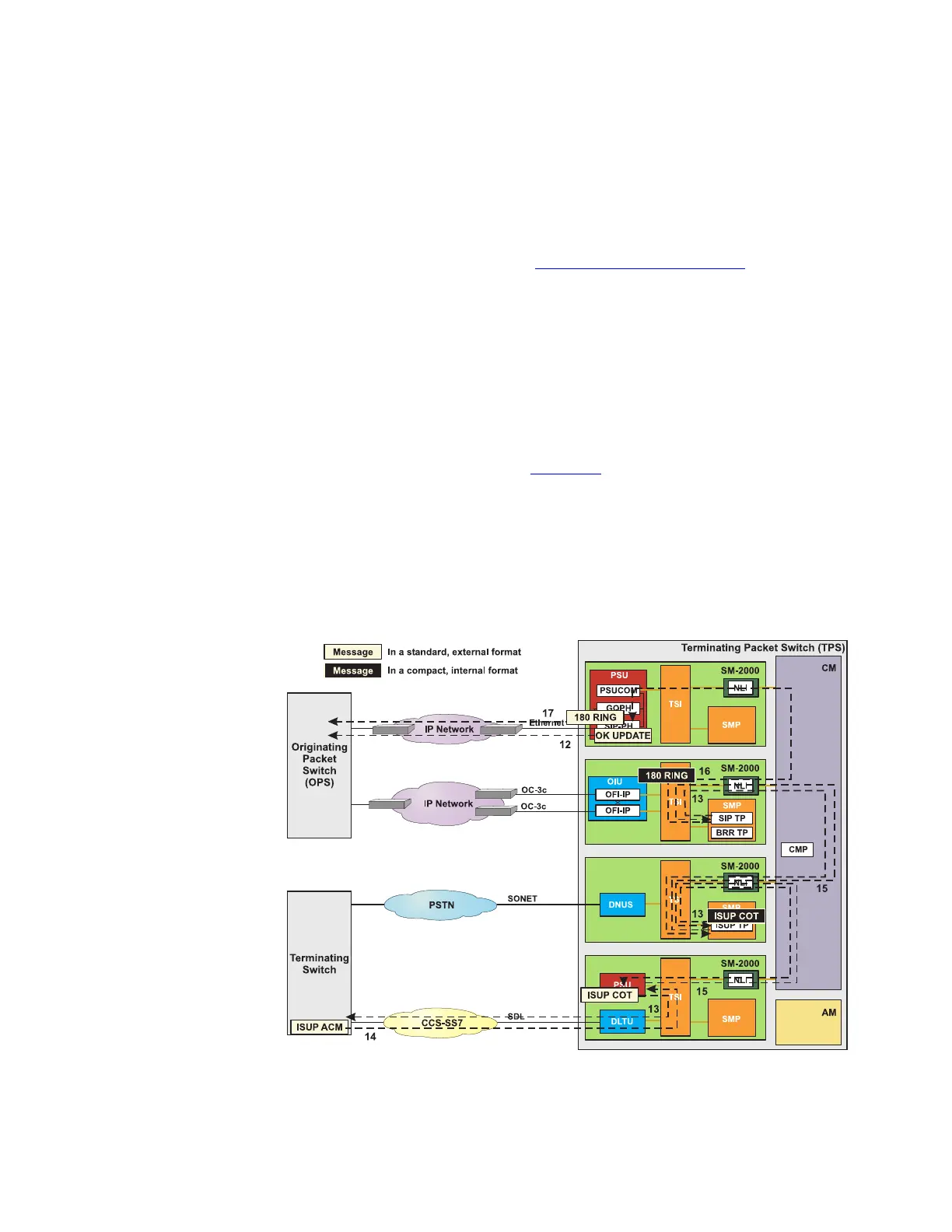
6. The SIP terminal process develops a 183 SESSION PROGRESS
message. This message is in a compact, internal SIP format. This
message contains the IP address and port for the terminating
bearer resource. The SIP message is forwarded to the SIP PH in
the SIP GSM.
7. The SIP PH expands the 183 SESSION PROGRESS message to
standard, external SIP format, adds the appropriate SCTP and IP
headers, and forwards it to OPS via the IP signaling network.
8. The SIP terminal process passes notification to the ISUP terminal
process. An ISUP IAM message is formulated and forwarded to
the ST PH in the SS7 GSM. Finally, the message is sent to the
terminating switch.
9. The TPS waits for the OPS to respond.
10. The SIP PH receives an UPDATE message from the OPS. The
message informs the TPS that the OPS has opened the upstream
port and that the bearer path is now available.
11. The SIP PH strips the SCTP and IP headers, compacts the
message to the internal SIP format, and forwards the message to
the SIP terminal process.
Detailed Call Scenarios - SIP Base
Call Flow
....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
3-34
Lucent Technologies 235-200-118
Issue 3.02B, March 2007
 Loading...
Loading...