PROG P6: AMS/C.KTrk (AMS Mixer/Common Keyboard Track) 6–1: OSC1 AMS Mix1
73
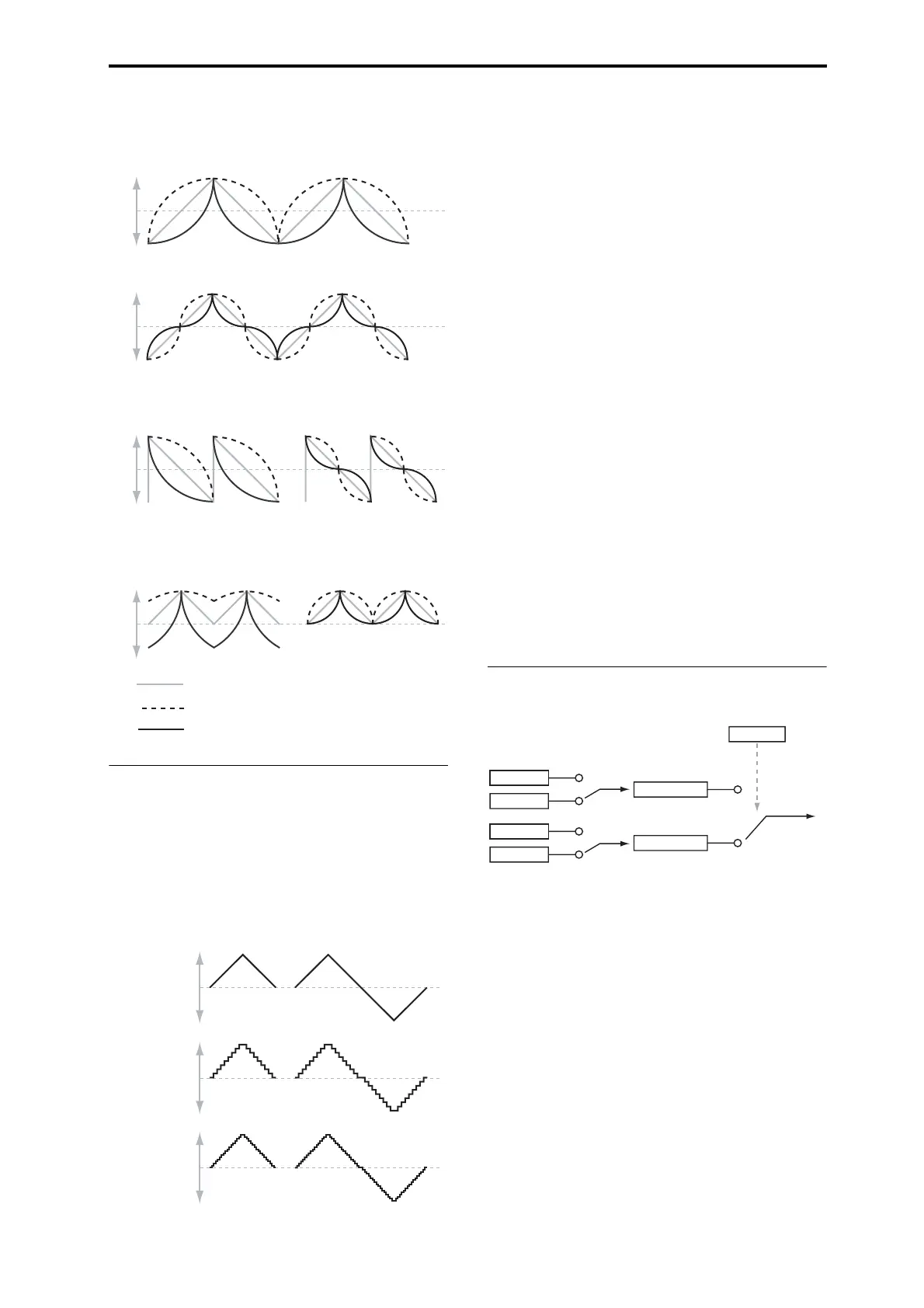
AMS Mixer Shape examples
Quantize
This Mixer Type changes the input from a continuous signal
into a series of discrete steps. Instead of moving smoothly
between values, it will snap immediately from one value to
another.
You can use this to change the shape of LFOs or EGs, or to
force a controller to land on a few specific values.
AMS Mixer Quantize examples
AMS A [List of AMS Sources]
This selects the AMS input source to be quantized.
For a list of AMS sources, please see “AMS (Alternate
Modulation Source) List” on page 588.
Number Of Steps [2...32]
This controls the severity of the effect. The lower the number
of steps, the more “steppy” the output will be.
For instance, when this is set to 2, there will be “steps” at 0,
50, and 99. With a bipolar AMS input, there will also be steps
at –50 and –99.
As another example, when it is set to 5, there will be steps at
0, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 99 (as well as –20, –40, –60, –80, and –99
for bipolar inputs).
Tip: Quantized Ribbon Pitch Bend
You can use the KYBD-61/73/88’s ribbon controller to
create quantized pitch bends that simulate sliding across the
frets of a guitar, or jump-bend sounds caused by differences
in the length of the tube of a trumpet. To do so:
1. Select the AMS Mixer as the Oscillator Pitch AMS
input.
2. Set the Pitch AMS Intensity to any exact half-step
value, such as +5.00, +7.00, etc.
3. Set the Ribbon amount to 0.00.
4. In the AMS Mixer, select the Ribbon as AMS A.
5. Set the Number Of Steps to the same number you used
in Step 2.
Now, playing the Ribbon will create quantized pitch bends.
JSX will still produce smooth pitch bends, as usual, so you
can use both techniques together.
Gate Control
AMS Mixer, Type = Gate Control
This Mixer Type lets you set up two different AMS sources
(or fixed AMS amounts), and then switch between the two
using a third AMS source.
It’s similar to an audio gate with a side-chain, but with even
more flexibility–since you get to choose what happens when
the gate is closed (below the threshold), as well as when it’s
open (above the threshold).
You can also choose whether the gate will be able to open
and close continuously in response to the control source, or
whether it only opens or closes at the beginning of the note,
and then stays that way over the note’s entire duration.
You can use the Gate to:
• Use a foot-switch (or other controller) to apply pitch-
bend or other effects to some notes, but not to others
• The parameter will be applied when the controller
reaches a specific threshold. For example, the velocity
value could control the filter resonance only if the
velocity value exceeds 90.
• Use the KYBD-61/73/88’s joystick, switches, or
controllers to change between two separate LFOs (or
other AMS sources).
+99
0
–99
+99
0
–99
+99
0
–99
Symmetric
Asymmetric
Bipolar Triangle Wave
SymmetricAsymmetric
Bipolar Sawtooth Wave
Shape = 0 (original waveform)
Shape = +99
Shape = –99
+99
0
–99
Asymmetric
(not recommended)
Unipolar Triangle Wave
Symmetric
+99
0
–99
+99
0
–99
+99
0
–99
Unipolar (e.g., JS+Y) Bipolar (e.g., LFO)
Original
AMS A
Quantize
Steps = 8
Quantize
Steps = 16
Control
Below
At & Above
Fixed Value
AMS
Fixed Value
AMS
 Loading...
Loading...

















