TM Palletizing Operator User’s Manual Product Version: 1.0 / Document Version: 1.0 44
Output
Signal in
Regular
Status
Definition of
Triggered
Status
Output signal
of Triggered
Status
Action of
Output when
System Cat. 1
Stop Occurs
Action of
Fault Detection
ESTOP result
from SF0, SF1
and SF2
C3 Discrepancy:
Cat.0 Stop
Protective Stop
result from SF3
C3 Discrepancy:
Cat.0 Stop
Safeguard-
Human-Machine
Safety Settings
Output
Human-Machine
Safety Settings
triggered from
SF4
C3 Discrepancy:
Cat.0 Stop
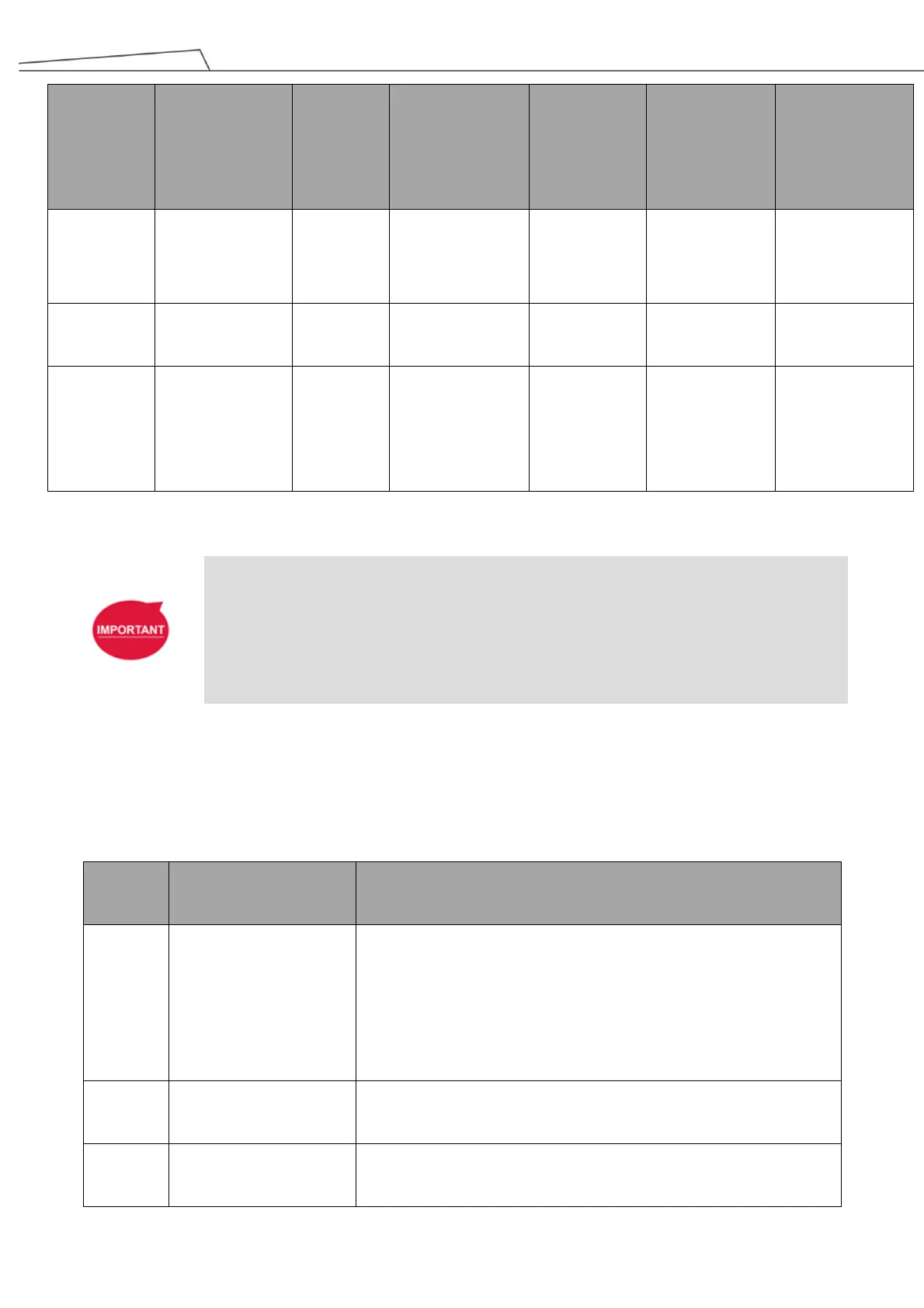
Table 12: Stop Category and Action of Fault Detection of SF7, SF8 and SF9
IMPORTANT:
The resume of outputs follows the corresponded inputs. For example, the SF7-Emergency
Stop Output would output signal LOW when the SF1-Pendant Emergency Stop is pressed.
When the SF1-Pendant Emergency Stop button is rotated and pop-up, the ESTOP result is
removed and SF7-Emergency Stop Output would resume to output signal HIGH.
3.3.6 SF10~SF15 Defined Safety Functions
The name and description of SF10 to SF15 safety functions are listed in the following table as shown
below:
The additional torque that joint received after compensating the
weight of tool in TCP setting, weight of workpiece in payload setting
in programming, and the weight of the robot body. Each joint’s
torque limit condition can be set. When the robot exceeds its set
value, it will trigger a protective stop.
Each joint’s motion angle limit can be set. When the robot exceeds
its set value, it will trigger a protective stop.
Each joint’s motion speed range can be set. When the robot
exceeds its set value, it will trigger a protective stop.
 Loading...
Loading...