Basic OSPF Topology Configuration
22-6 Configuring OSPFv2
To elect a DR from a host of candidates on the network, each router multicasts a hello packet and
examines the priority of hello packets received from other routers. The router with the highest
priority is elected the DR, and the router with the next highest priority is elected the BDR. Any
router with a priority of 0 will opt out of the DR election process.
If DR candidates all share non-zero priorities, OSPF applies the router ID as a tie-breaker where
the highest ID is chosen DR and the next highest ID is chosen BDR.
Configuring Router Priority
When two routers attached to a network both attempt to become the designated router, the one
with the highest router priority takes precedence. A router whose router priority is set to 0 is
ineligible to become the designated router on the attached network. Router priority is specified
per router interface and is advertised in hello packets sent out by the interface.
Use the ip ospf priority command in interface configuration command mode to specify the router
priority that will be included in LSAs going out this interface.
Example
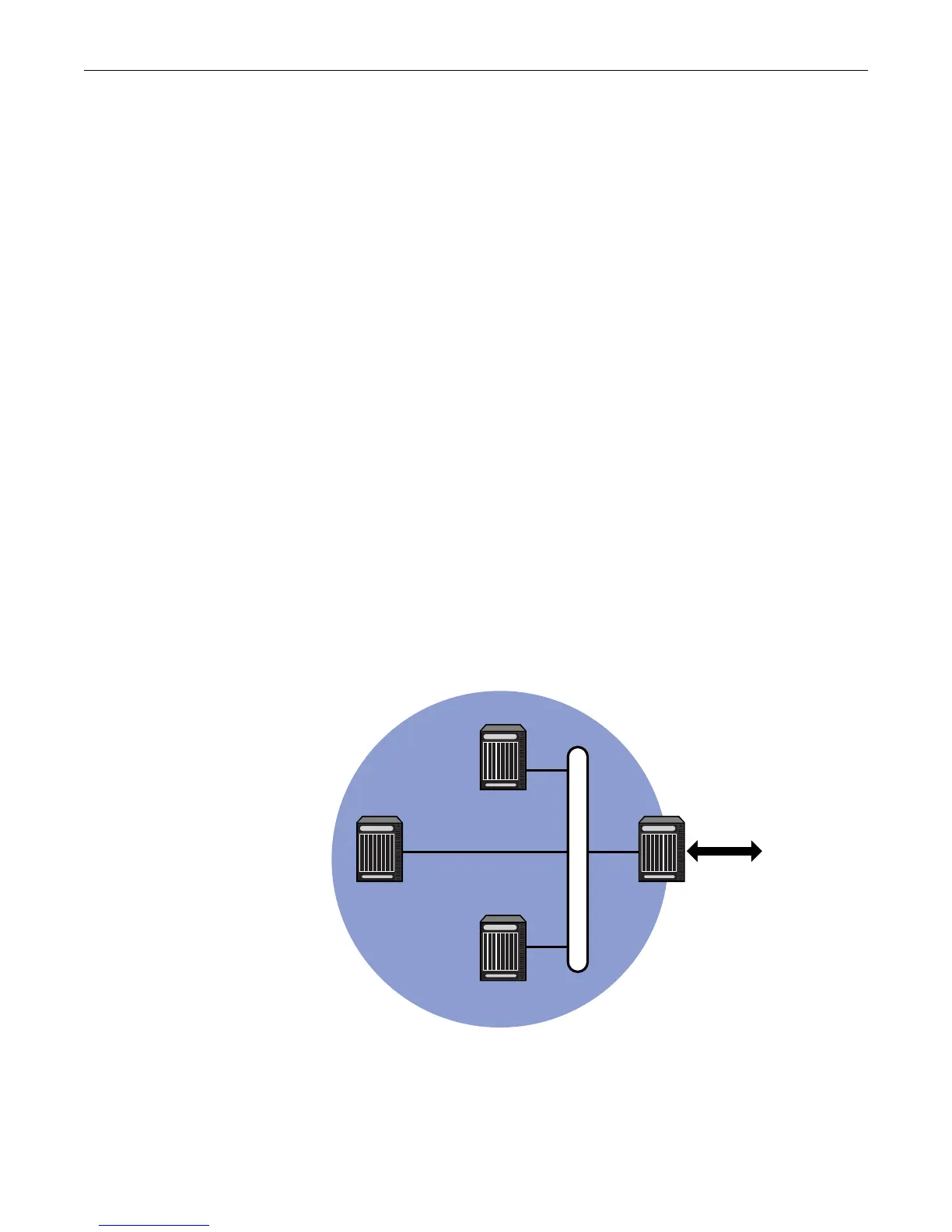
Figure 22-2 displays a designated router topology example. The code example below Figure 22-2
will configure the four displayed routers with the following priorities:
• Router 1 = 25
• Router 2 = 10
• Router 3 = 30
• Router 4 = 0
Router 4 will not take part in the election process at all. Router 3 has the highest priority and
therefore will be elected DR. Router 1 has the second highest priority and will be elected BDR.
Figure 22-2 OSPF Designated Router Topology
Router 1 CLI Input
Router 1(su)->router(Config)#interface vlan 1
Router 1(su)->router(Config-if(Vlan 1))#ip ospf priority 25
Area 1
BDR
DR
Router 4Router 2
Router 1
Router 3

 Loading...
Loading...











