Version 7.2 1331 Mediant 800B Gateway & E-SBC
User's Manual 73. Channel Capacity
73 Channel Capacity
The following table lists maximum concurrent SIP signaling, concurrent media, and
registered users capacity.
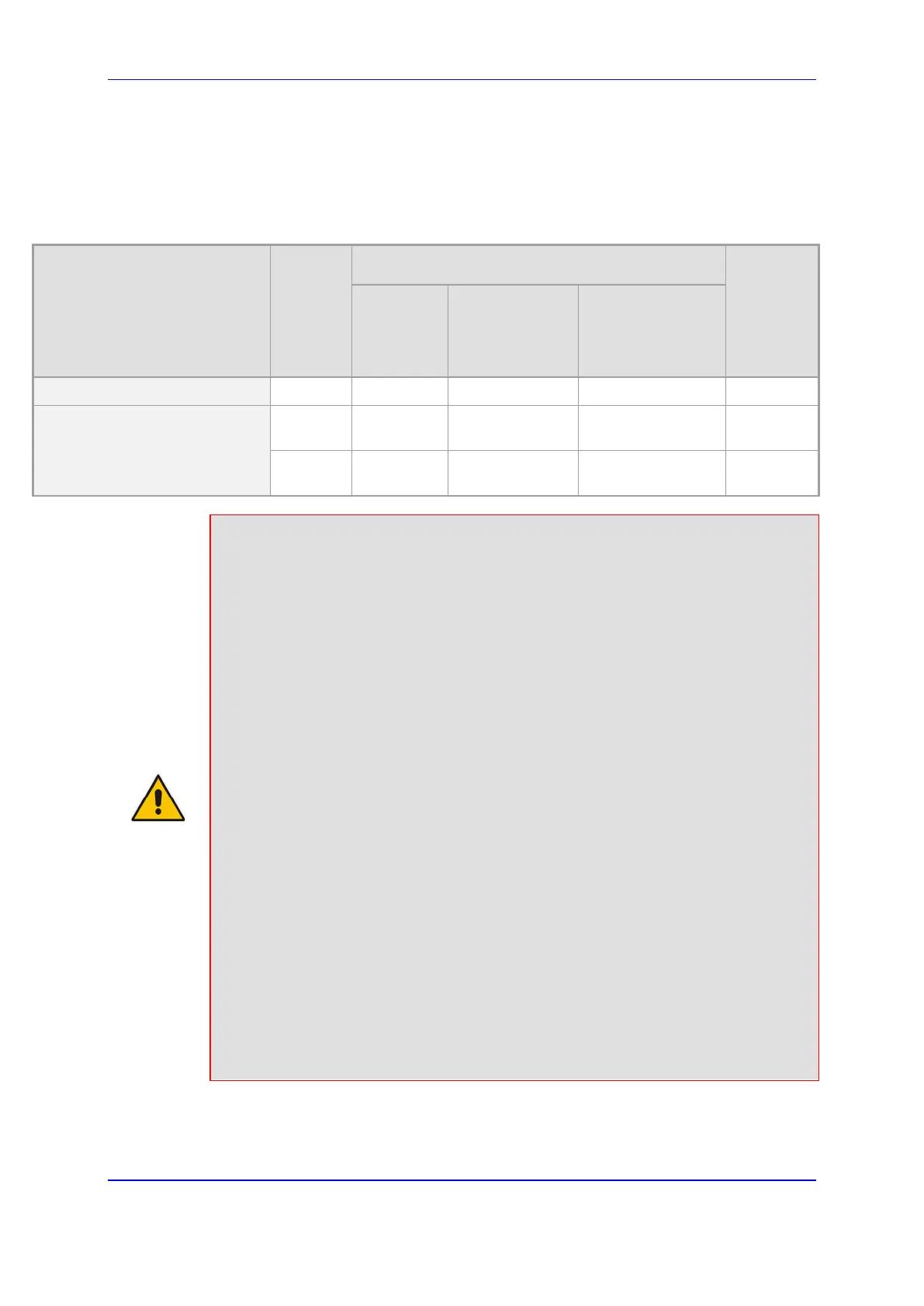
Table 73-1: Maximum Signaling, Media Sessions and Registered Users
Product
Max.
Signaling
Sessions
Max. Media Sessions
Max.
Users
RTP
(RTP-RTP
and/or
TDM-RTP)
SRTP
(SRTP-RTP
and/or TDM-
SRTP)
Codec
Transcoding
Mediant 800 Gateway & E-SBC 60 60 60 See Section 73.1 200
Mediant 800B Gateway & E-
SBC
400 400 250 See Section 73.1 0
300 300 200 See Section 73.1 1,500
Note:
• Installation and use of voice coders is subject to obtaining the appropriate license
and royalty payments.
• The figures listed in the table are accurate at the time of publication of this
document. However, these figures may change due to a later software update. For
the latest figures, please contact your AudioCodes sales representative.
• Registered Users is the maximum number of users that can be registered with the
device. This applies to the supported application (SBC or CRP).
• Regarding signaling, media, and transcoding session resources:
√ A signaling session is a SIP dialog session between two SIP entities, traversing
the SBC and using one signaling session resource.
√ A media session is an audio (RTP or SRTP), fax (T.38), or video session
between two SIP entities, traversing the SBC and using one media session
resource.
√ A gateway session (i.e. TDM-RTP or TDM-SRTP) is also considered as a
media session for the calculation of media sessions. In other words, the
maximum Media Sessions specified in the table refer to the sum of Gateway
and SBC sessions.
√ In case of direct media (i.e., anti-tromboning / Non-Media Anchoring), where
only SIP signaling traverses the SBC and media flows directly between the SIP
entities, only a signaling session resource is used. Thus, for products with a
greater signaling session capacity than media, even when media session
resources have been exhausted, additional signaling sessions can still be
handled for direct-media calls.
√ For call sessions requiring transcoding, one transcoding session resource is
also used. For example, for a non-direct media call in which one leg uses
G.711 and the other leg G.729, one signaling resource, one media session
resource, and one transcoding session resource is used.

 Loading...
Loading...











