Using Multicast in Your Network
19-4 Configuring Multicast
IGMP snooping is disabled by default on Enterasys devices. You can enable it using the set
igmpsnooping adminmode command on Enterasys stackable and standalone devices as
described in “Configuring IGMP” on page 19-15.
• Actively sending IGMP query messages to learn locations of multicast switches and member
hosts in multicast groups within each VLAN.
• Configuration of static IGMP groups using the set igmpsnooping add-static on the fixed
switches. Static IGMP configuration provides for specifying the IP address (group address)
and VLAN of a non-IGMP capable device, forcing the sending of IGMP messages to the
device. The static IG groups commands are described in “Configuring IGMP” on page 19-15.
Example: Sending a Multicast Stream
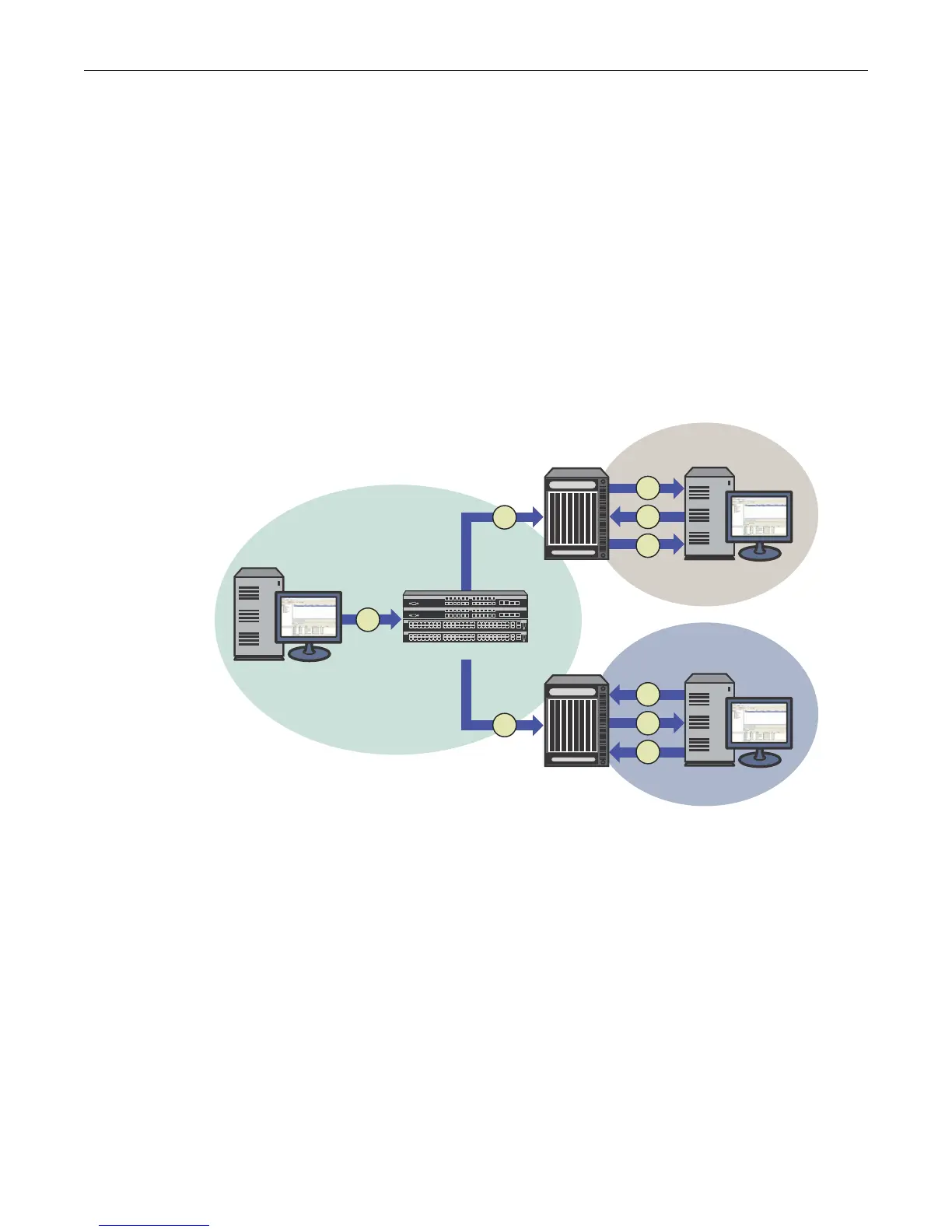
Figure 19-2 provides an example of IGMP processing on Enterasys devices when there are no
directly attached hosts.
Figure 19-2 Sending a Multicast Stream with No Directly Attached Hosts
1. A single IP multicast server, with no directly attached hosts, sends a multicast stream into the
network via Switch 1.
2. Because IGMP snooping is disabled, Switch 1 floods the multicast stream to all ports which
are linked to Router 1 and Router 2.
Each router performs an IGMP forwarding check to see if there are any hosts that want to join
the multicast group on its locally attached network. Each router drops multicast packets until
a host joins the group using one of the following messages:
– solicited join (sent in response to an IGMP query produced by the router’s interface)
In Figure 19-2, this type of exchange occurs between Router 1 and Host 1 when:
(3) Router 1 sends a query to potential Host 1.
(4) Host 1 responds with a join message.
(5) Router 1 forwards the multicast stream.
2
3
4
5
1
2
Router 1
Host 1
Solicited Join
Network A
Unsolicited Join
& IGMP Leave
Host 2
Multicast Server
Switch 1
Router 2
6
7
8

 Loading...
Loading...











