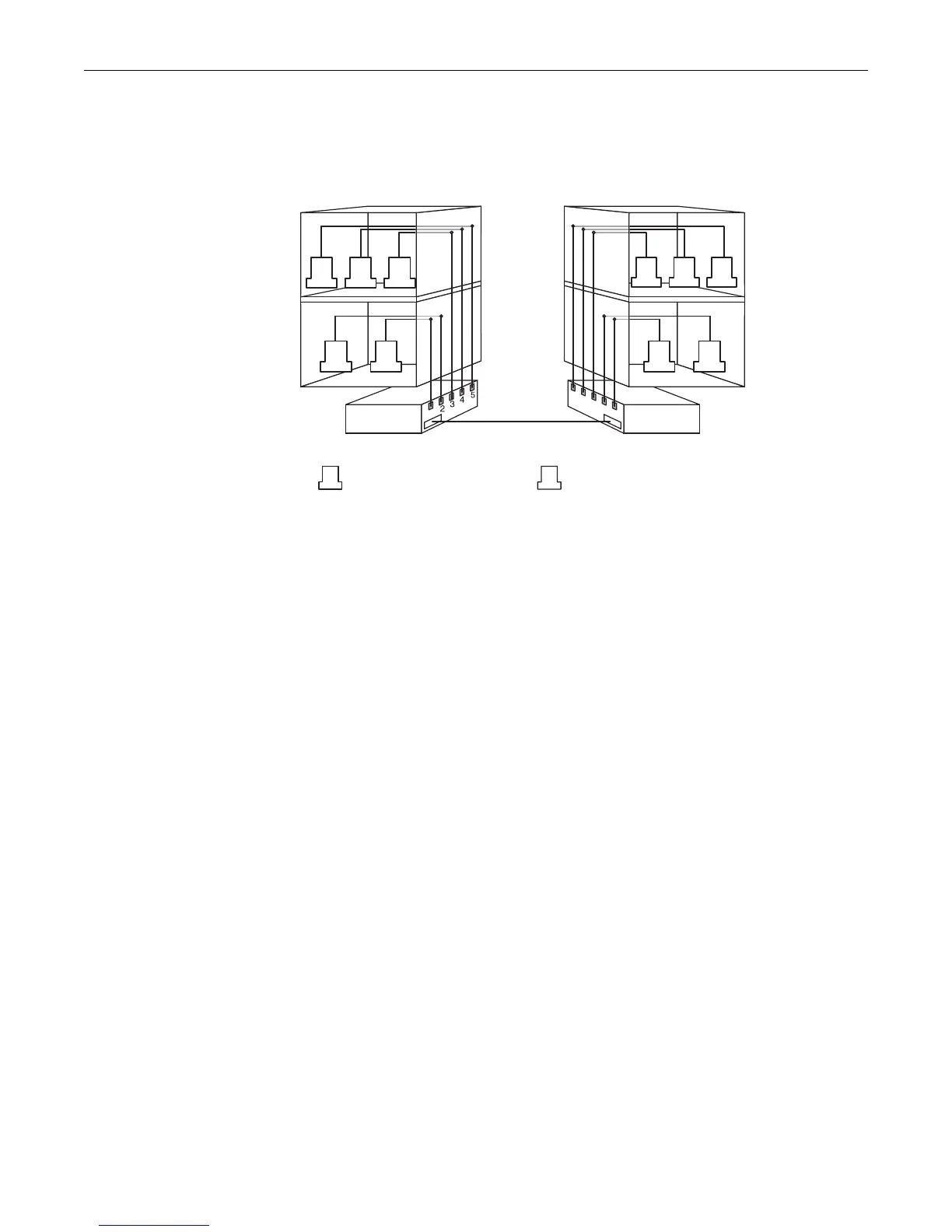
building has its own internal network. The end stations in each building connect to a switch on the
bottom floor. The two switches are connected to one another with a high speed link.
Figure 9-1 VLAN Business Scenario
Without any VLANs configured, the entire network in the example in Figure 9-1 would be a
broadcast domain, and the switches would follow the IEEE 802.1D bridging specification to send
data between stations. A broadcast or multicast transmission from a Sales workstation in Building
One would propagate to all the switch ports on Switch A, cross the high speed link to Switch B,
and then be propagated out all switch ports on Switch B. The switches treat each port as being
equivalent to any other port, and have no understanding of the departmental memberships of
each workstation.
Once Sales and Finance are placed on two separate VLANs, each switch understands that certain
individual ports or frames are members of separate workgroups. In this environment, a broadcast
or multicast data transmission from one of the Sales stations in Building One would reach Switch
A, be sent to the ports connected to other local members of the Sales VLAN, cross the high speed
link to Switch B, and then be sent to any other ports and workstations on Switch B that are
members of the Sales VLAN. Separate VLANs also provides unicast separation between Sales and
Finance. Finance cannot ping Sales unless there is a routed VLAN configured for both Finance and
Sales.
Another benefit to VLAN use in the preceding example would be your ability to leverage existing
investments in time and equipment during company reorganization. If, for instance, the Finance
users change location but remain in the same VLAN connected to the same switch port, their
network addresses do not change, and switch and router configuration is left intact.
Implementing VLANs
By default, all Enterasys switches run in 802.1Q VLAN operational mode. All ports on all
Enterasys switches are assigned to a default VLAN (VLAN ID 1), which is enabled to operate and
assigns all ports an egress status of untagged. This means that all ports will be allowed to transmit
frames from the switch without a VLAN tag in their header. Also, there are no forbidden ports
(prevented from transmitting frames) configured.
You can use the CLI commands described in this document to create additional VLANs, to
customize VLANs to support your organizational requirements, and to monitor VLAN
configuration.
1
SS
FF
A
6
SSS
FF
B
7
8
9
10
Building One Building Two
SmartSwitch SmartSwitch
trunk
2263-01
S
Member of Sales Network
Member of Finance Network
S
F

 Loading...
Loading...











