Spanning Tree Protocol Overview
15-2 Configuring Spanning Tree
While the network is in a steady state, alternate and backup ports are in blocking state; root and
designated ports are in forwarding state.
STP allows for the automatic reconfiguration of the network. When bridges are added to or
removed from the network, root election takes place and port roles are recalculated.
Why Use Spanning Trees?
Redundant links must be factored into even the simplest of topologies to protect against data loss
and downtime due to any single point of failure. STP prevents redundant links from forming data
loops which would consume all available network bandwidth. STP manages redundant links by
keeping them in a blocking state and automatically unblocking them when changes in topology
require that they be used. See Table 15-3 on page 15-13 for a summary of Spanning Tree port
states.
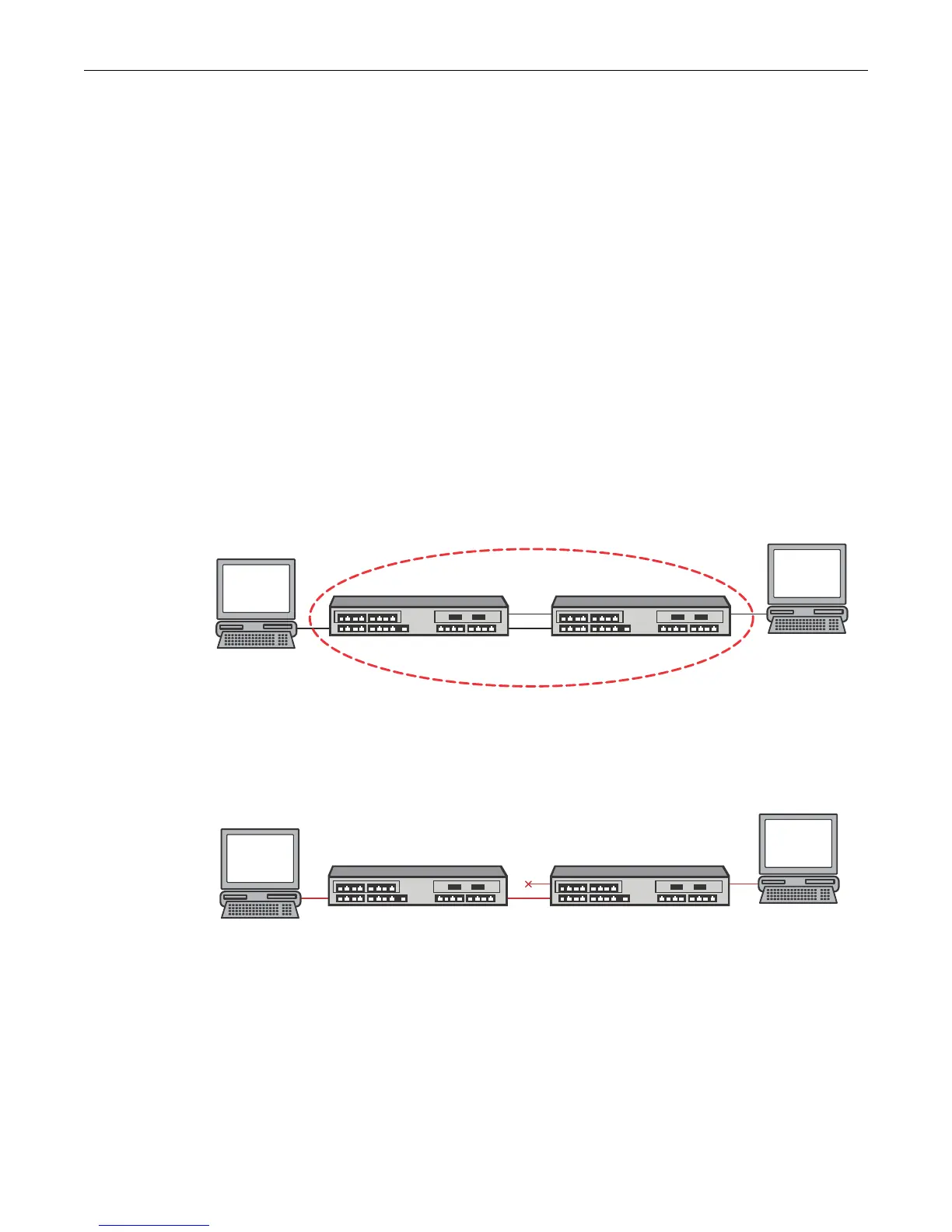
As shown in Figure 15-1, a planned redundant link between Switch 1 and Switch 2 makes it
possible for a bridging loop to occur. If Station 1 transmits a multicast or broadcast packet to
Station 2 in this scenario, the packet would continue to circulate endlessly between both switching
devices. Without Spanning Tree blocking one of the links, there would be nothing at layer 2 to stop
this loop from happening and unnecessarily consuming network resources. As administrator, you
would be forced to manually disable one of the links between Switch 1 and 2 for the Figure 15-1
network to operate.
Figure 15-1 Redundant Link Causes a Loop in a Non-STP Network
STP automatically blocks redundant paths, as shown in Figure 15-2. In the event that the primary
(unblocked) path fails, STP places the blocked path into service. If the original primary path
recovers, the redundant path will once again block and the primary path will be used.
Figure 15-2 Loop Avoided When STP Blocks a Duplicate Path
Spanning Tree on Enterasys Platforms
By default, Spanning Tree is enabled globally on stackable, and standalone fixed switch devices
and is enabled on all ports. The design of the Spanning Tree protocol and the default configuration
values on these devices make user configuration unnecessary in order to add redundant ports to
your network. You will want to make configuration changes to select a root bridge, take advantage
of Multiple Spanning Tree, or use any of the advanced features described below. Before
configuring STP it is important to understand how it works.
Switch 1
Station 1
Switch 2
Station 2
Switch 1
Station 1
Switch 2
Station 2

 Loading...
Loading...











