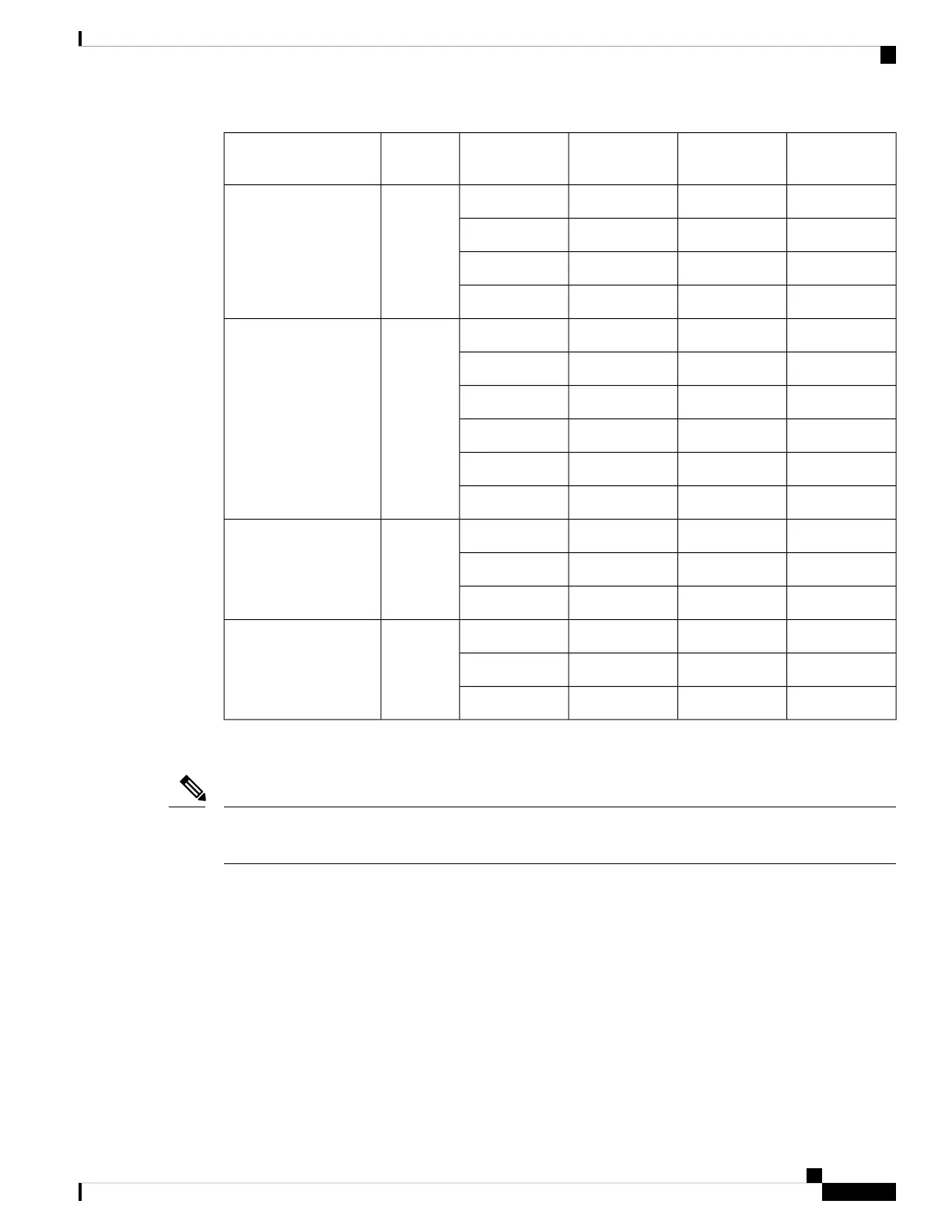
Bottom Region
Entries
Zoning Region
Entries
Forwarding
Engine Number
Port RangesForwarding
Engines
Switch or Module
1966449136
01–124DS–X9248–256K9
1966449136113–24
1966449136225–36
1966449136337–48
1966449136
01–86DS–X9448–768K9
196644913619–16
1966449136217–24
1966449136325–32
1966449136433–40
1966449136541–48
1966449136
01–83DS–X9334–K9
196644913619–16
1966449136217–24
1966449136
01–163DS–X9648–1536K9
1966449136117–32
1966449136233–48
F and TF Port Channels
We do not recommend using interface, fWWN, or domain-ID based zoning for devices that are connected to
the edge Cisco N-Port Virtualization (NPV) switches.
Note
F port channels provide fault tolerance and performance benefits on connections to N-Port Virtualization
(NPV) switches, including Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects (FIs). F port channels present unique challenges
to ACL TCAM programming. When F ports are aggregated into a port channel, ACL TCAM programming
is repeated on each member interface. Consequently, these types of port channels multiply the amount of
TCAM entries needed. Because of this, it is imperative that the member interfaces are allocated as optimally
as possible, and that zoning best practices are also followed. If you also consider the fact that these F port
channels can contain 100+ host logins, TCAM can easily be exceeded, especially for fabric switches if best
practices are not followed.
The following is a sample topology:
Cisco MDS 9000 Series Fabric Configuration Guide, Release 8.x
145
Configuring and Managing Zones
F and TF Port Channels

 Loading...
Loading...


















