VRRP Overview
23-2 Configuring VRRP
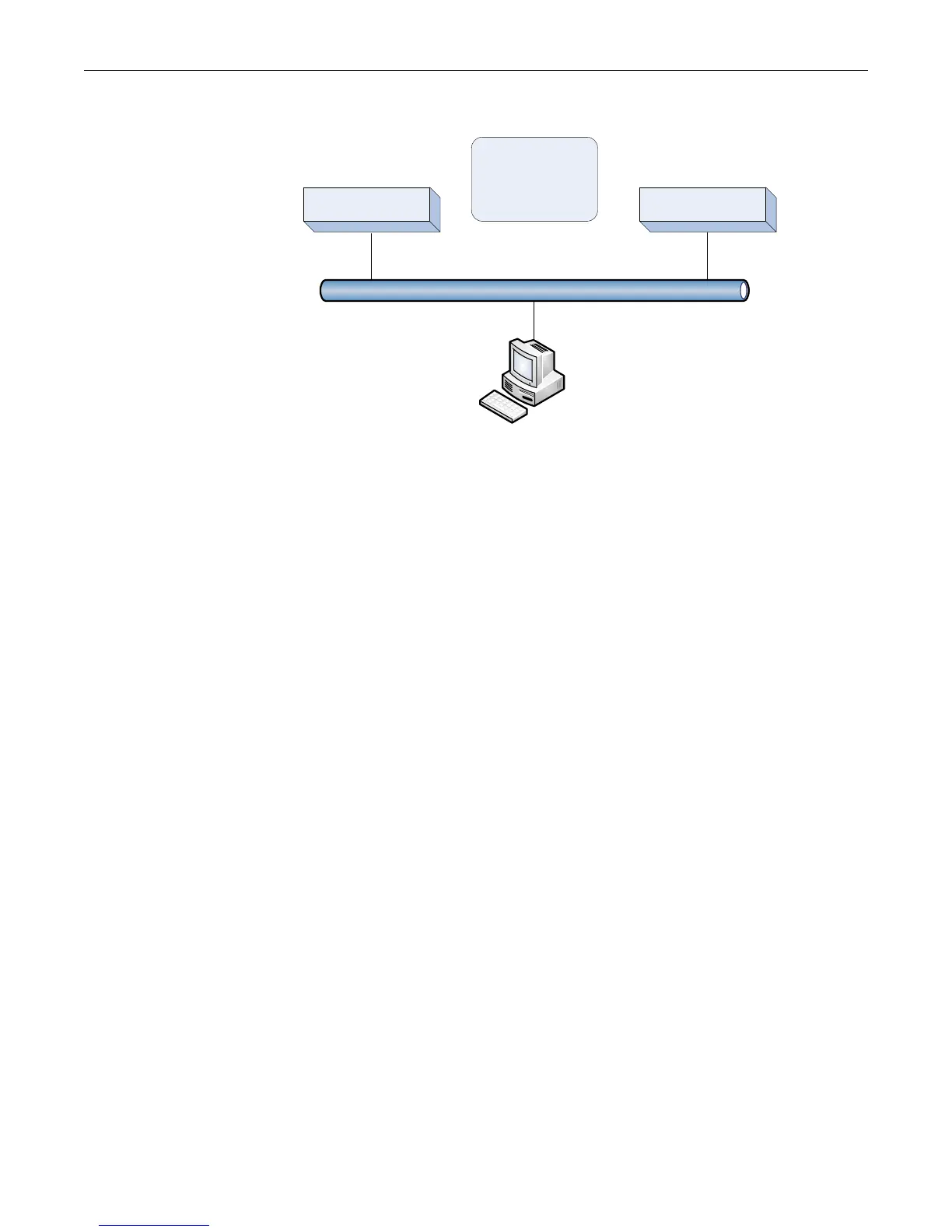
Figure 23-1 Basic VRRP Topology
Figure 23-1 shows a basic VRRP topology with a single virtual router. Routers R1 and R2 are both
configured with one virtual router (VRID 1). Router R1 serves as the master and Router R2 serves
as the backup. The hosts are configured to use 172.111.1.1/16 as the default route.
If Router R1 should become unavailable, Router R2 would take over virtual router VRID 1 and its
associated IP addresses. Packets sent to 172.111.1.1/16 would go to Router R2. When Router R1
comes up again, it would take over as master, and Router R2 would revert to backup.
VRRP Virtual Router Creation
Each virtual router has its own instance. Create a VRRP virtual router instance using the create
command in router configuration command mode specifying the VRID for this instance. The
virtual router instance must be created before any other VRRP settings can be configured.
‘Refer to the Release Notes for your fixed switch product to determine the maximum number of
VRRP instances that can be created.
VRRP Master Election
After the virtual router instance has been created, assign the IP addresses associated with this
virtual router using the address command. You must specify the VLAN on which to configure the
virtual router address, the virtual router ID (VRID), the virtual router IP address, and whether the
router owns the IP address as one of its interface. A virtual router IP address can be either an
address configured on the routing interface or an address that falls within the range of any
networks configured on this routing interface.
If the virtual router IP address is the same as the routing interface (VLAN) address owned by a
VRRP router, then the router owning the address becomes the master. The master sends an
advertisement to all other VRRP routers declaring its status and assumes responsibility for
forwarding packets associated with its VRID.
If the virtual router IP address is not owned by any of the VRRP routers, then the routers compare
their priorities and the higher priority owner becomes the master. VRRP router priority is set
using the priority command in router configuration command mode. If priority values are the
same, then the VRRP router with the highest IP address is selected master.
VRRP advertisements are sent by the master router to other routers participating in the VRRP
master selection process, informing them of its configured values. Once the master is selected,
Router R1 Router R2
VRID 1
172.111.1.1
Host 1
172.111.1.100/16
Default Gateway 172.111.1.1
ge.1.1
VLAN 111
172.111.1.2/16
ge.1.1
VLAN 111
172.111.1.1/16

 Loading...
Loading...











