Configuring VLANs
9-8 Configuring VLANs
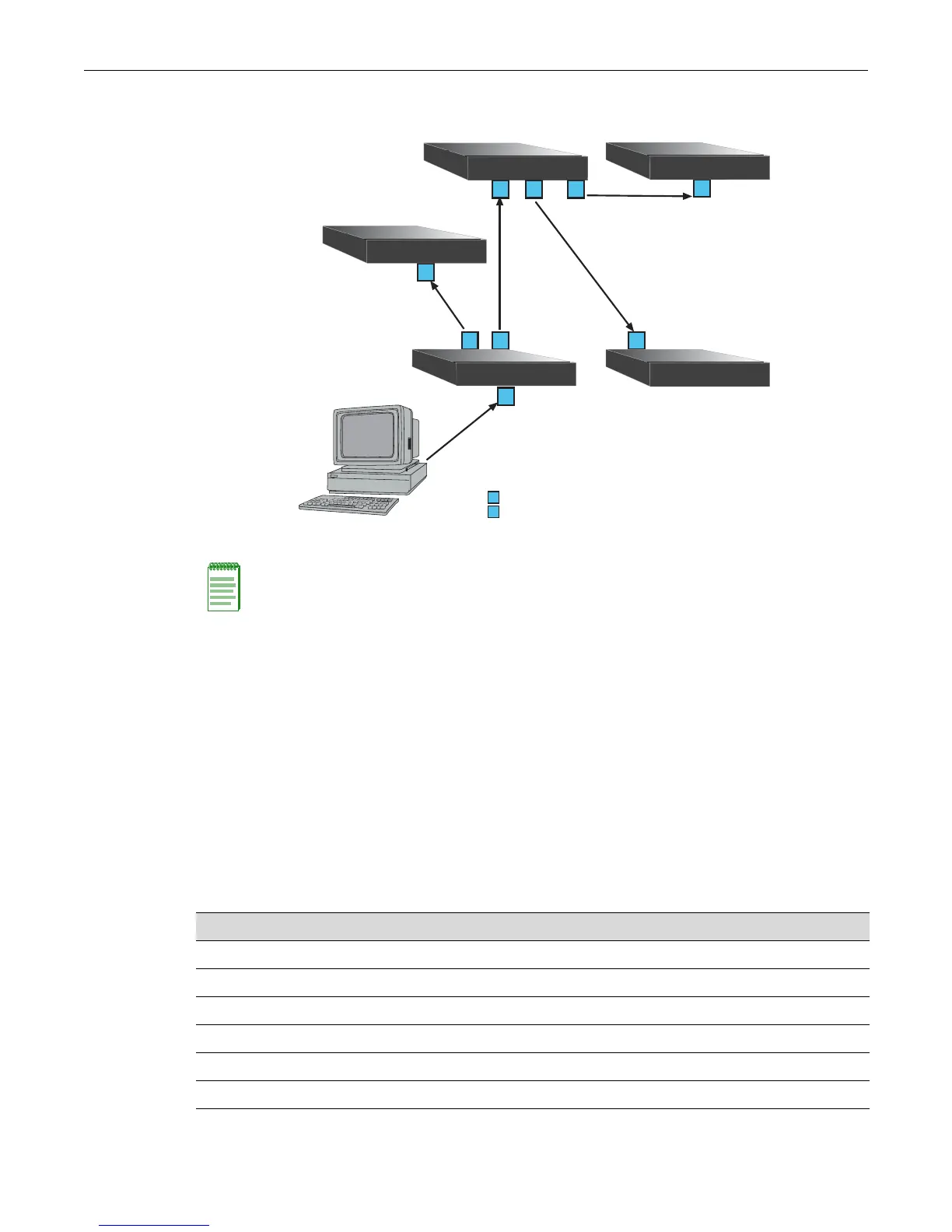
Figure 9-3 Example of VLAN Propagation Using GVRP
Administratively configuring a VLAN on an 802.1Q switch creates a static VLAN entry that will
always remain registered and will not time out. However, GVRP-created dynamic entries will
time out, and their registrations will be removed from the member list if the end station is
removed. This ensures that, if switches are disconnected or if end stations are removed, the
registered information remains accurate.
The end result of GVRP dynamic VLAN configuration is that each port’s egress list is updated
with information about VLANs that reside on that port, even if the actual station on the VLAN is
several hops away.
Configuring VLANs
Once you have planned your implementation strategy as described in “Preparing for VLAN
Configuration” on page 9-3, you can begin configuring VLANs as described in this section.
Note: If a port is set to “forbidden” for the egress list of a VLAN, then the VLAN’s egress list will not
be dynamically updated with that port.
End
Station A
Switch 4
Switch 5
= Port registered as a member of VLAN Blue
= Port declaring VLAN Blue
D
R
VLANpropagation GVMP
1
1
2
3
D
R
D
Switch 1
1
R
R
3
Switch 2
12
D
R
D
Switch 3
1
R
For information about... Refer to page...
Default Settings 9-9
Configuring Static VLANs 9-9
Creating a Secure Management VLAN 9-11
Configuring Dynamic VLANs 9-12
Configuring Protocol-Based VLAN Classification 9-13
Monitoring VLANs 9-14

 Loading...
Loading...











