User's Manual 170 Document #: LTRT-10632
Mediant 800B Gateway & E-SBC
12.11 DNS
You can use the device's embedded domain name server (DNS) or an external, third-party
DNS to translate domain names into IP addresses. This is useful if domain names are used
as the destination in call routing. The device supports the configuration of the following
DNS types:
Internal DNS table - see 'Configuring the Internal DNS Table' on page 170
Internal SRV table - see 'Configuring the Internal SRV Table' on page 171
12.11.1 Configuring the Internal DNS Table
The Internal DNS table, similar to a DNS resolution can translate up to 20 host (domain)
names into IP addresses. This functionality can be used when a domain name (FQDN) is
configured as an IP destination in a routing rule, typically used for alternative Tel-to-IP call
routing. Up to three different IP addresses can be assigned to the same host name.
Note: The device first attempts to resolve a domain name using the table. If the
domain name is not configured in the table, the device performs a DNS resolution
using an external DNS server for the related IP network interface (see 'Configuring IP
Network Interfaces' on page 146).
The following procedure describes how to configure the DNS table through the Web
interface. You can also configure it through ini file (DNS2IP) or CLI (configure network >
dns dns-to-ip).
To configure the device's DNS table:
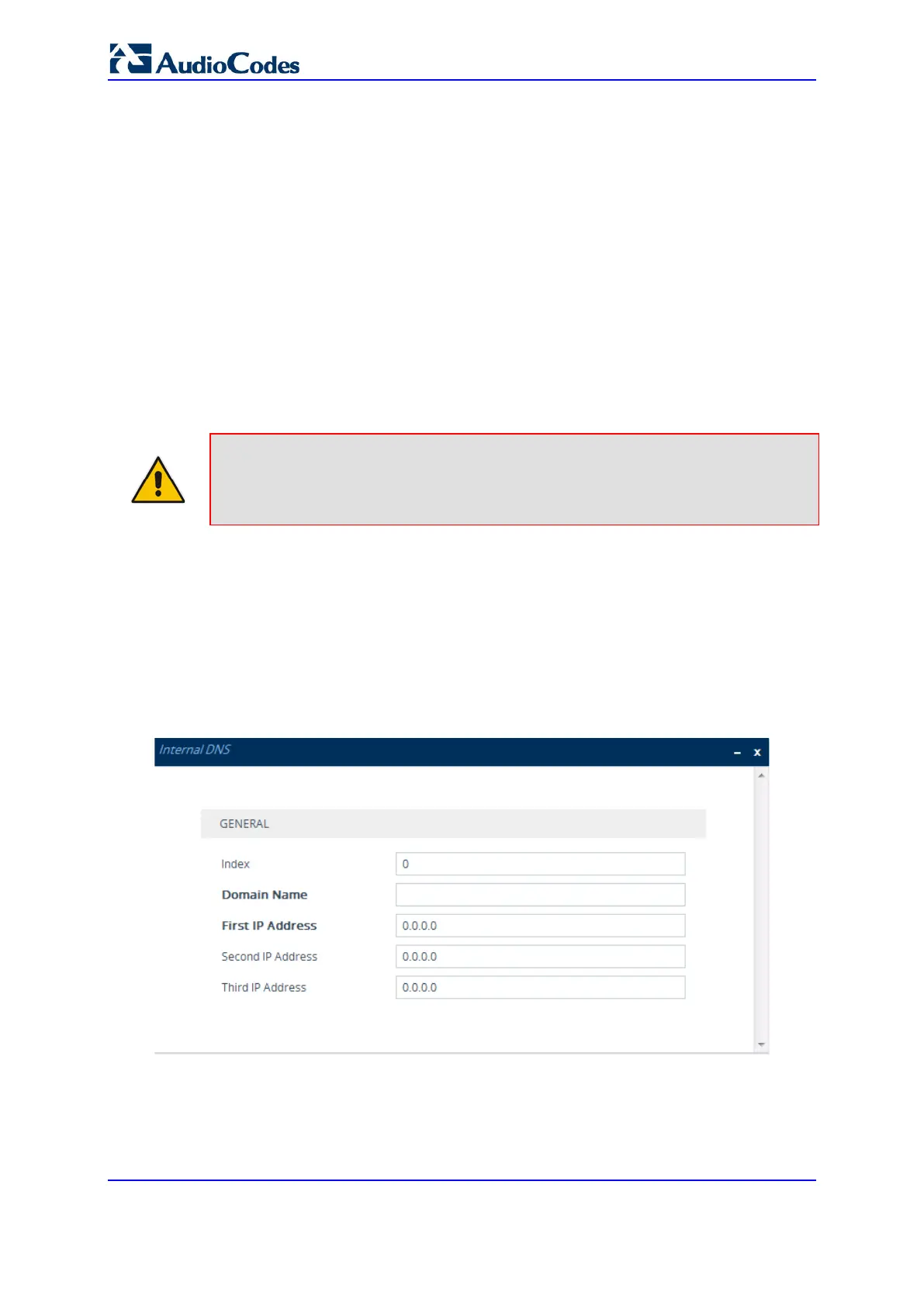
1. Open the Internal DNS table (Setup menu > IP Network tab > DNS folder > Internal
DNS).
2. Click New; the following dialog box appears:
Figure 12-14: Internal DNS Table - Add Dialog Box
3. Configure a DNS rule according to the parameters described in the table below.
4. Click Apply.

 Loading...
Loading...











