User's Manual 146 Document #: LTRT-10632
Mediant 800B Gateway & E-SBC
12.5 Configuring IP Network Interfaces
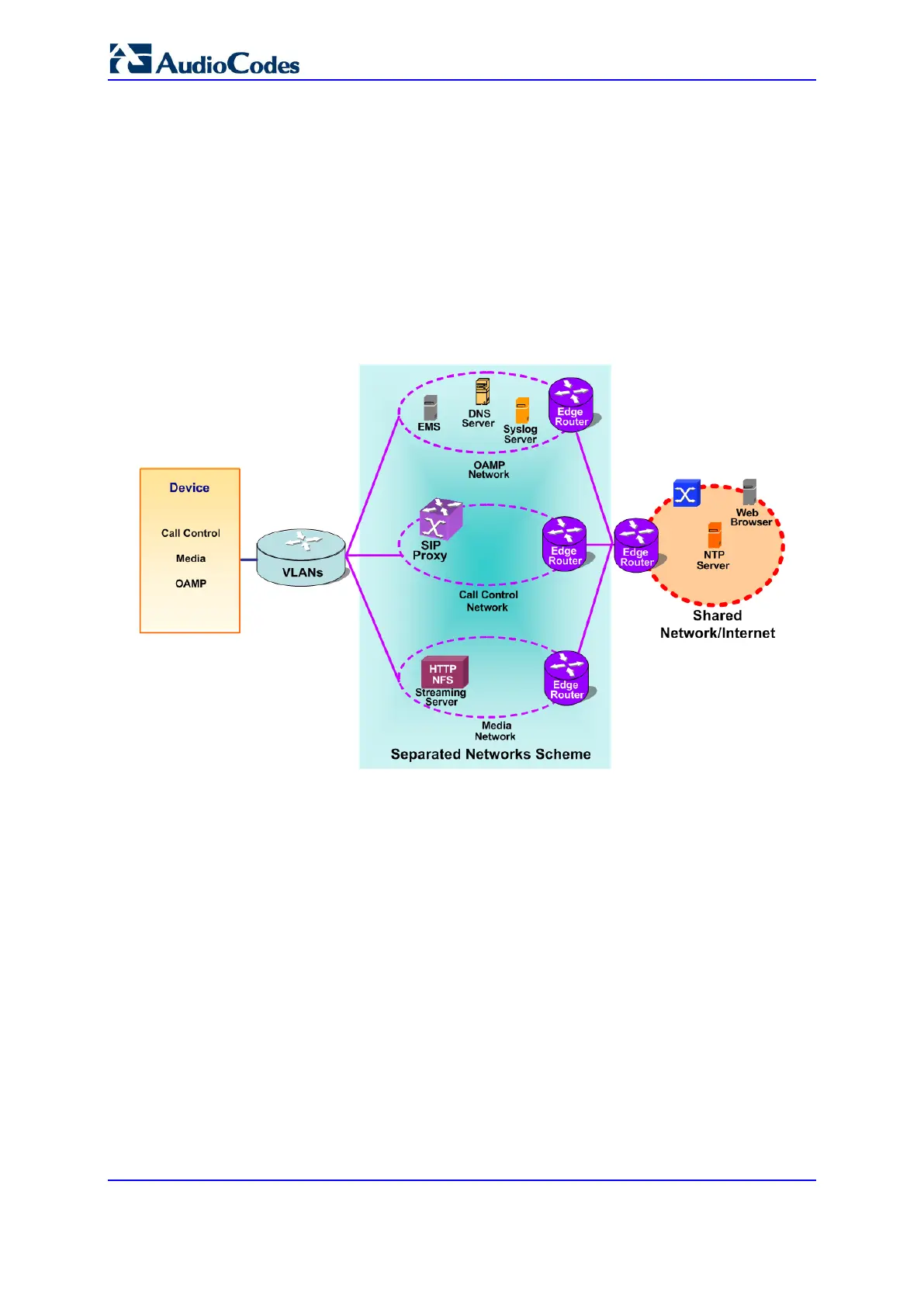
You can configure a single VoIP network interface for all applications, including OAMP
(management traffic), call control (SIP signaling messages), and media (RTP traffic), or
you can configure multiple logical, IP network interfaces for these applications. You may
need to logically separated network segments for these applications for administration and
security. This can be achieved by employing Layer-2 VLANs and Layer-3 subnets. The
figure below illustrates a typical network architecture where the device is configured with
three network interfaces, each representing the OAMP, call control, and media
applications. The device is connected to a VLAN-aware switch for directing traffic from and
to the device to the three separated Layer-3 broadcast domains according to VLAN tags
(middle pane).
Figure 12-2: Multiple Network Interfaces
The device is shipped with a default OAMP interface (see 'Default OAMP IP Address' on
page 43). The IP Interfaces table lets you change this OAMP interface and configure
additional network interfaces for control and media, if necessary. You can configure up to
12 interfaces, consisting of up to 11 Control and Media interfaces including a Maintenance
interface if your device is deployed in a High Availability (HA) mode, and 1 OAMP interface.
Each IP interface is configured with the following:
Application type allowed on the interface:
• Control: call control signaling traffic (i.e., SIP)
• Media: RTP traffic
• Operations, Administration, Maintenance and Provisioning (OAMP): management
(i.e., Web, CLI, and SNMP based management)
• Maintenance: This interface is used in HA mode when two devices are deployed
for redundancy, and represents one of the LAN interfaces or Ethernet Groups on
each device used for the Ethernet connectivity between the two devices. For
more information on HA and the Maintenance interface, see Configuring High
Availability on page 801.
IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) and subnet mask (prefix length)
To configure Quality of Service (QoS), see 'Configuring the QoS Settings' on page
165.

 Loading...
Loading...











