Using the Equipment
• Cancel – This will stop a retune process.
With Retune now, a tune can be forced any time. This is especially useful when all
parameters are valid and the card has not locked (e.g. when Cancel has been
pressed).
Scanning Channels
To scan for channels available to the tuner, the following controls are used:
• Scan Channels – This goes through all channels and checks whether there is
something transmitted on that channel. If there is, its modulation name is
appended to the channel item in the “Channel” combo.
• Cancel – This will stop a scan process.
Note: After scanning is ended or cancelled, the retune must be triggered either by
pressing Retune now or it will be automatically done after a period set in
Unlocking period if Force Retune is active.
• Scanning Status – During this basic channel scanning, the number of already
scanned channels is displayed. During tuning Normal retuning is displayed. If
an error occurs during scanning, Error will be displayed. If any of the operations
(tuning, scanning) are cancelled, Cancelled will be displayed.
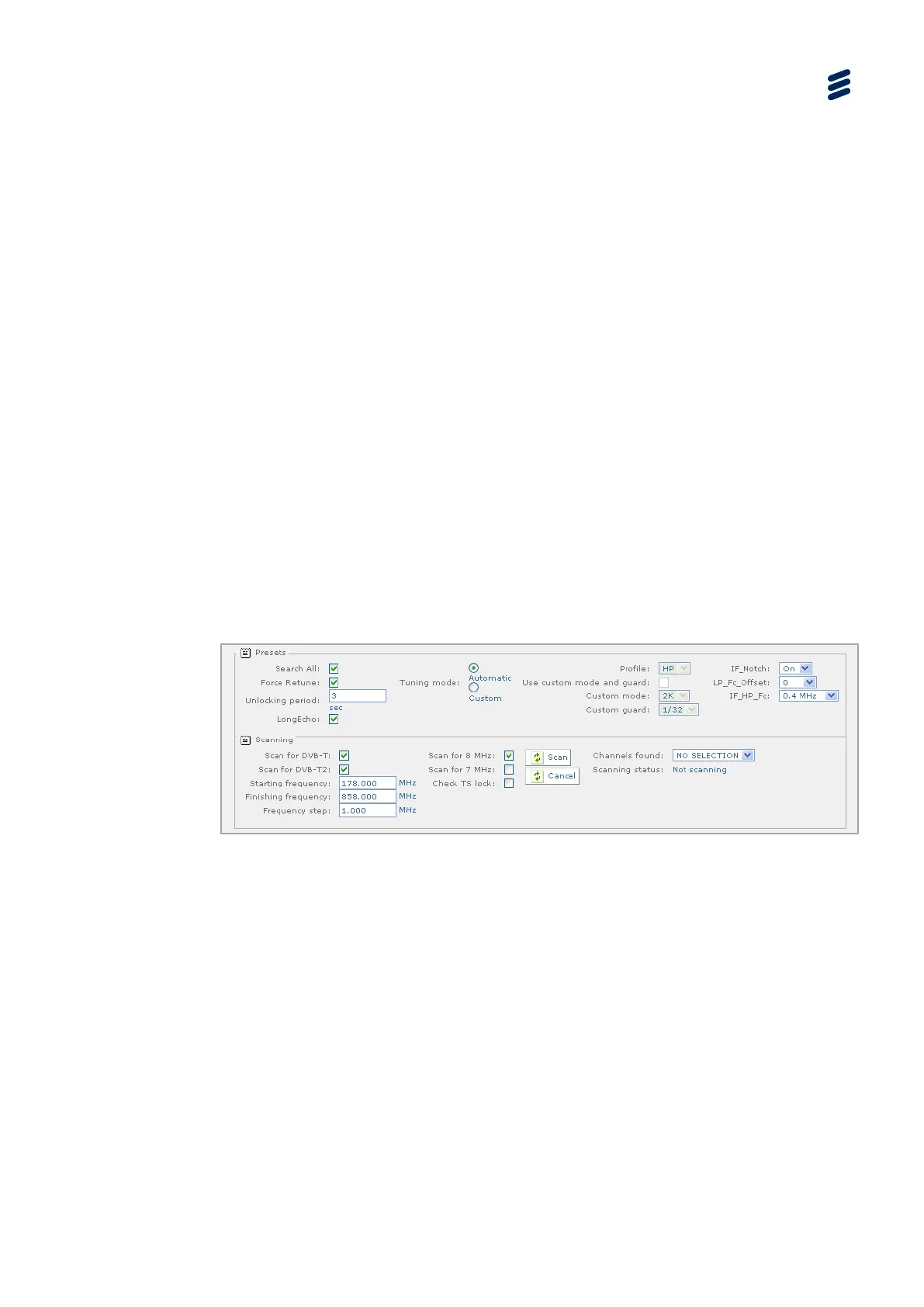
Advanced Page (Presets)
Figure 3.58 Advanced Configuration
• Search All – If enabled, it tries all modulations and bandwidths during tuning. If
tuning with “Custom” selected and Tuning mode fails, it will also try the
“Automatic” tuning, i.e. presets will be ignored.
• Force Retune – If enabled, the tuner will periodically check the TS Lock in
demodulator, and if it is not locked for “n” seconds a retune will be attempted.
• Unlocking period – This defines the time (in seconds) before force retune is
tried.
• Tuning mode – (DVB-T only) This allows the unit to be set into “Automatic” or
“Custom” modes. In custom mode you can set the profile and custom mode.
• Profile – This allows the user to select between the high priority stream and the
low priority stream.
 Loading...
Loading...