• Uses a topology database to keep track of the state of the links on all switches in the fabric and associates
a cost with each link.
• Guarantees a fast reconvergence time in case of a topology change. Uses the standard Dijkstra algorithm,
but there is a static dynamic option for a more robust, efficient, and incremental Dijkstra algorithm. The
reconvergence time is fast and efficient as the route computation is done on a per VSAN basis.
FSPF Examples
This section provides examples of topologies and applications that demonstrate the benefits of FSPF.
The FSPF feature can be used on any topology.
Note
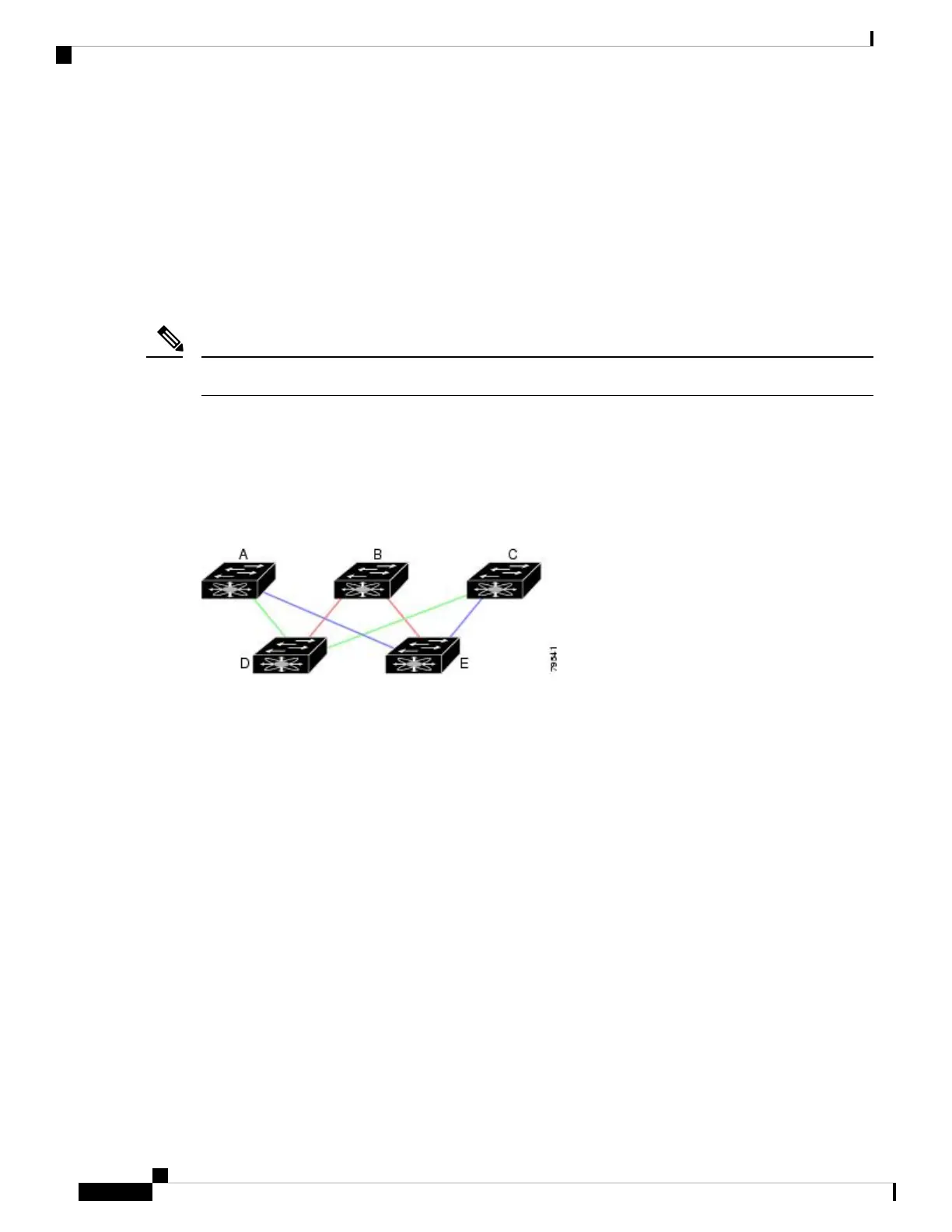
Fault Tolerant Fabric
Figure 46: Fault Tolerant Fabric, on page 186 depicts a fault tolerant fabric using a partial mesh topology. If
a link goes down anywhere in the fabric, any switch can still communicate with all others in the fabric. In the
same way, if any switch goes down, the connectivity of the rest of the fabric is preserved.
Figure 46: Fault Tolerant Fabric
For example, if all links are of equal speed, the FSPF calculates two equal paths from A to C: A-D-C (green)
and A-E-C (blue).
Redundant Links
To further improve on the topology in Figure 46: Fault Tolerant Fabric, on page 186, each connection between
any pair of switches can be replicated; two or more links can be present between a pair of switches Figure 47:
Fault Tolerant Fabric with Redundant Links, on page 187 shows this arrangement. Because switches in the
Cisco MDS 9000 Family support PortChanneling, each pair of physical links can appear to the FSPF protocol
as one single logical link.
By bundling pairs of physical links, FSPF efficiency is considerably improved by the reduced database size
and the frequency of link updates. Once physical links are aggregated, failures are not attached to a single
link but to the entire PortChannel. This configuration also improves the resiliency of the network. The failure
of a link in a PortChannel does not trigger a route change, thereby reducing the risks of routing loops, traffic
loss, or fabric downtime for route reconfiguration.
Cisco MDS 9000 Series Fabric Configuration Guide, Release 8.x
186
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
FSPF Examples

 Loading...
Loading...


















