1014 | Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
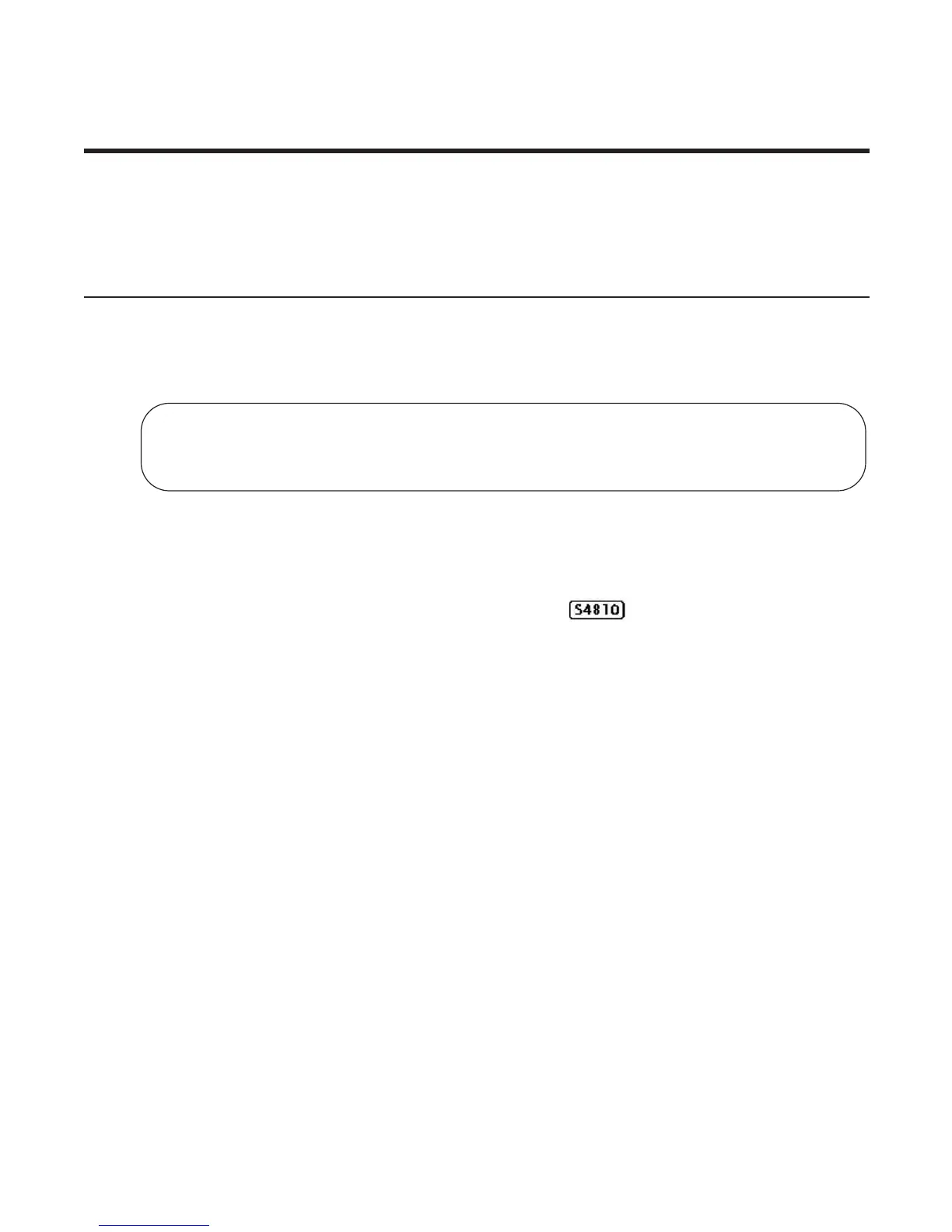
View only the root information using the show spanning-tree root command (see Figure 49-5) from EXEC
privilege mode.
Figure 49-5. show spanning-tree root Command Example
STP Root Guard
STP Root Guard is supported only on platforms: c e
s
Use the STP Root Guard feature in a Layer 2 network to avoid bridging loops. In STP, the switch in the
network with the lowest priority (as determined by STP or set with the
bridge-priority command) is selected
as the root bridge. If two switches have the same priority, the switch with the lower MAC address is
selected as the root. All other switches in the network use the root bridge as the reference used to calculate
the shortest forwarding path.
Because any switch in an STP network with a lower priority can become the root bridge, the forwarding
topology may not be stable. The location of the root bridge can change, resulting in unpredictable network
behavior. The STP root guard feature ensures that the position of the root bridge does not change.
Root Guard Scenario
For example, in Figure 49-6 (STP topology 1 upper left) Switch A is the root bridge in the network core.
Switch C functions as an access switch connected to an external device. The link between Switch C and
Switch B is in a blocking state. The flow of STP BPDUs is shown in the illustration.
In STP topology 2 (Figure 49-6 upper right), STP is enabled on device D on which a software bridge
application is started to connect to the network. Because the priority of the bridge in device D is lower than
the root bridge in Switch A, device D is elected as root, causing the link between Switches A and B to enter
a blocking state. Network traffic then begins to flow in the directions indicated by the BPDU arrows in the
topology. If the links between Switches C and A or Switches C and B cannot handle the increased traffic
flow, frames may be dropped.
Task Command Syntax Command Mode
Assign a number as the bridge priority or designate it as the
root or secondary root.
priority-value range: 0 to 65535. The lower the number
assigned, the more likely this bridge will become the root
bridge. The default is 32768.
• The primary option specifies a bridge priority of 8192.
• The secondary option specifies a bridge priority of 16384.
bridge-priority {priority-value |
primary | secondary}
PROTOCOL
SPANNING TREE
FTOS#show spanning-tree 0 root
Root ID Priority 32768, Address 0001.e80d.2462
We are the root of the spanning tree
Root Bridge hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
FTOS#

 Loading...
Loading...











